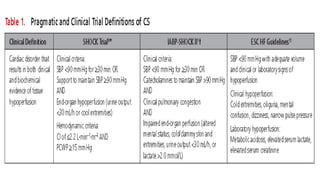
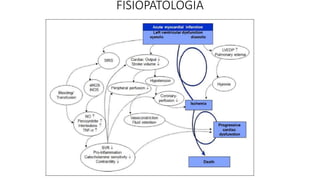
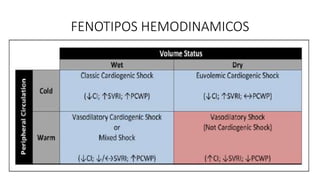
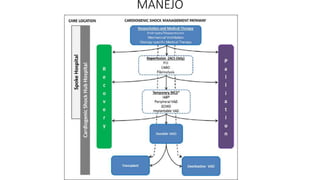
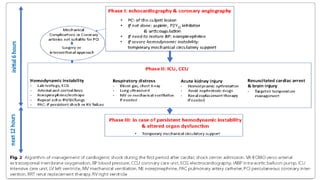
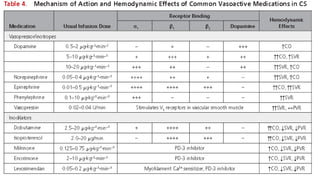
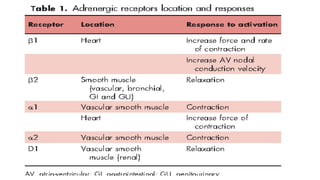
1. Cardiogenic shock is defined as a state of acute cardiac hemodynamic instability resulting from disorders impairing the myocardium, valves, conduction system, or pericardium.
2. An analysis of hospital data showed an increase in cardiogenic shock from 6% to 10% of overall patients presenting with STEMI, and from 7% to 12% of patients over age 75. In-hospital mortality decreased slightly but remained high at 34% overall and 55% for patients over age 75.
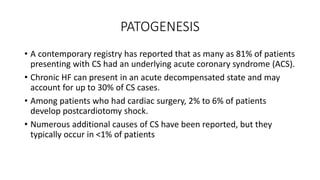
3. The most common underlying causes of cardiogenic shock are acute coronary syndrome (81% of cases) and acute decompensation of chronic heart failure (30% of cases).