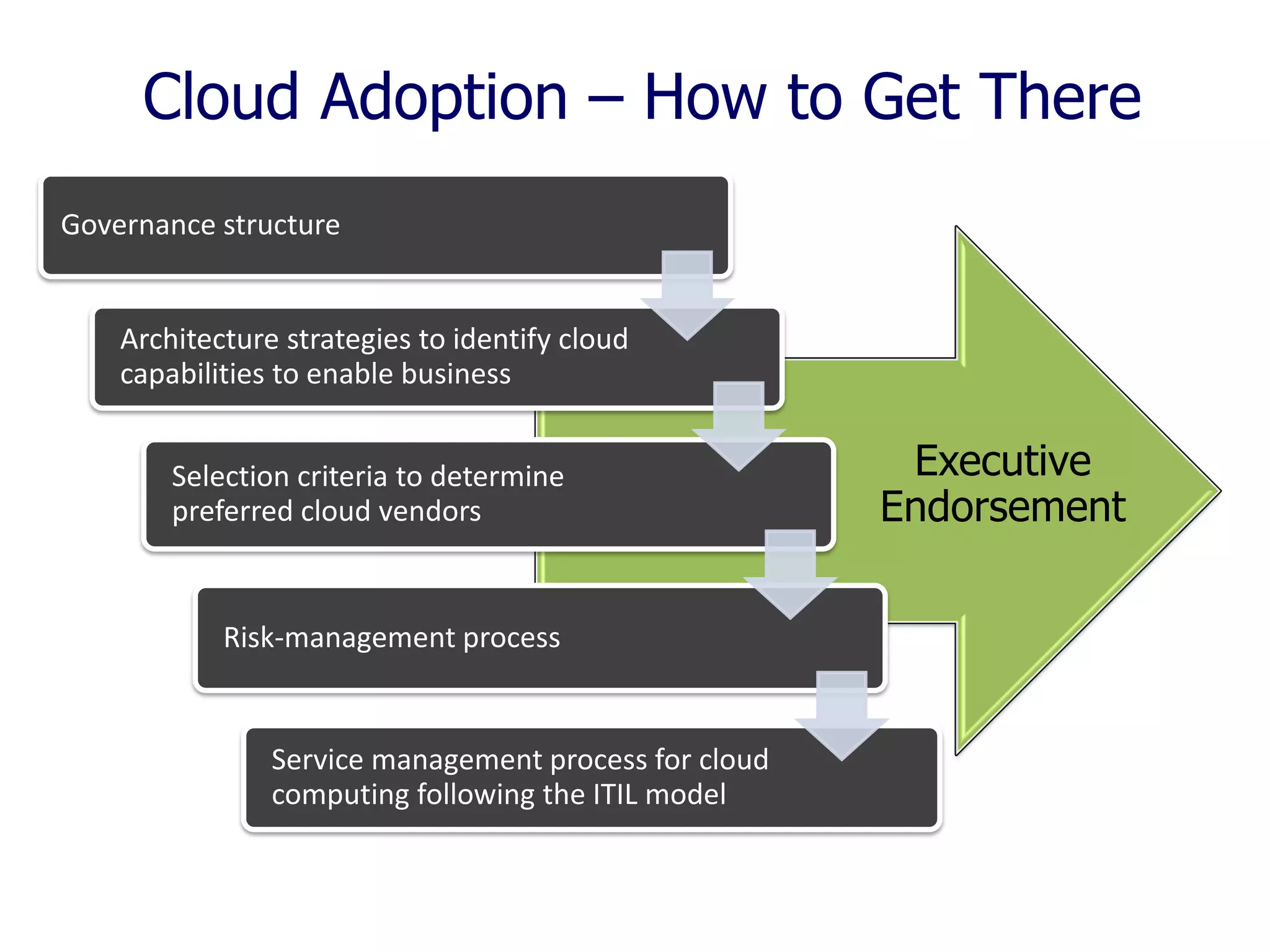
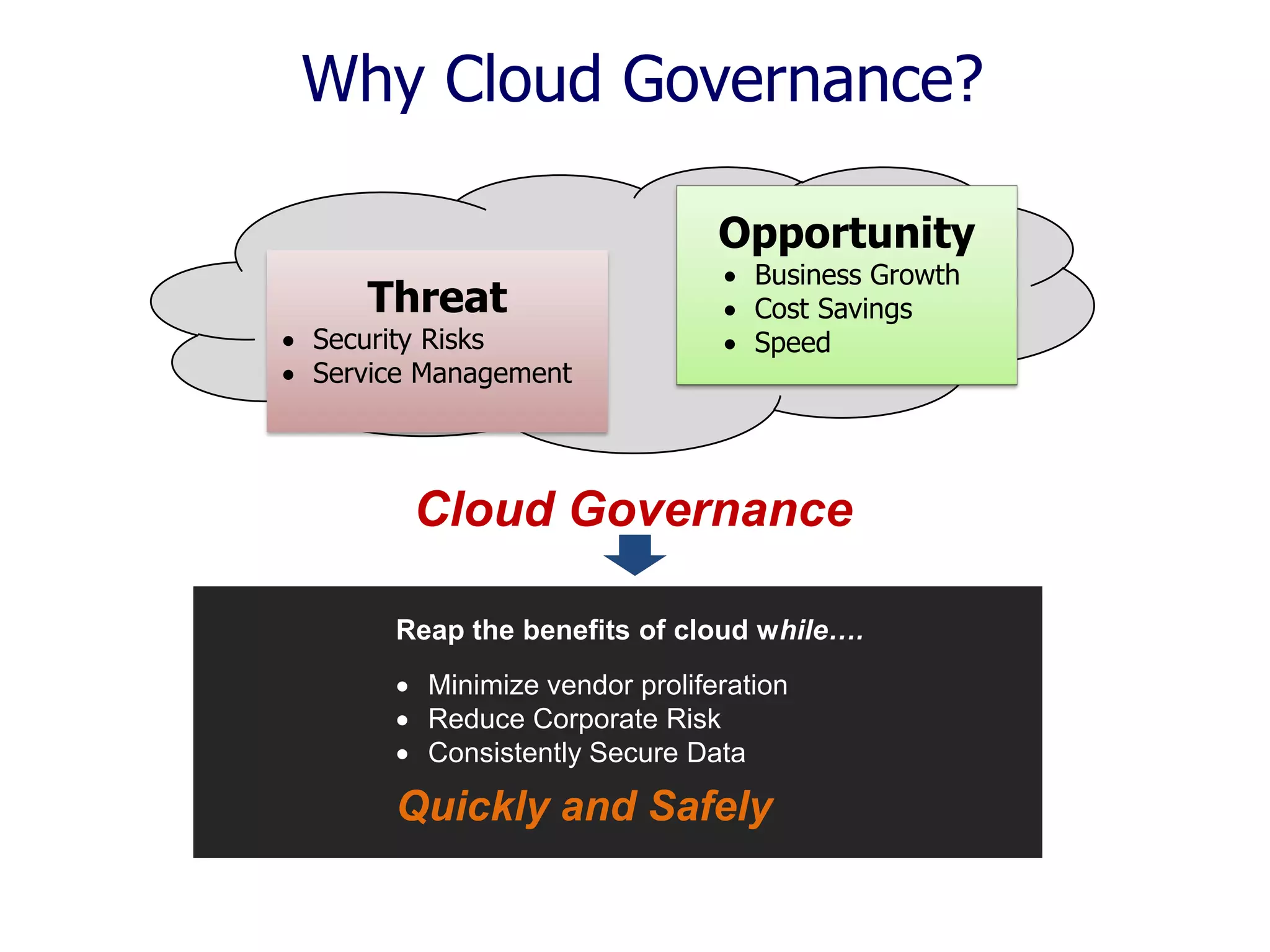
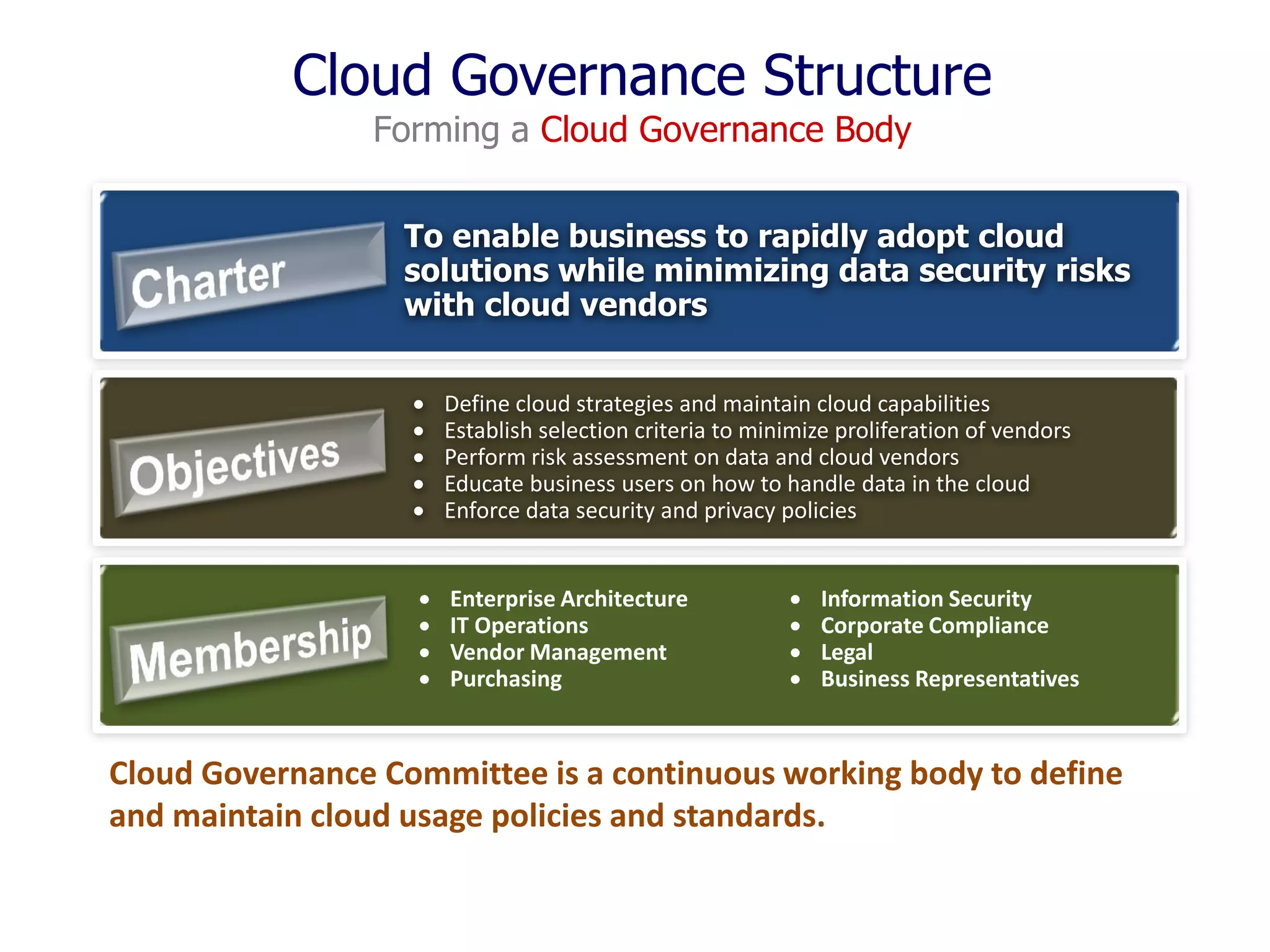
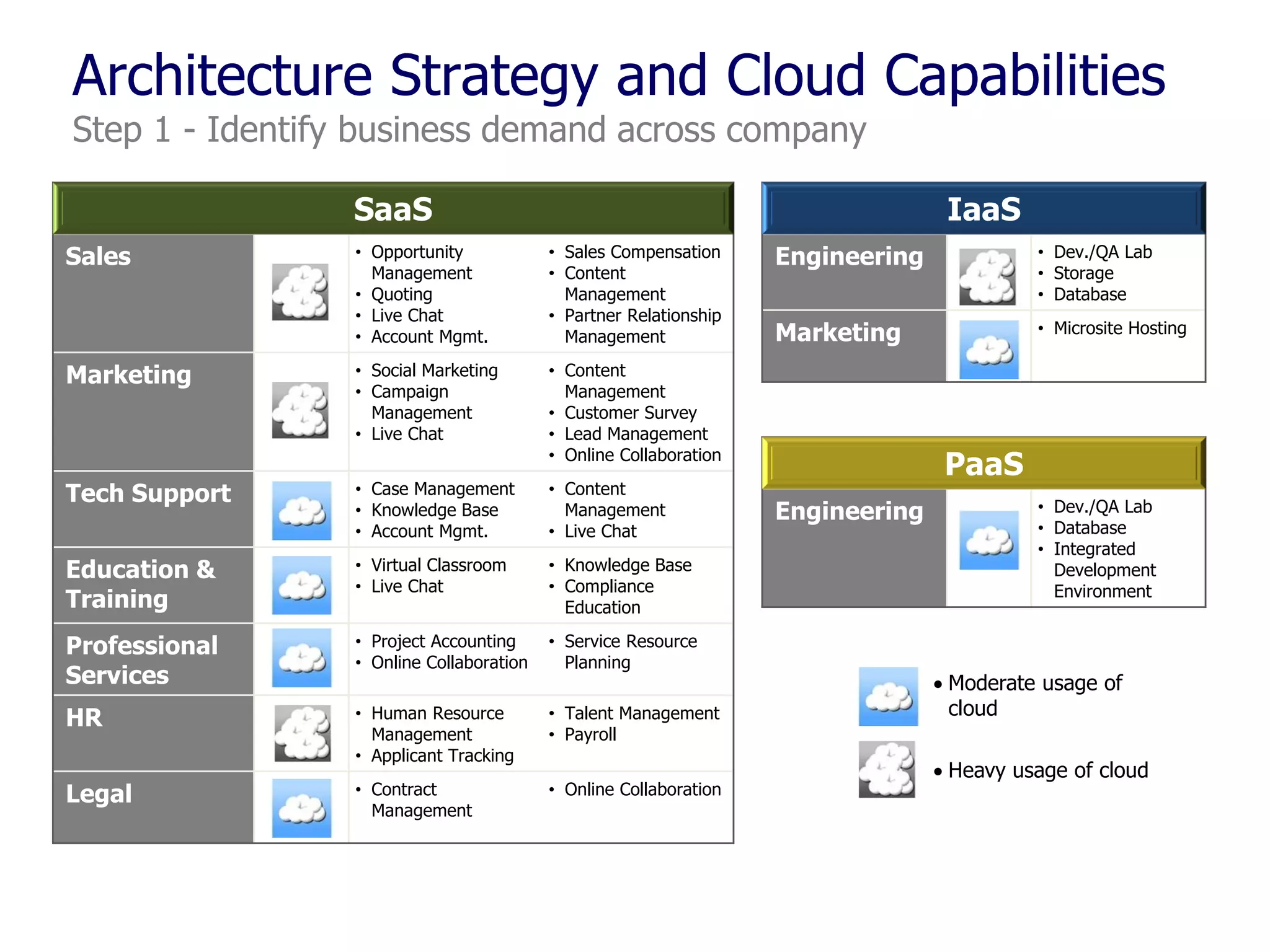
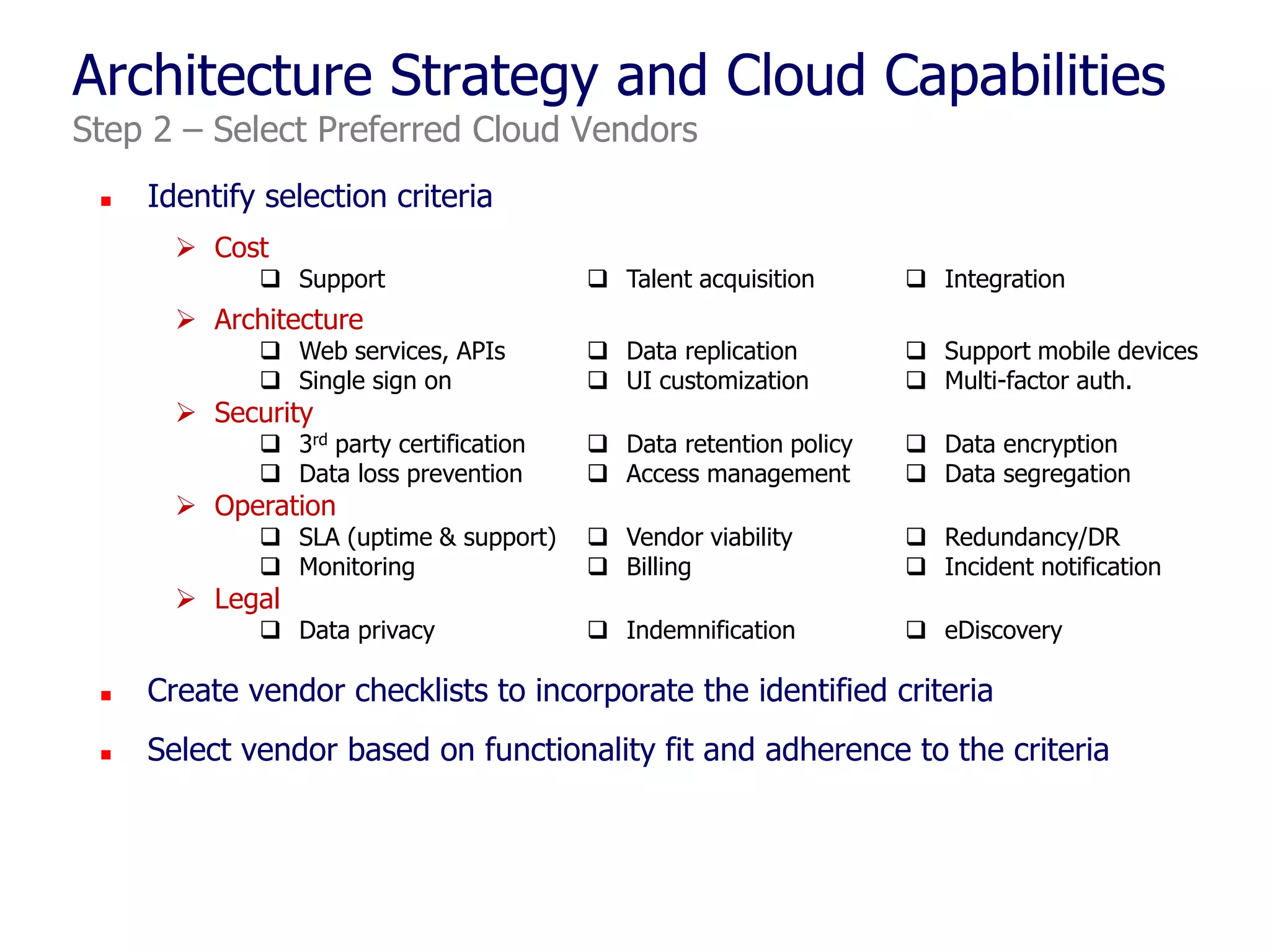
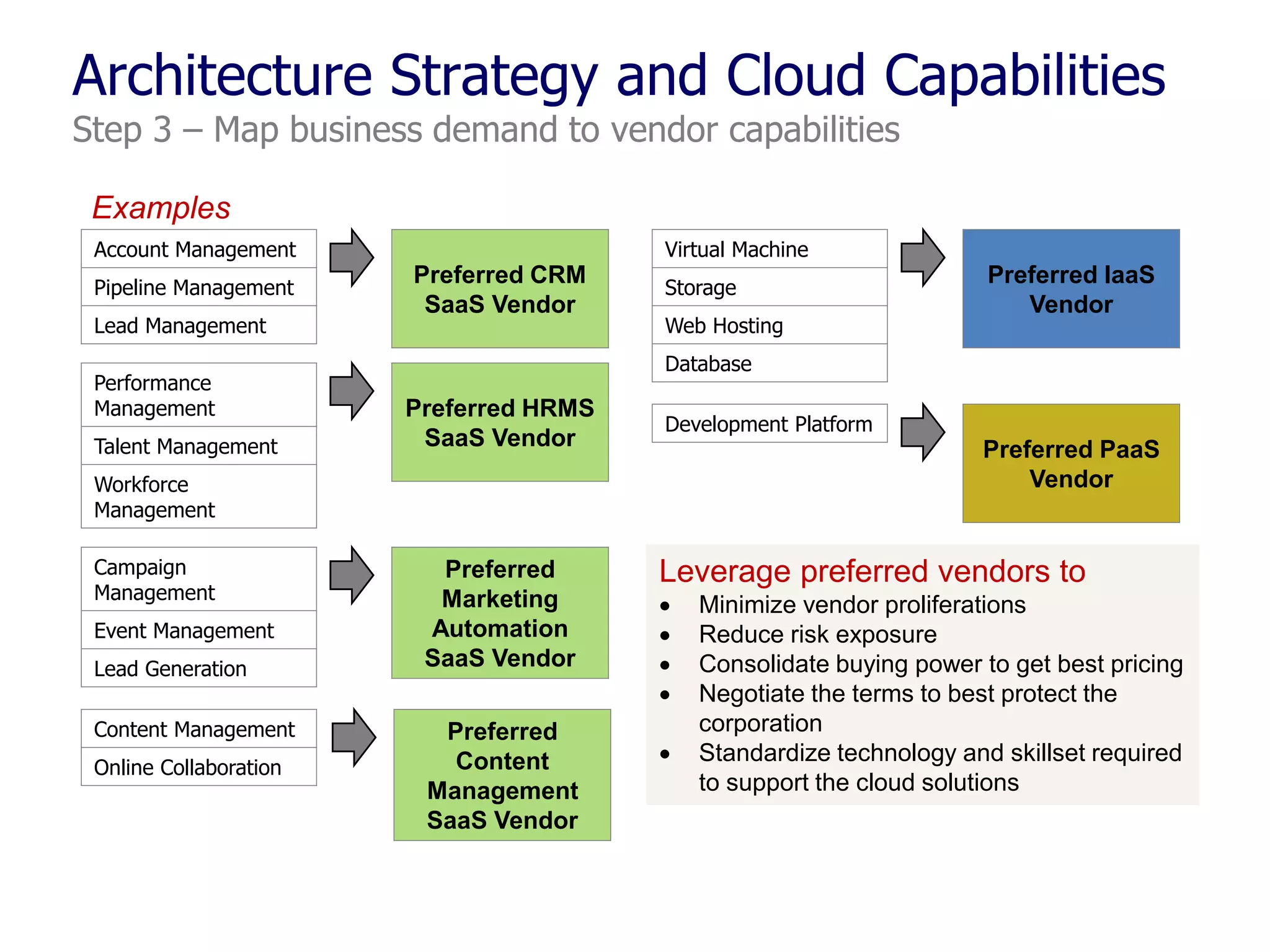
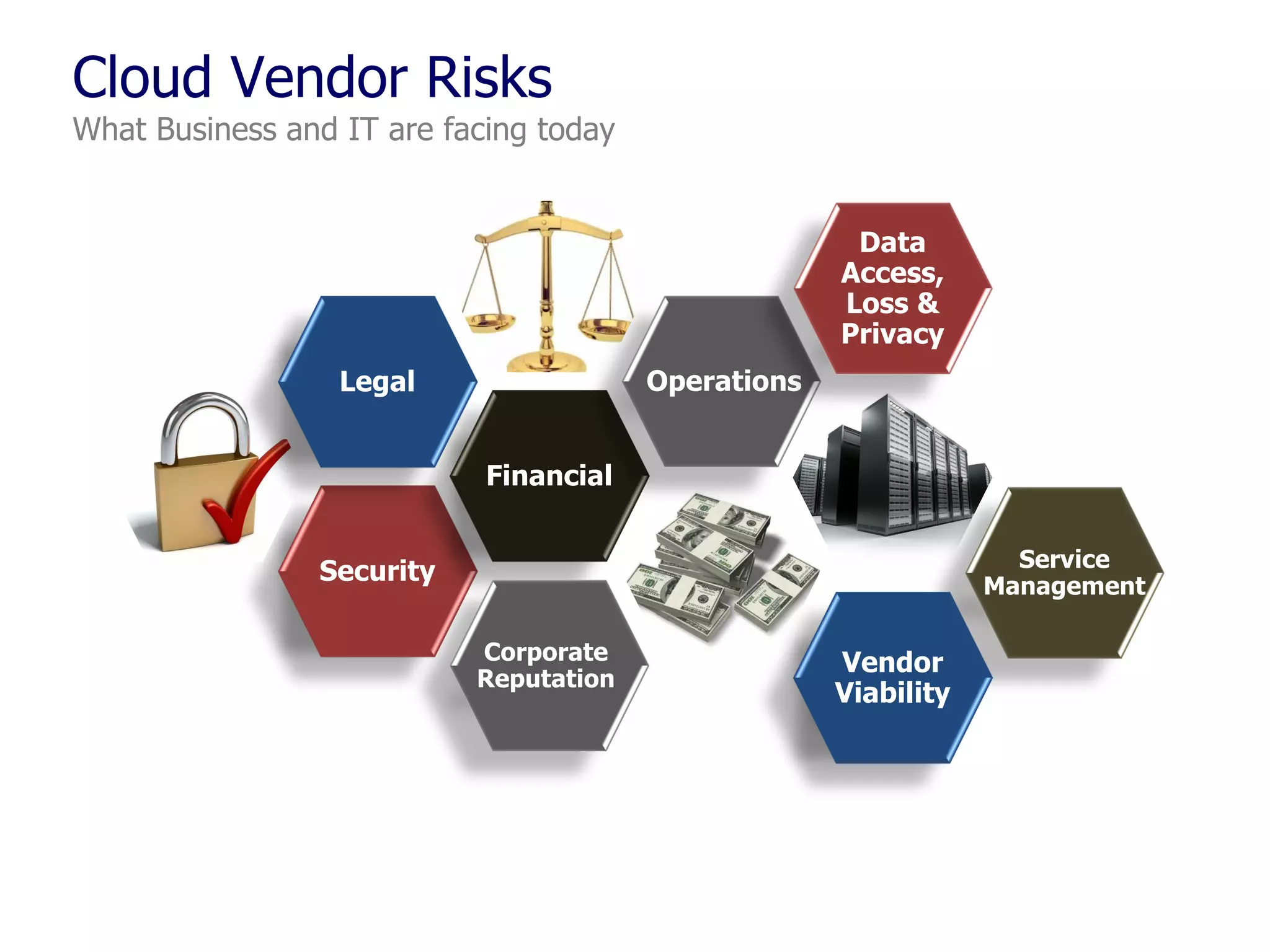
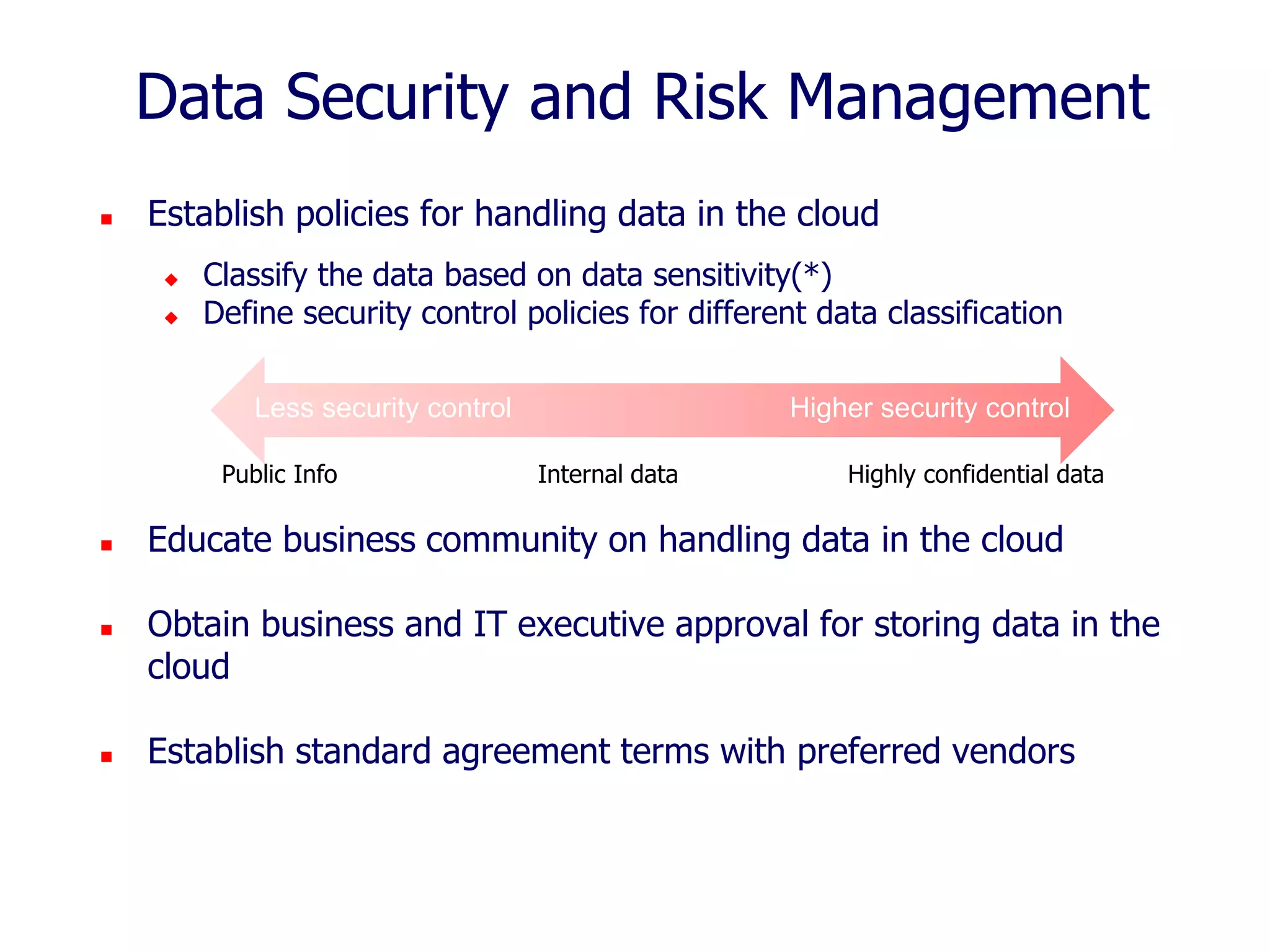
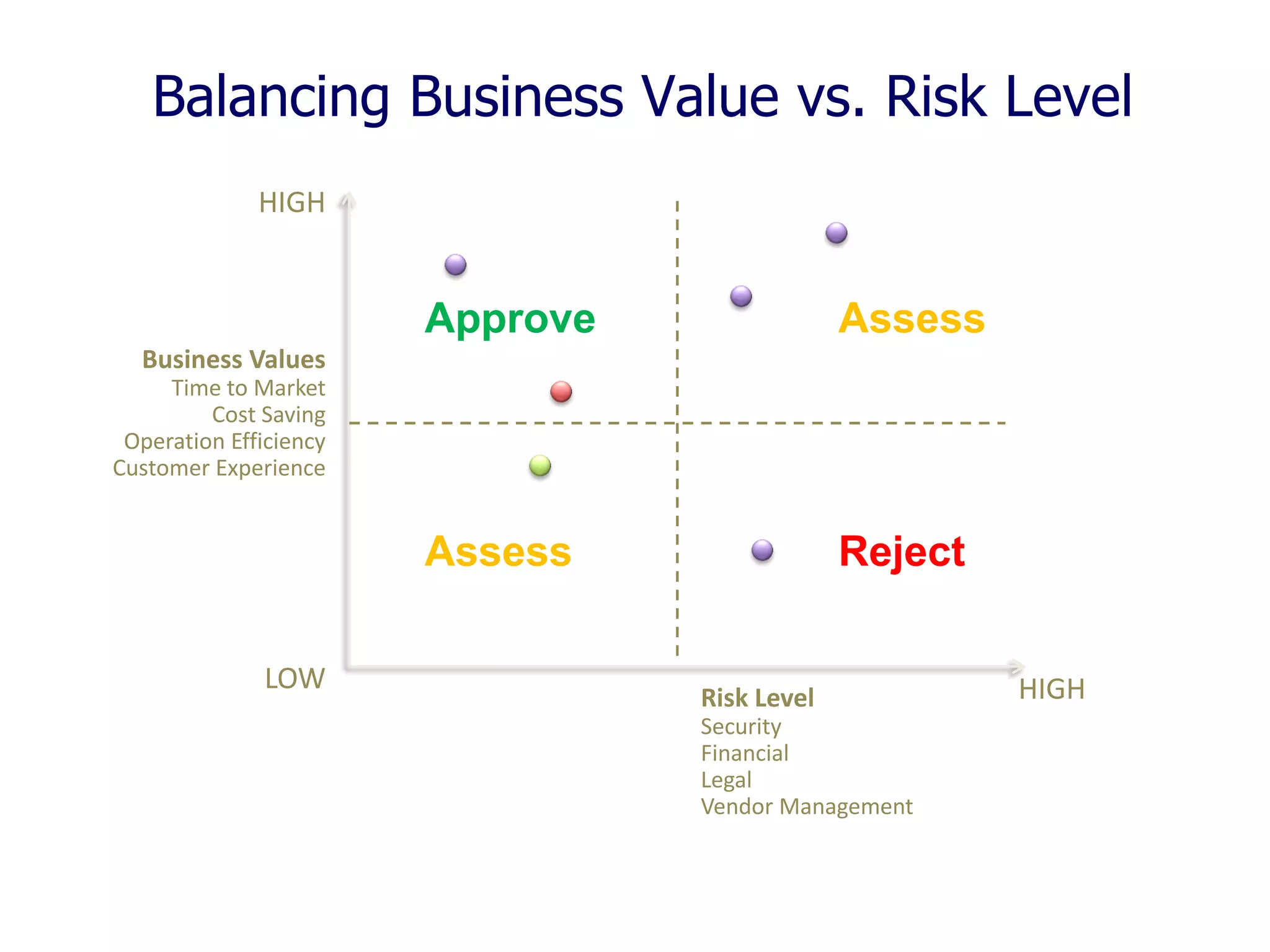
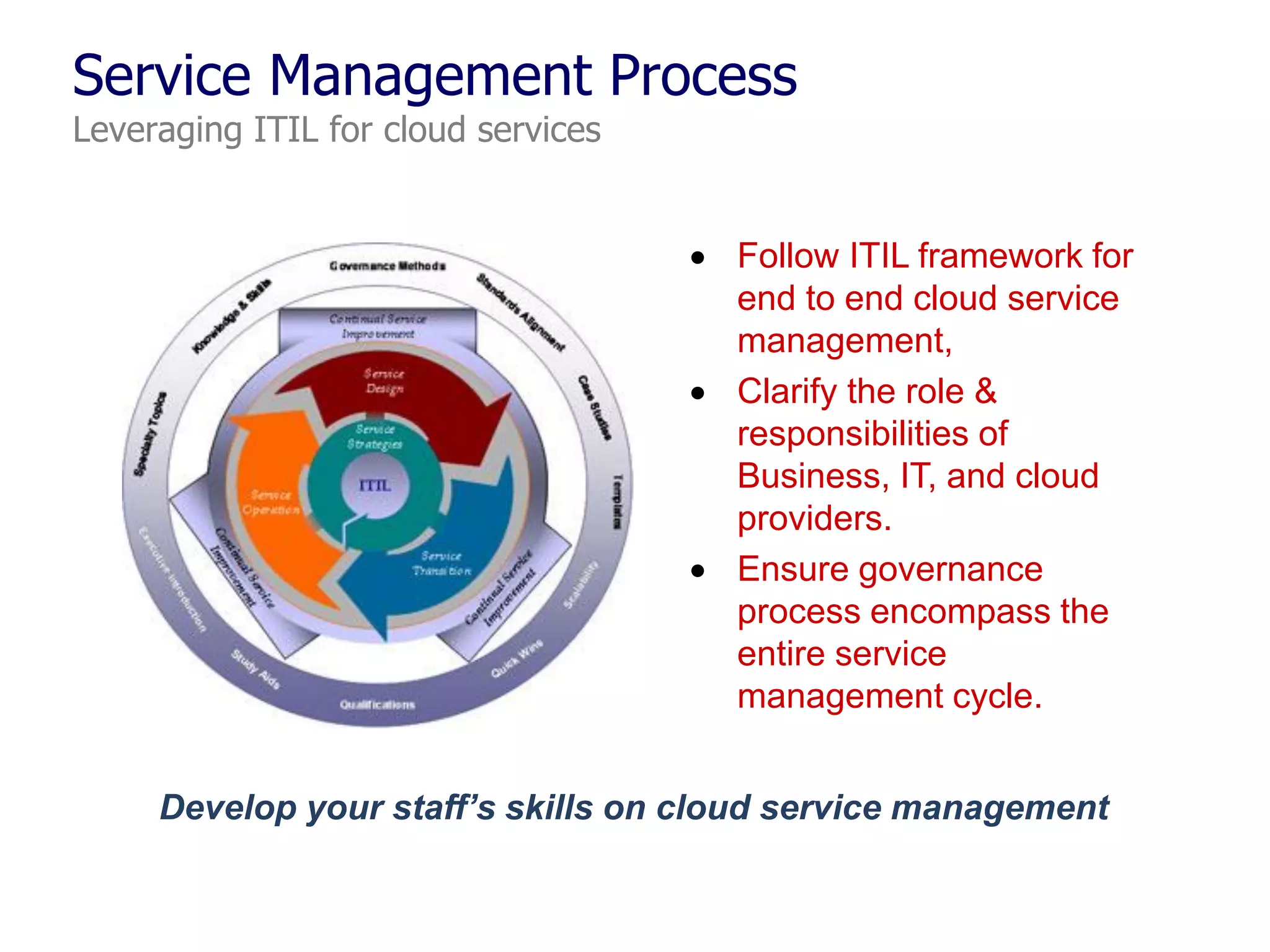
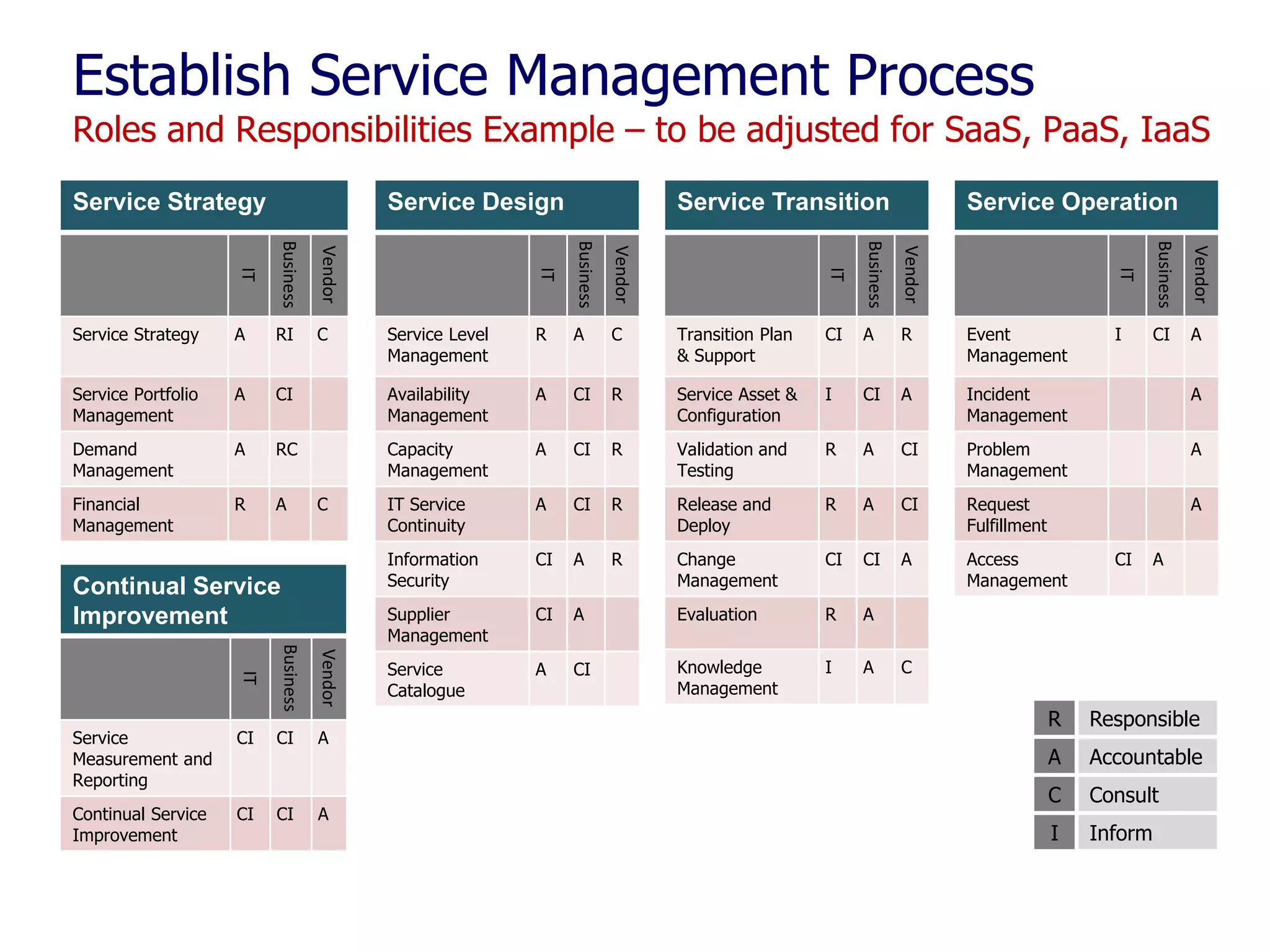
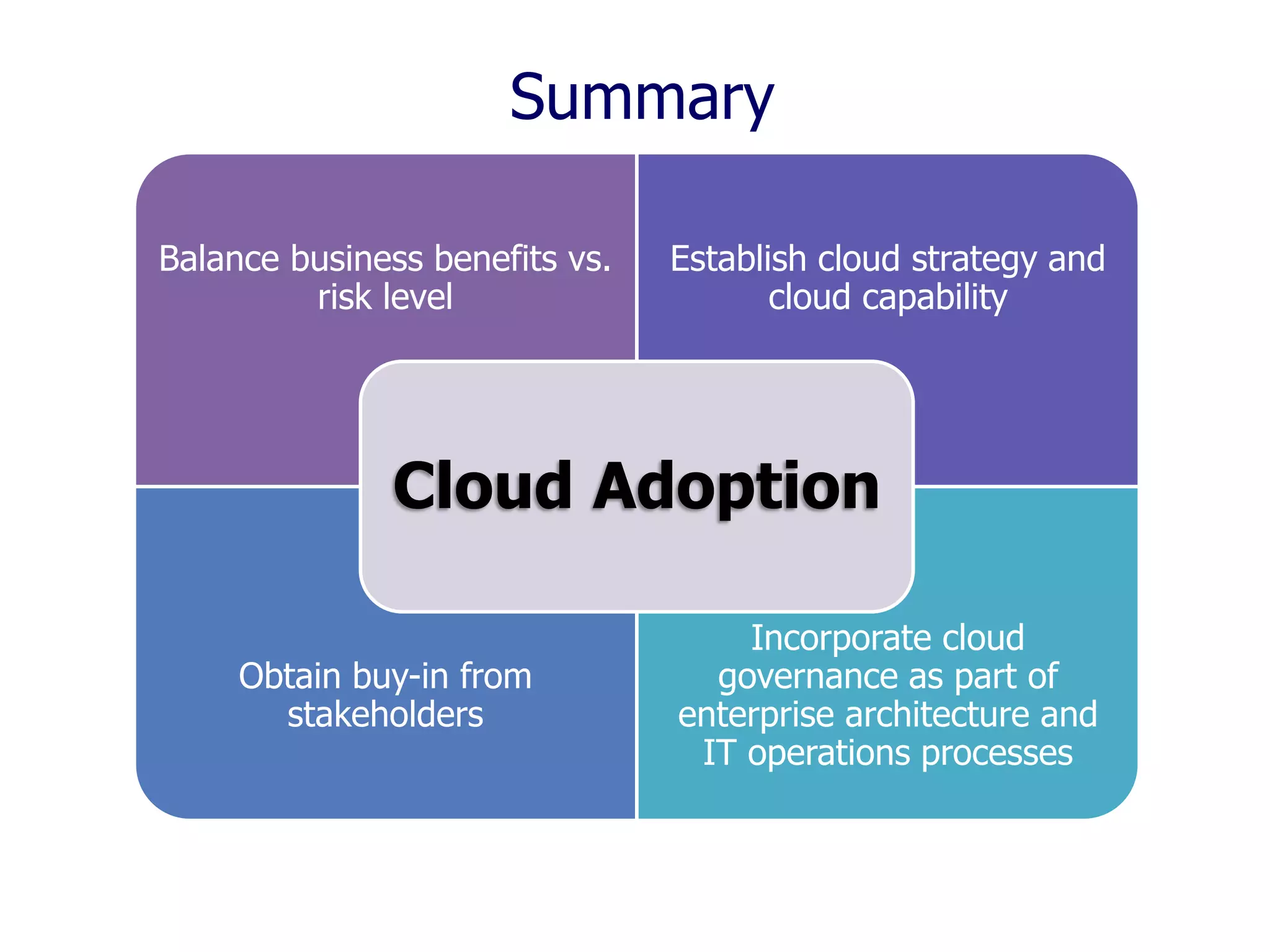
The document outlines a comprehensive strategy for cloud adoption in IT service management, focusing on governance structure, vendor selection, and risk management processes. It emphasizes the need for a cloud governance body to minimize risks while enabling business growth and efficiency through effective cloud capabilities. Additionally, it highlights the importance of executive endorsement and collaboration between business and IT to ensure successful cloud integration.