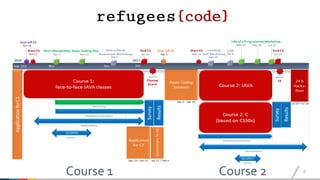
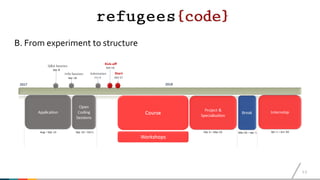
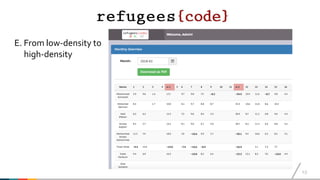
The document discusses best practices for coding integration courses aimed at refugees in Austria, detailing the course history, structure, and completion rates. It emphasizes key learnings such as the importance of flexibility, iterative approaches, and addressing challenges related to technology and migration. The courses targeted varied nationalities and included both traditional and online learning formats with low completion rates across the programs.