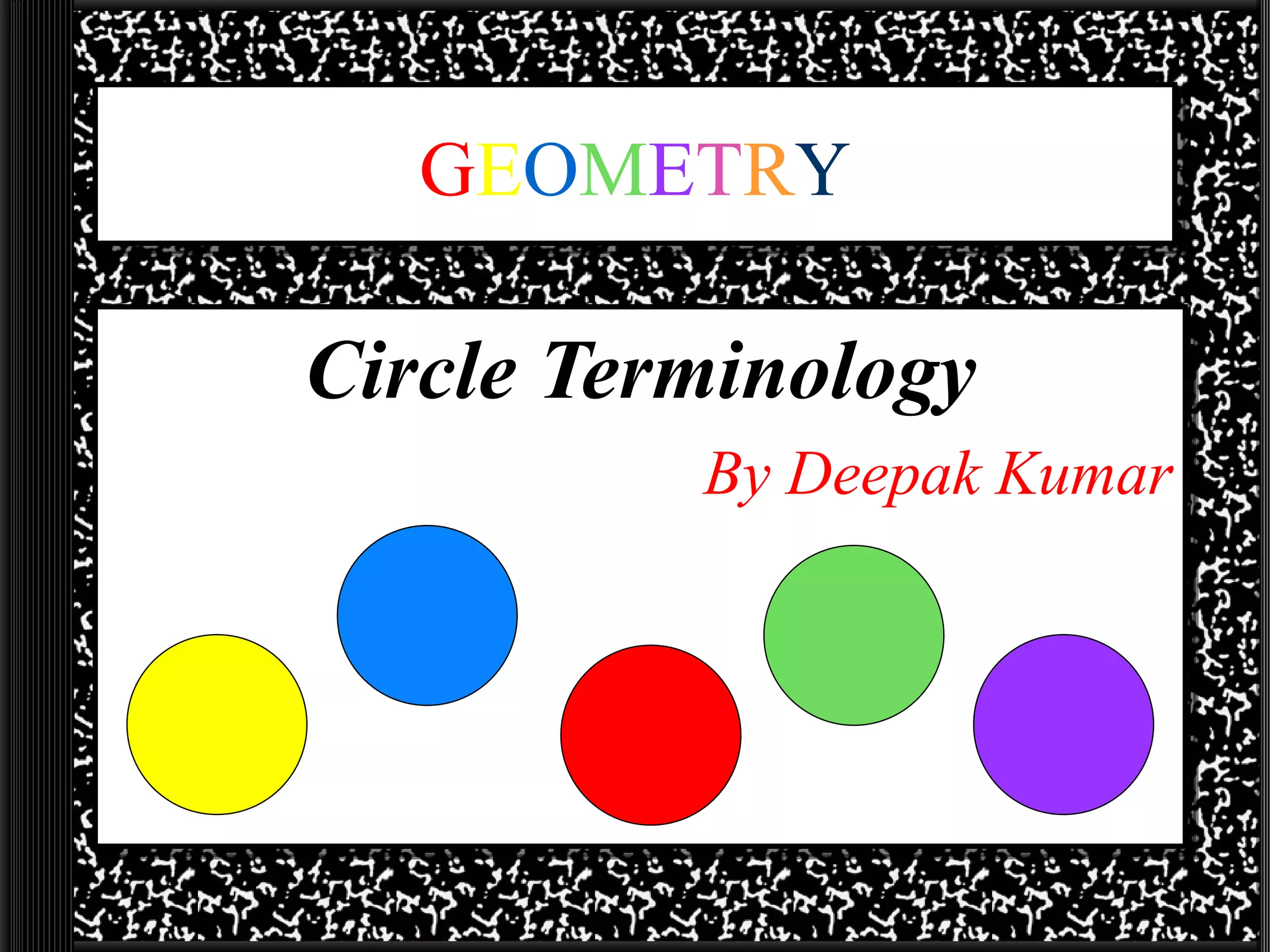
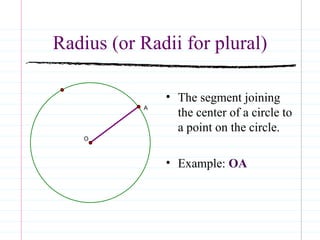
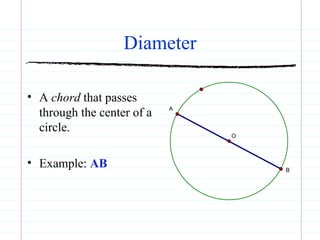
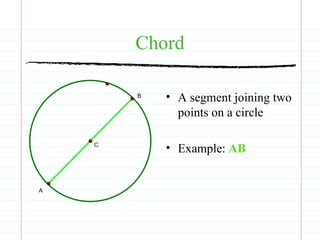
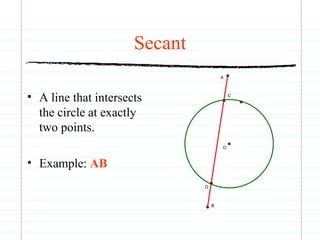
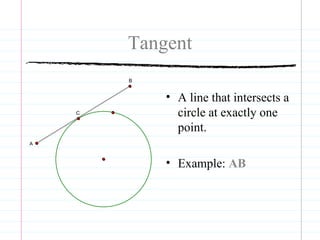
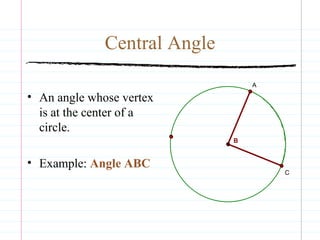
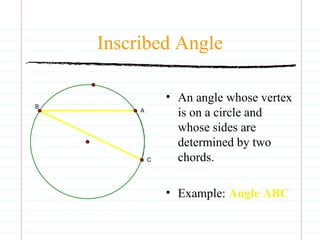
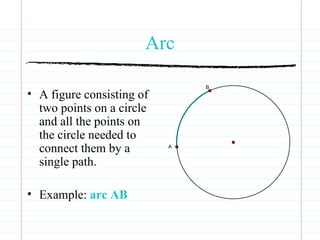
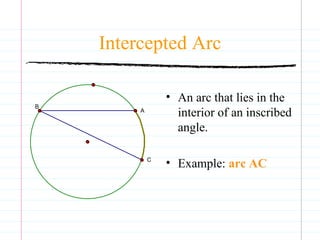
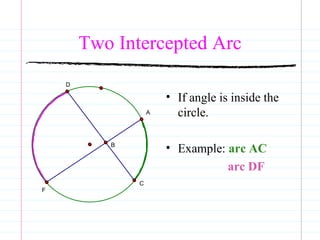
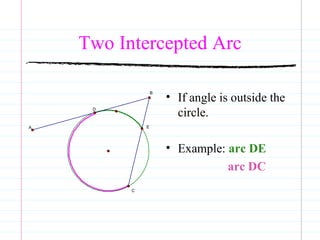
This document defines common circle terminology used in geometry, including radius, diameter, chord, secant, tangent, central angle, inscribed angle, arc, intercepted arc, and two intercepted arcs. Examples are provided to illustrate each term, such as the radius being the segment from the center to a point on the circle.