COLEAD is an international non-profit organization that supports the sustainable and inclusive development of the agricultural and horticultural sectors, with a strong focus on capacity building, market access, and investment readiness for agribusinesses.
COLEAD stands for Committee Linking Entrepreneurship – Agriculture – Development.
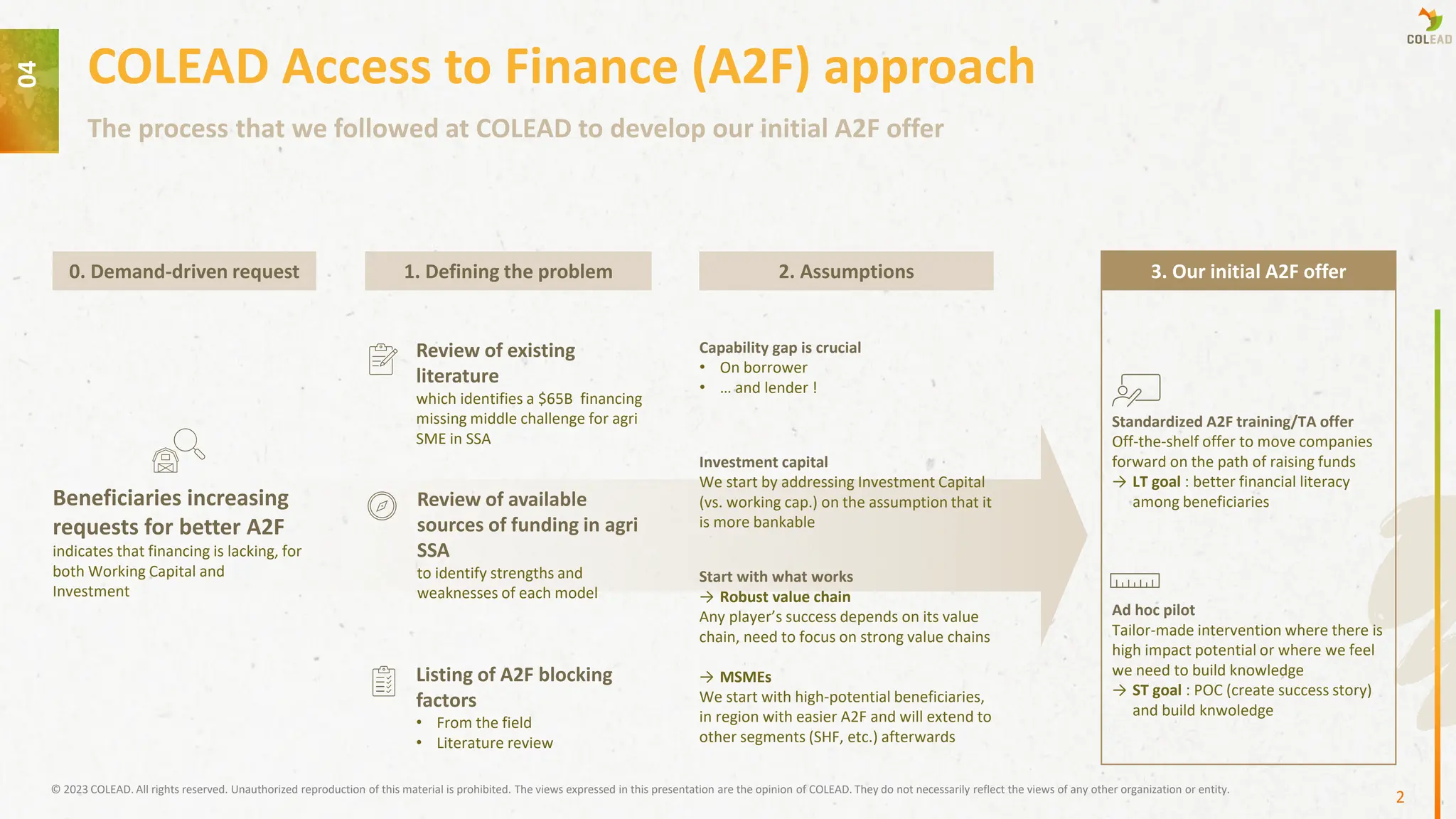
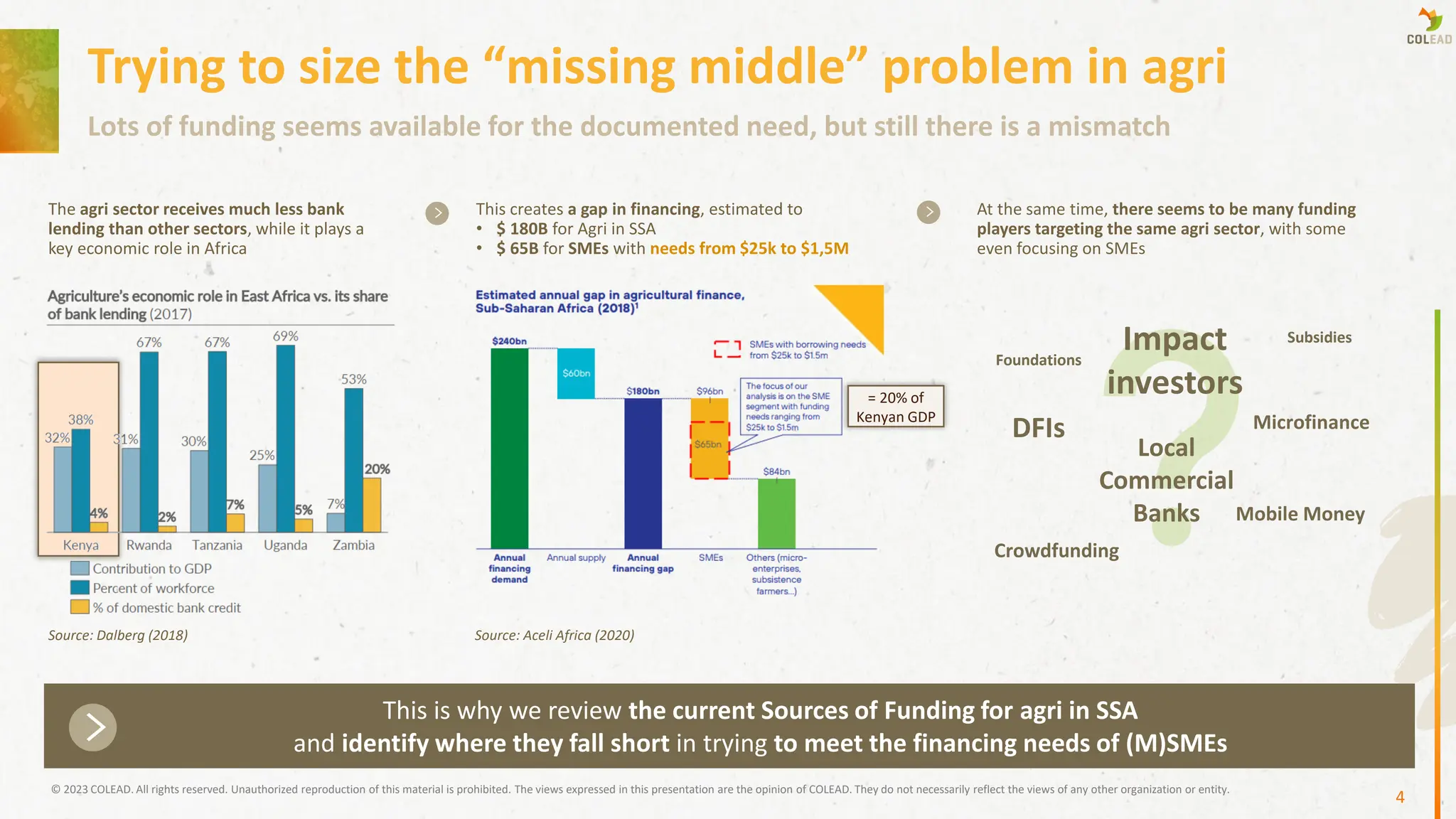
COLEAD’s Access to Finance (A2F) approach addresses the “missing middle” financing gap for agricultural SMEs in Sub-Saharan Africa, a segment with needs between USD 25,000 and 1.5 million that remains underserved despite the apparent presence of multiple funding players. This gap stems from both operational expenditure (OPEX) and capital expenditure (CAPEX) needs being unmet, which slows growth, limits access to markets, and creates a “development ceiling.” COLEAD starts by focusing on investment capital rather than working capital, prioritizing high-potential beneficiaries in strong value chains and more finance-accessible regions before expanding to smaller-scale producers.
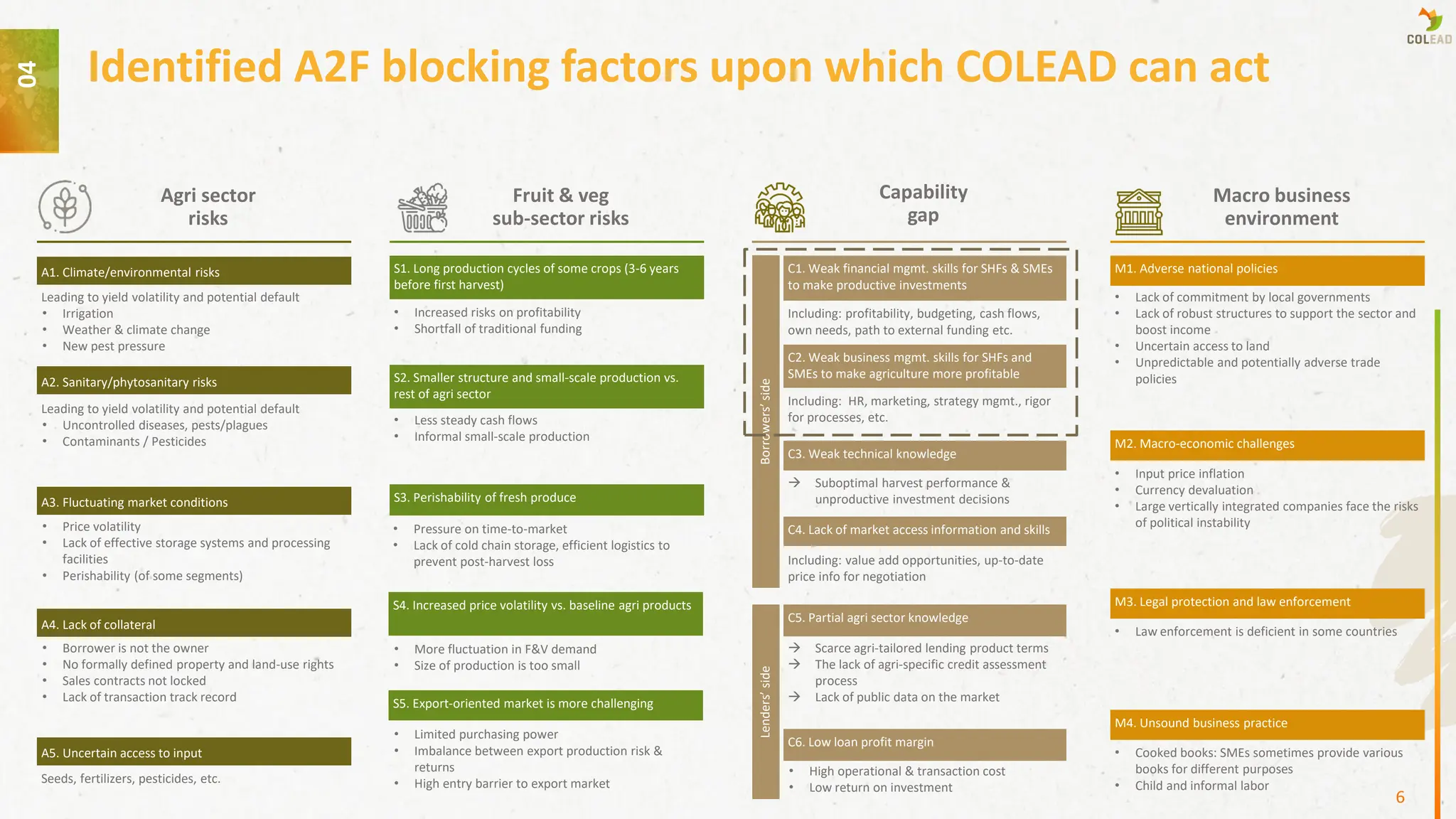
The approach is rooted in tackling capability gaps on both borrower and lender sides, addressing weaknesses in financial literacy, business management, technical knowledge, and agri-specific lending practices, alongside broader challenges in the macroeconomic and policy environment.
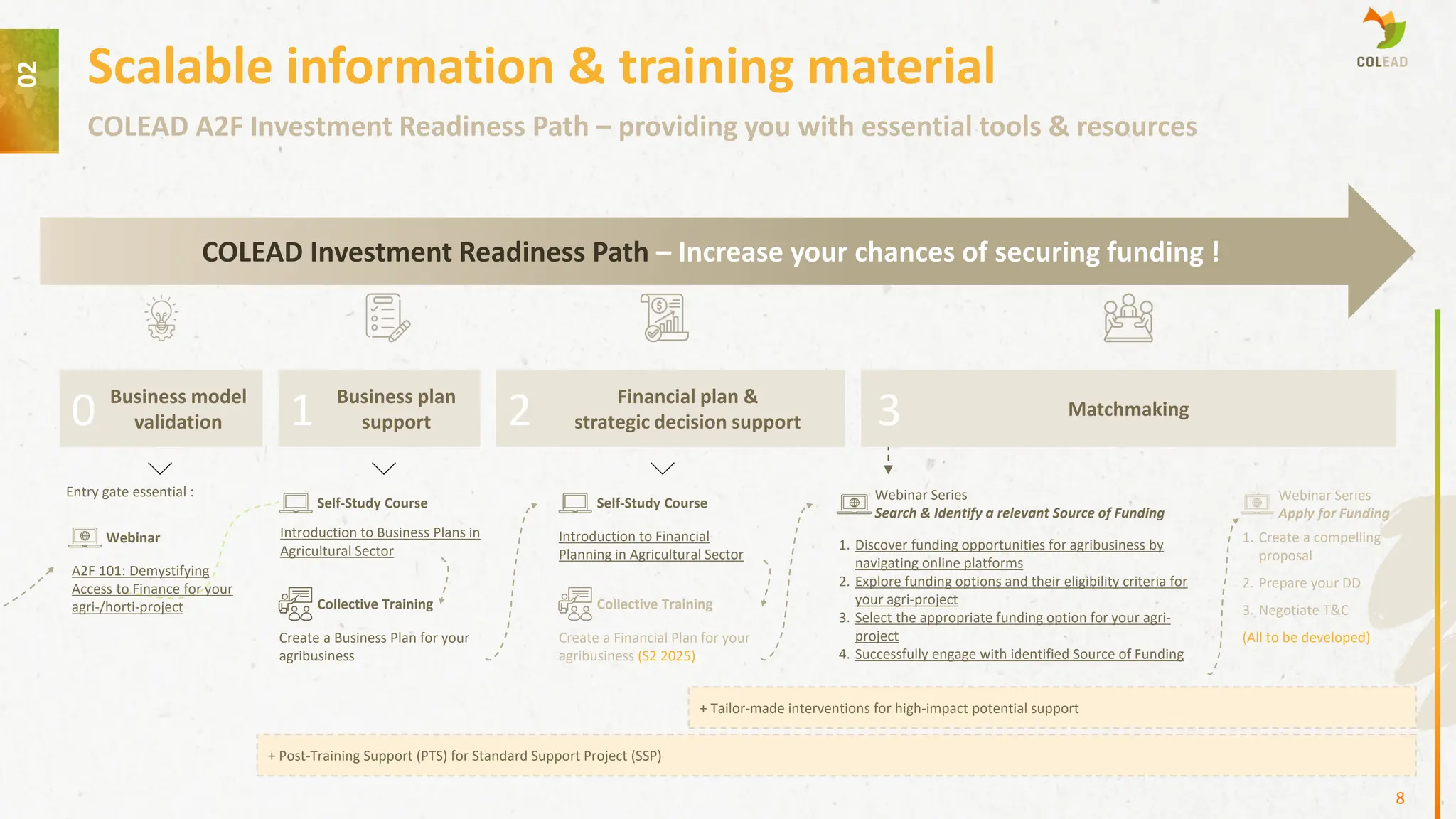
To bridge these barriers, COLEAD offers a dual pathway of standardized training and tailored interventions aimed at improving investor readiness. Its “Investment Readiness Path” provides scalable self-study courses, webinars, and business model validation tools to help SMEs develop bankable business and financial plans, identify appropriate funding sources, and navigate the application process.
This is complemented by targeted pilot projects designed to generate proof-of-concept success stories and build institutional knowledge.
Post-training support ensures that participants can apply their learning effectively, while matchmaking opportunities connect them directly with potential financiers.
By combining capacity building, practical tools, and strategic partnerships, COLEAD’s A2F approach seeks to systematically unlock financing for agribusinesses and strengthen their integration into competitive value chains.