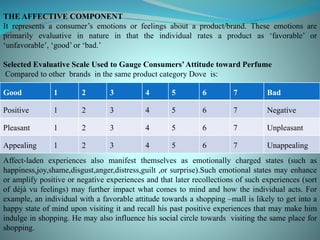
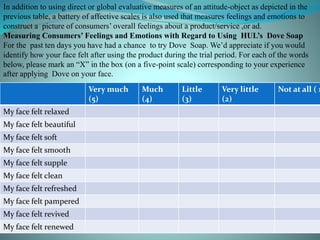
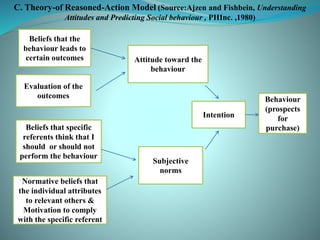
The document discusses various models of consumer attitude formation and change. It describes the tri-component attitude model which includes cognitive, affective, and conative components. The cognitive component represents beliefs, the affective represents feelings/emotions, and the conative represents intentions or likelihood of behavior. Multi-attribute attitude models portray attitudes as a function of perceptions and assessments of key attributes. The elaboration likelihood model describes two routes to persuasion: central and peripheral. Behavior can precede or follow attitude formation according to cognitive dissonance theory and attribution theory.







![ATTITUDE-TOWARD-THE -AD MODELS [Source: Edell and Burke, The Power of
feelings in Understanding Advertising Effects, J. of Consumer Research 14 , Dec,1987]
It appears that for a novel product, like “contact lens for pets” the consumers’ attitude toward the
ad has a strong impact on brand attitude and purchase intentions than for a familiar product such
as ‘pet food.’ The same research found that beliefs about a brand (brand cognition) that result
from ad exposure plays a much stronger role in determining attitudes towards the brand for a
familiar product. That means in assessing the potential impact of advertising exposure
considering the nature of the attitude object is important.[Cox and Locander,JoA,16(1987)]
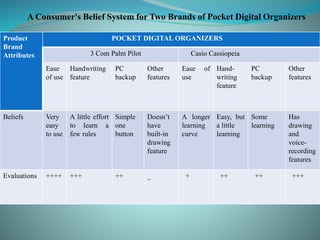
Attitude
towards the
brand
Exposure to an Ad
Beliefs about the
brand (brand
cognition)
Judgments about
the Ad
Attitude
towards the
Ad
Feelings
from the Ad](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consumerattitudeppts-221125152849-6b6ca503/85/Consumer-Attitude-PPTs-12-320.jpg)













