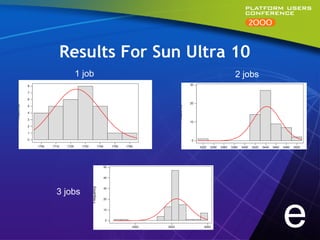
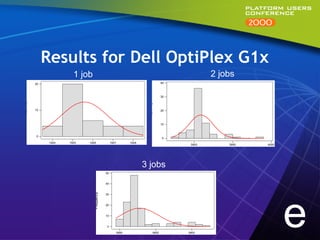
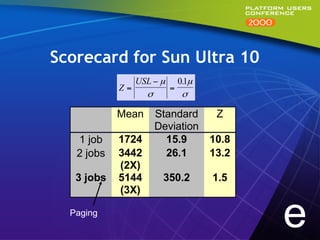
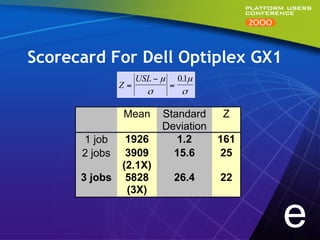
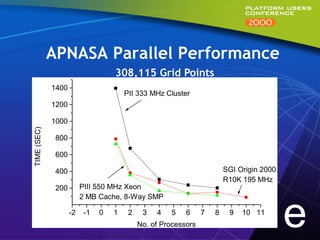
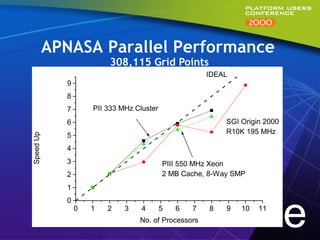
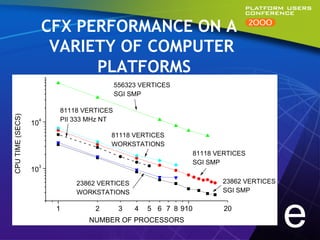
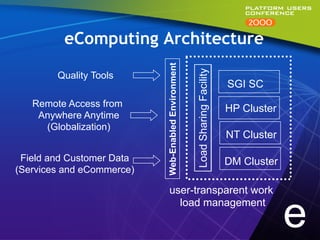
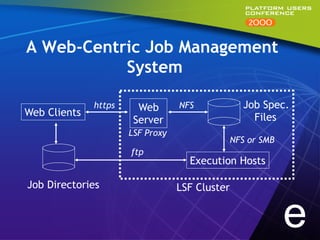
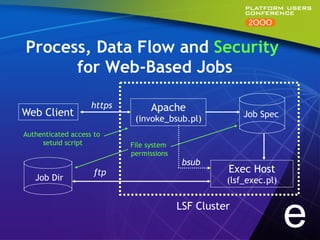
This document summarizes experiments comparing computer clusters built with different hardware for mechanical design workloads. The experiments found that a cluster of Dell OptiPlex PCs running Windows NT provided comparable stability and multitasking performance to a more expensive Sun workstation, while scaling better on parallel applications. NT also showed better memory management. Overall, the Dell cluster provided the best performance and value for mechanical design environments.