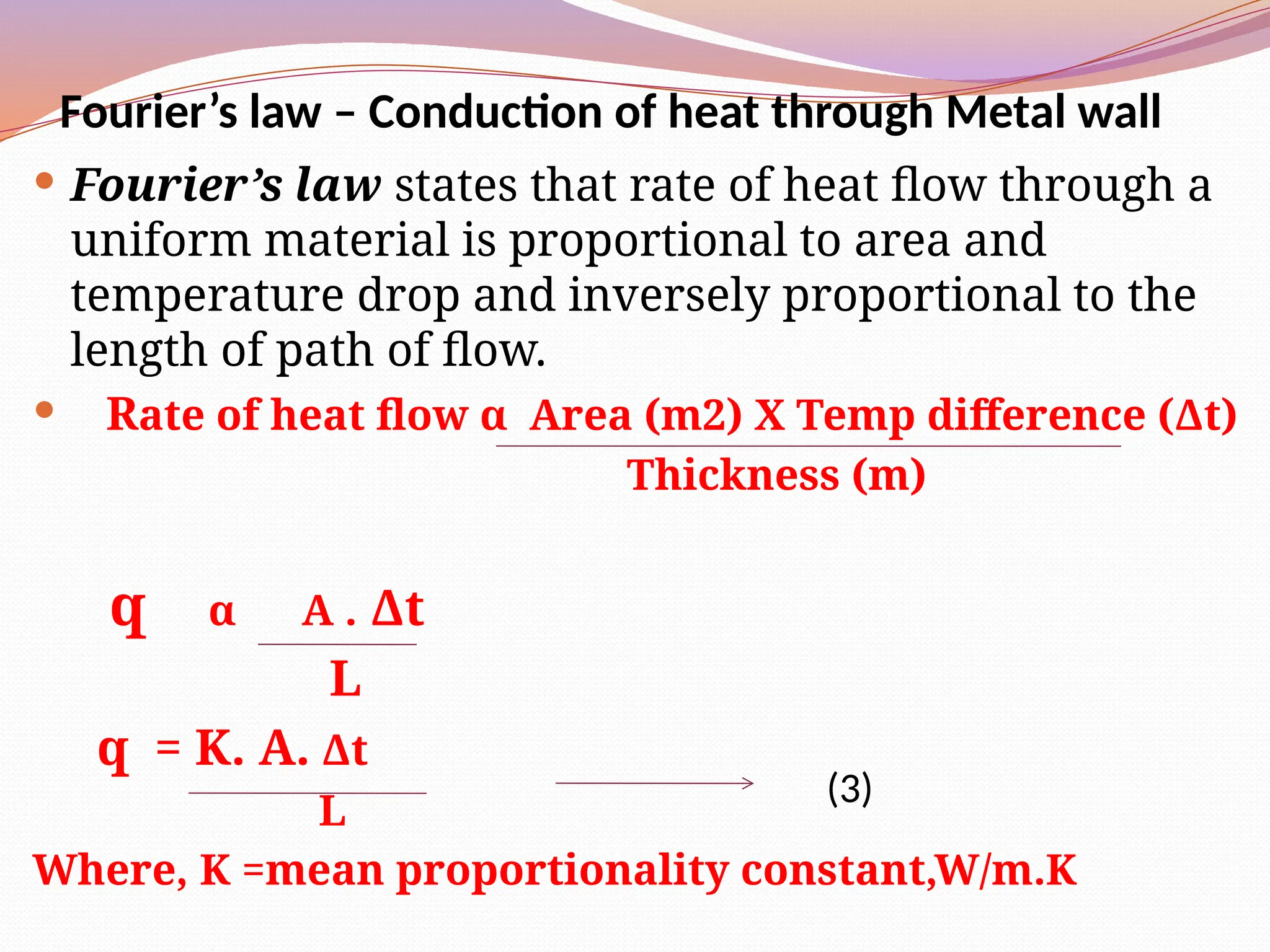
Heat transfer is the movement of heat from a high temperature to a low temperature region, occurring through three primary modes: conduction, convection, and radiation. Key applications include evaporation, distillation, drying, crystallization, and sterilization, which utilize these mechanisms to transfer heat effectively. Fourier's Law describes the heat flow during conduction, indicating that it is proportional to temperature differences and surface area while being inversely related to the distance heat travels.