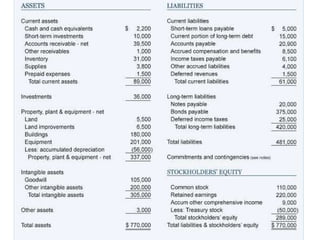
The three components of a balance sheet are:
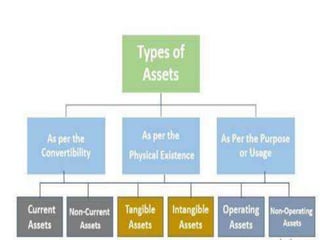
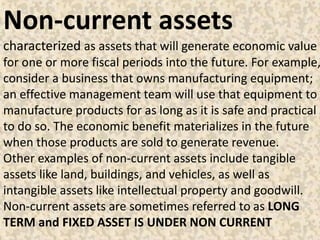
1. Assets - Resources owned or controlled by a company that have monetary value, including current assets (expected to convert to cash within a year) and non-current assets.
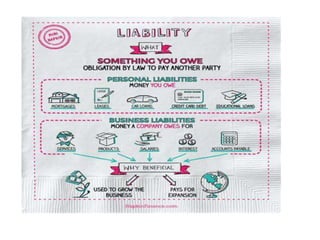
2. Liabilities - Debts or obligations owed by the company, categorized as current (due within a year) or non-current (due after a year).
3. Shareholders' equity - The amount invested in the company by its owners plus accumulated earnings, representing the owners' claim on the company's assets.