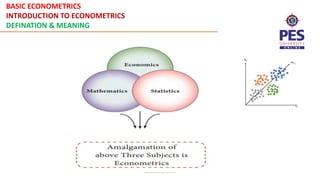
This document provides an introduction to the subject of basic econometrics. It defines econometrics as applying tools of economic theory, mathematics and statistical inference to analyze economic phenomena. Econometrics is concerned with empirically testing economic laws and considering economic theory, collecting data on economic variables, and applying statistical analysis to test hypotheses and draw conclusions to inform policymaking. Studying econometrics allows for empirical testing of economic theories and converting qualitative economic relationships into quantitative models that can be used to describe economic systems, test hypotheses, and forecast future economic activity.