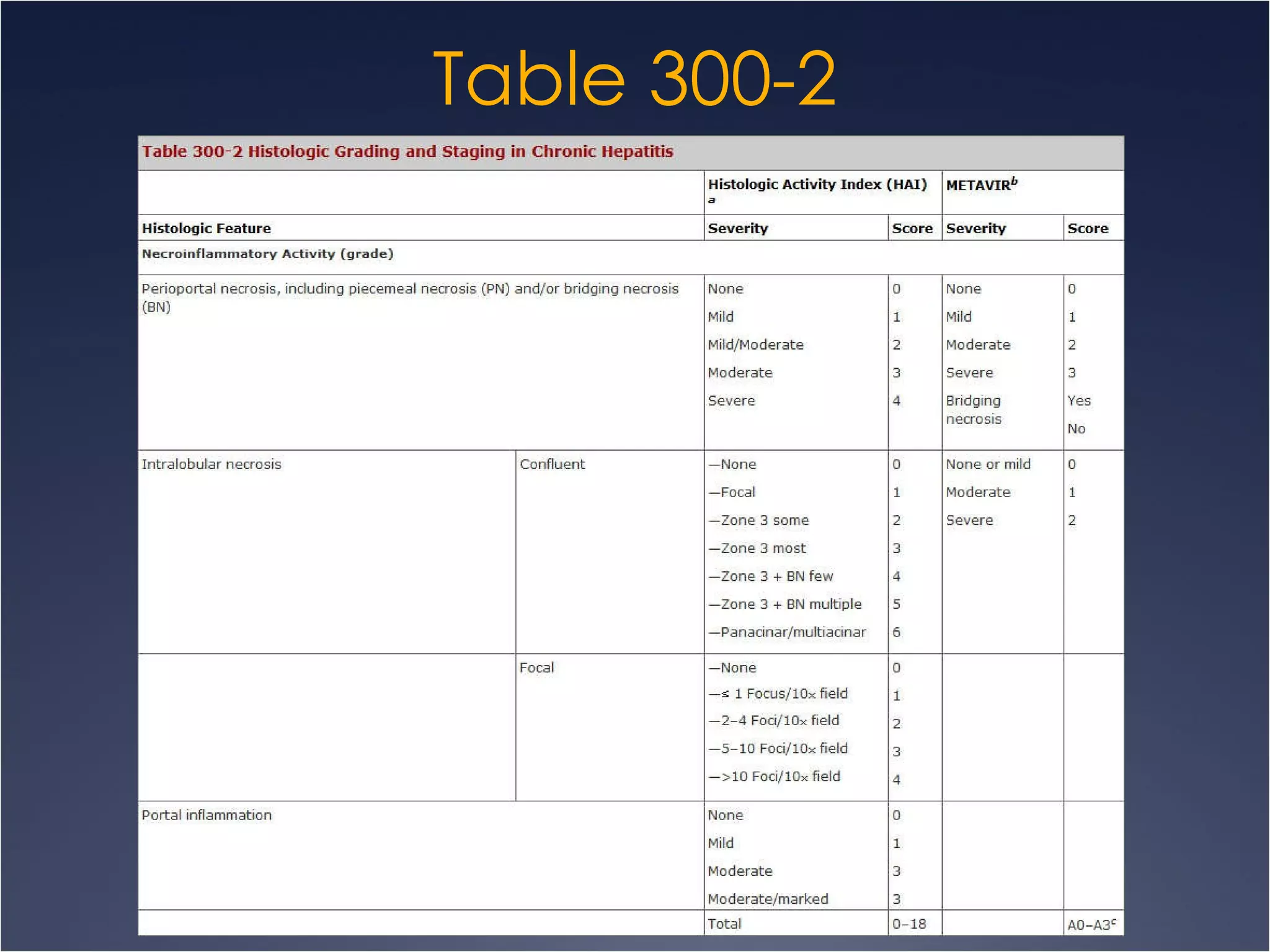
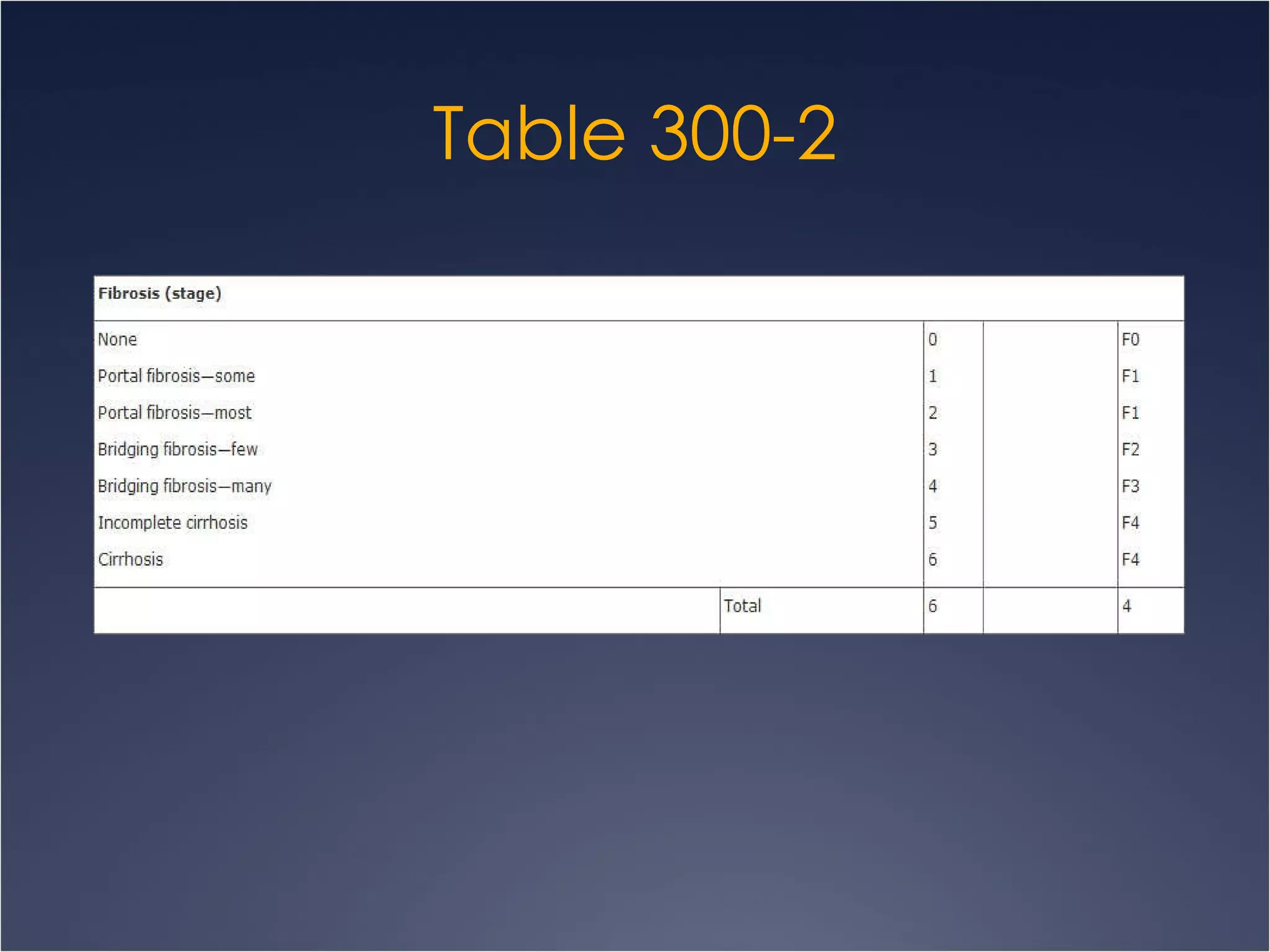
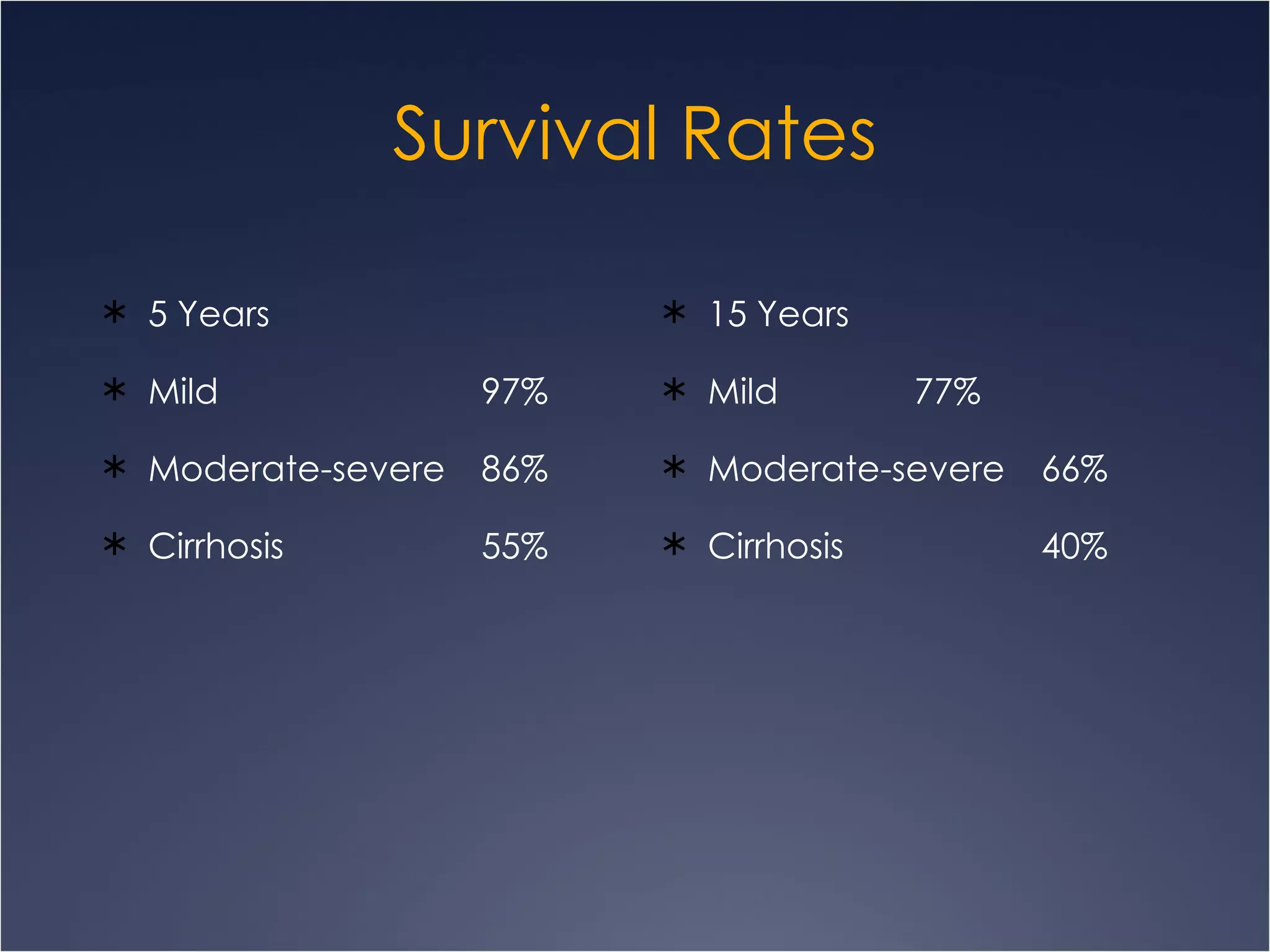
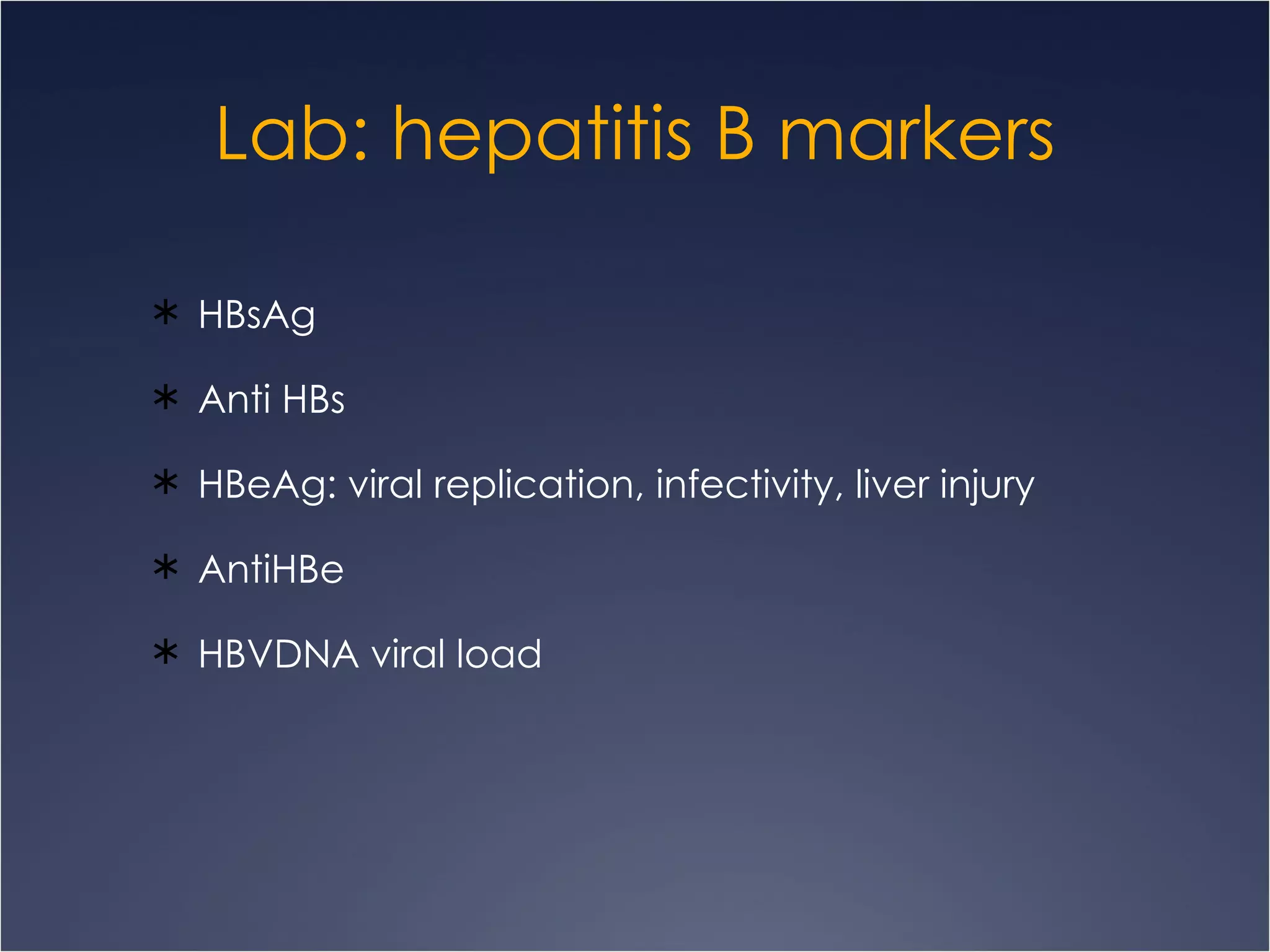
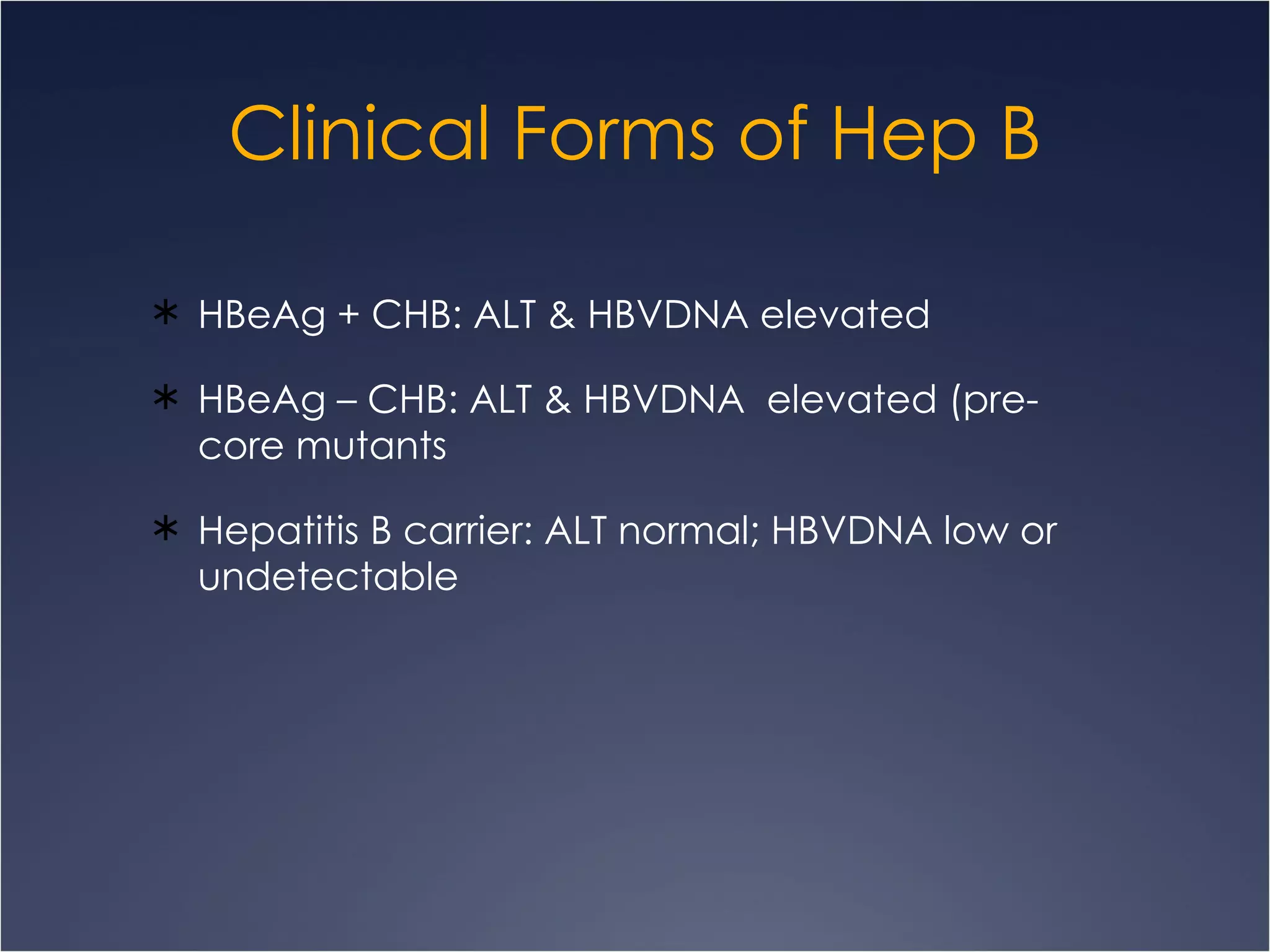
This document discusses chronic hepatitis, which is hepatic inflammation and necrosis that continues for at least 6 months. It can be classified by cause such as hepatitis B, C, autoimmune hepatitis, or drug-associated hepatitis. It can also be classified by grade based on the extent of necrosis and inflammation visible on biopsy. Chronic hepatitis B has varying likelihood of chronicity depending on age at infection and may present asymptomatically or with fatigue, jaundice, ascites, or bleeding varices. Laboratory findings include elevated liver enzymes and hypoalbuminemia. Chronic hepatitis B clinical forms are differentiated based on presence of HBeAg and levels of ALT and HBVDNA.