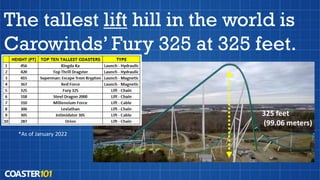
Lift hills use various mechanisms to transport roller coaster cars to an elevated point, gaining potential energy. Traditional chain lifts have been used for over 100 years, while newer designs include cable lifts, catch car lifts, vertical lifts, and lift/launch combinations. Factors like available space, height, and rider evacuation influence lift hill design, which continues to evolve with taller, more efficient structures.