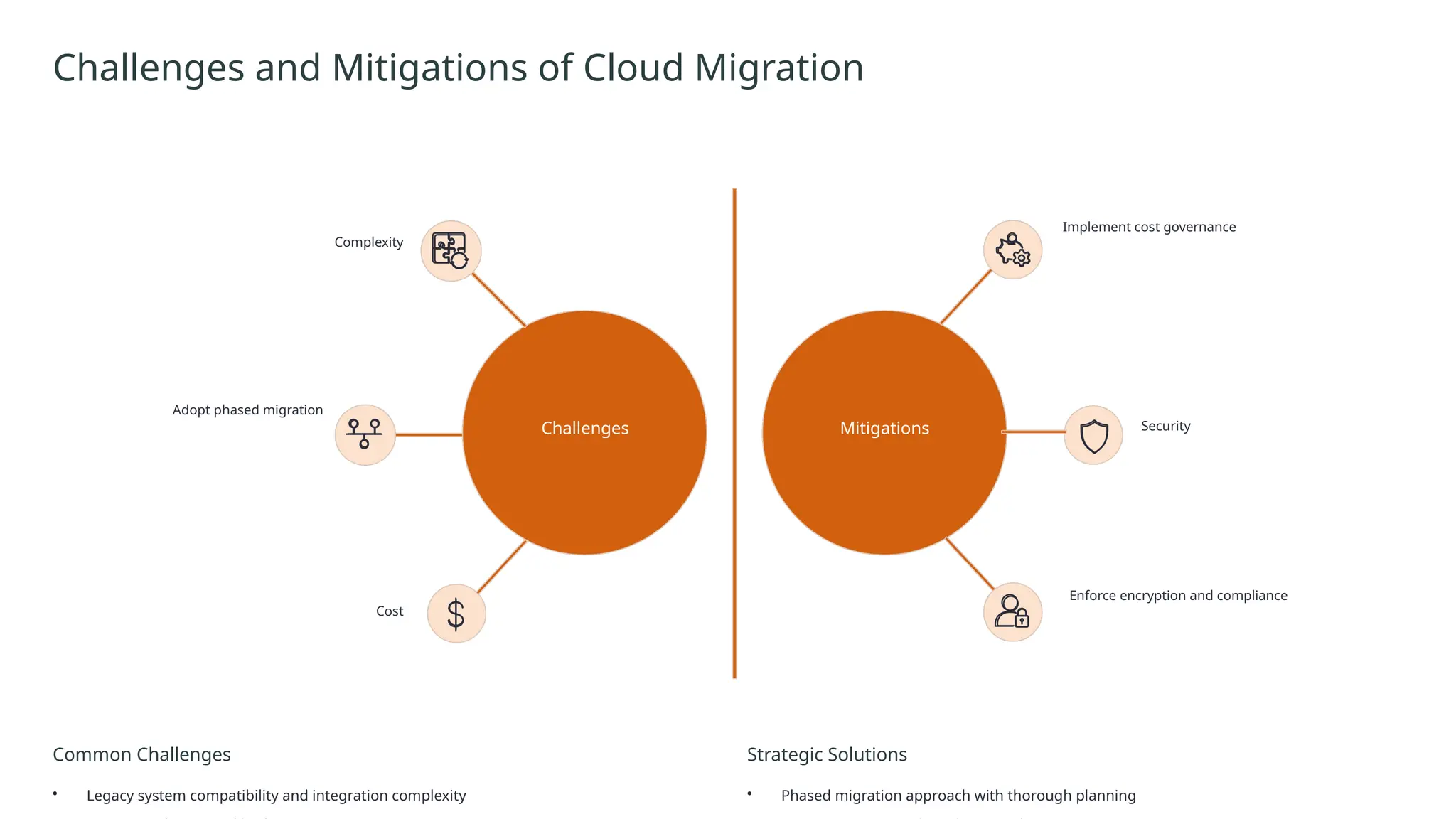
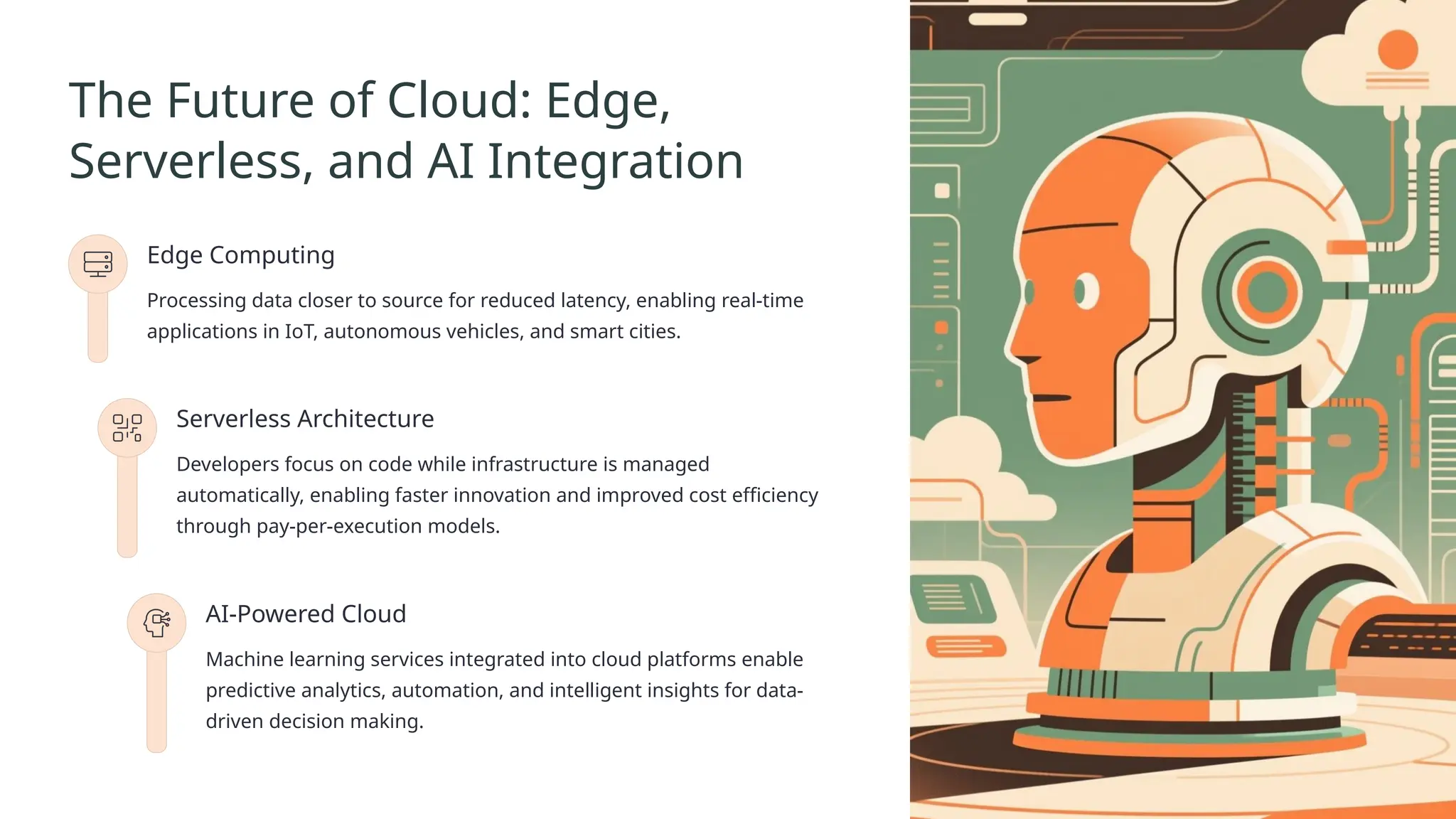
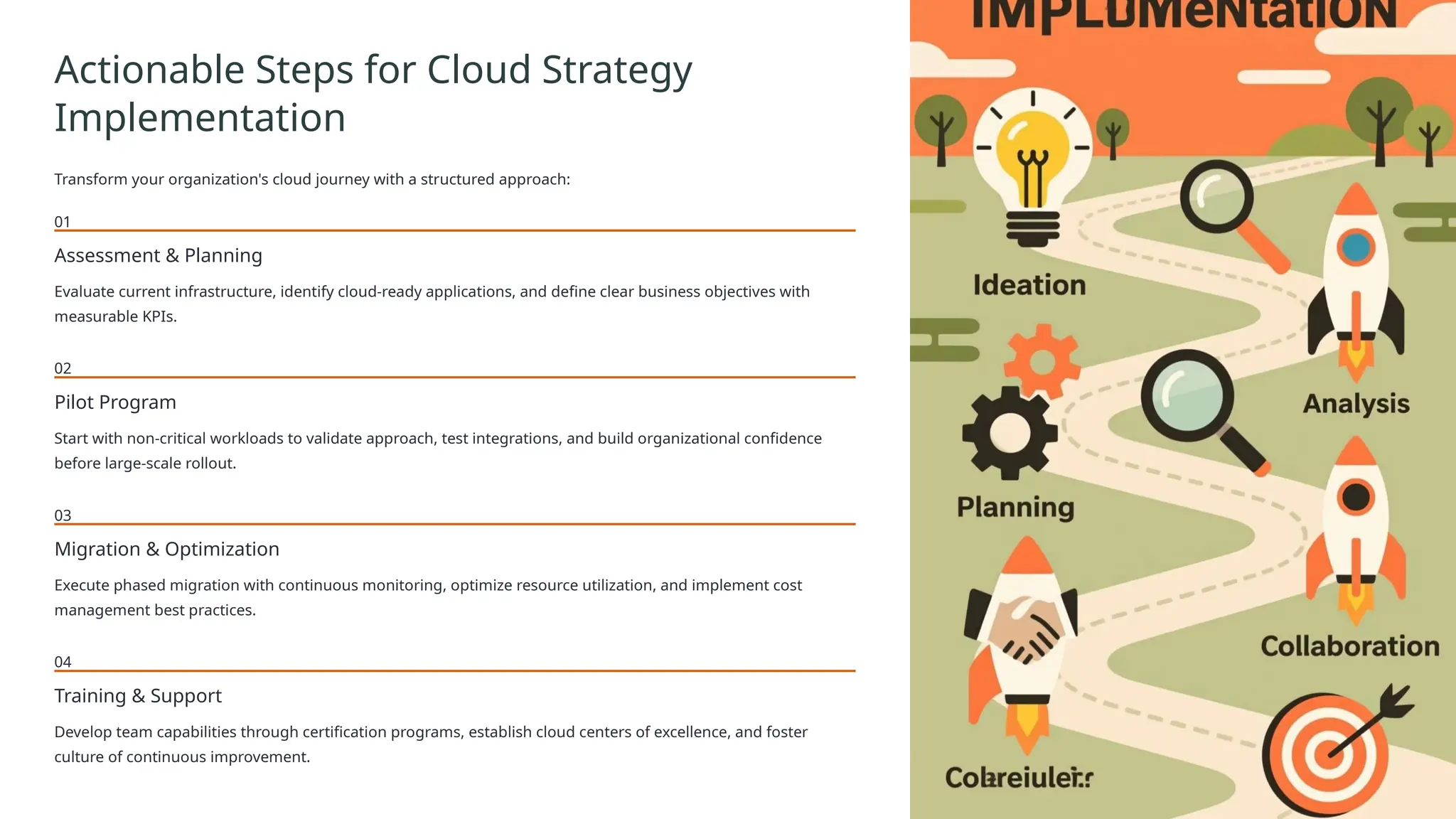
Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the internet ("the cloud") to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.