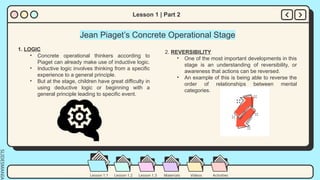
The document outlines the cognitive development of primary school-aged children, highlighting Jean Piaget's theories, including the concrete operational stage characterized by logic and reversibility. It details developmental milestones, emphasizing the transition from egocentric thinking and the increase in complex reasoning abilities around age 8. Additionally, it discusses the implications for childcare and education, advocating for recognizing varying intelligence profiles and fostering a rich learning environment.