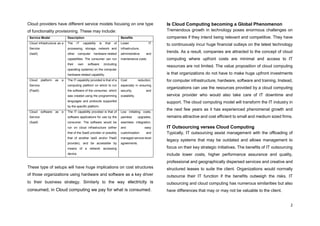
This document discusses cloud computing, including its benefits and risks for businesses. Cloud computing provides shared IT resources over the internet on-demand, allowing businesses to avoid large upfront costs. It can increase efficiency and scalability while reducing costs. However, it also presents security risks to sensitive data if responsibilities between clients and providers are not clear or if standards lack. When selecting a cloud provider, businesses should carefully consider the provider's security controls, access management, legal policies for data storage, and ability to exit the agreement if needed. Overall, cloud computing offers a potentially cost-effective way to access computing resources but also requires managing risks to data security and privacy.