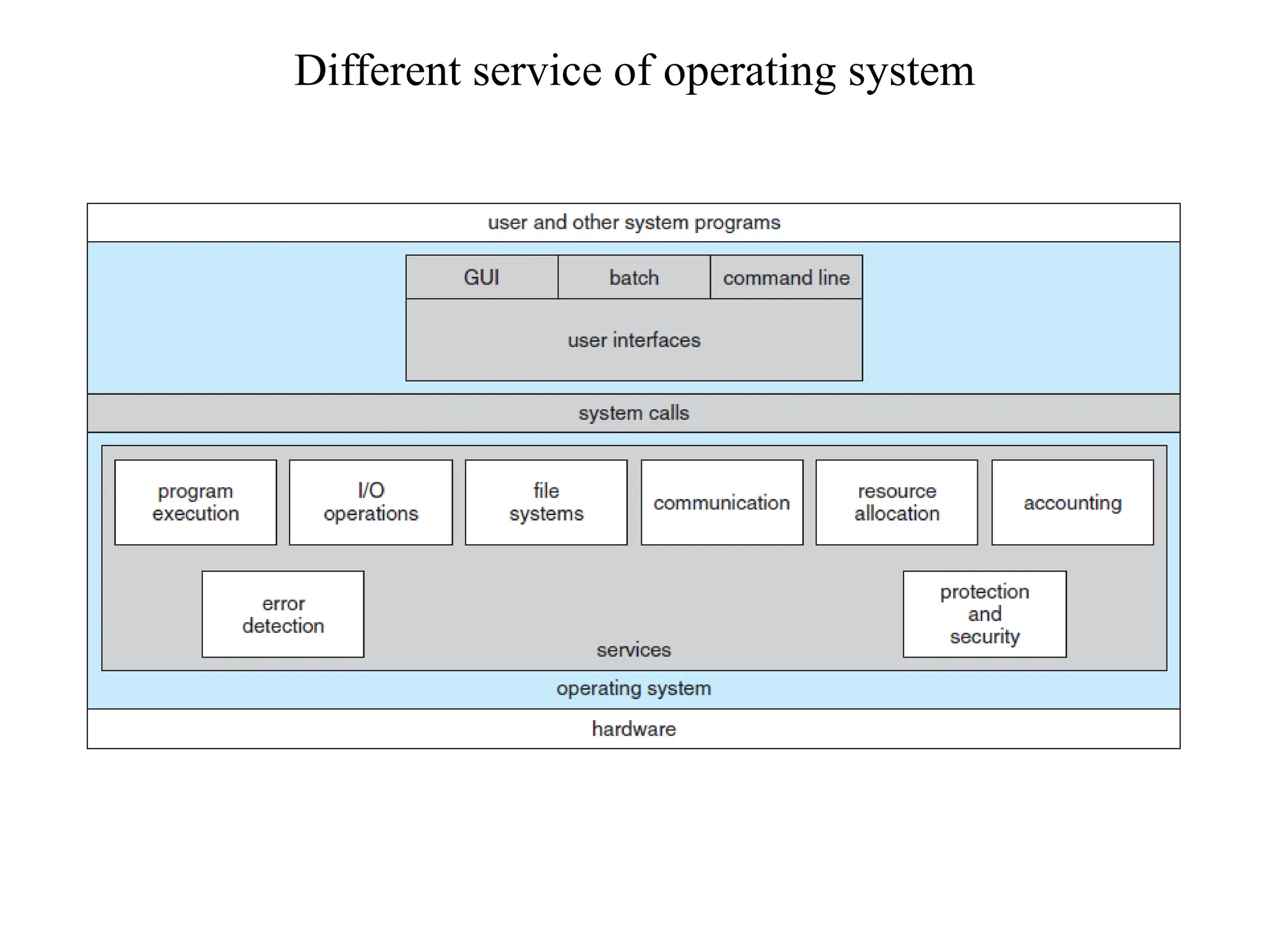
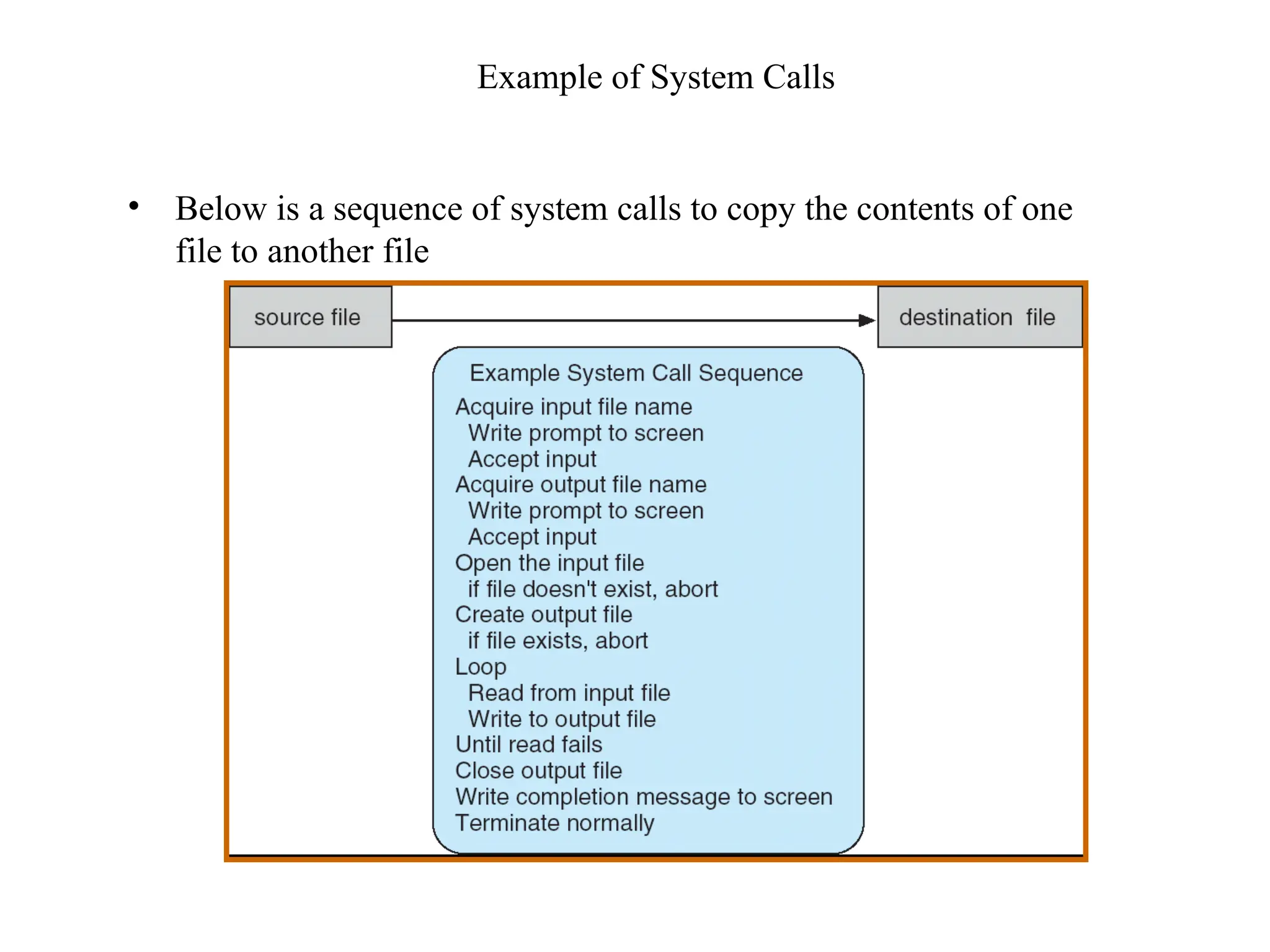
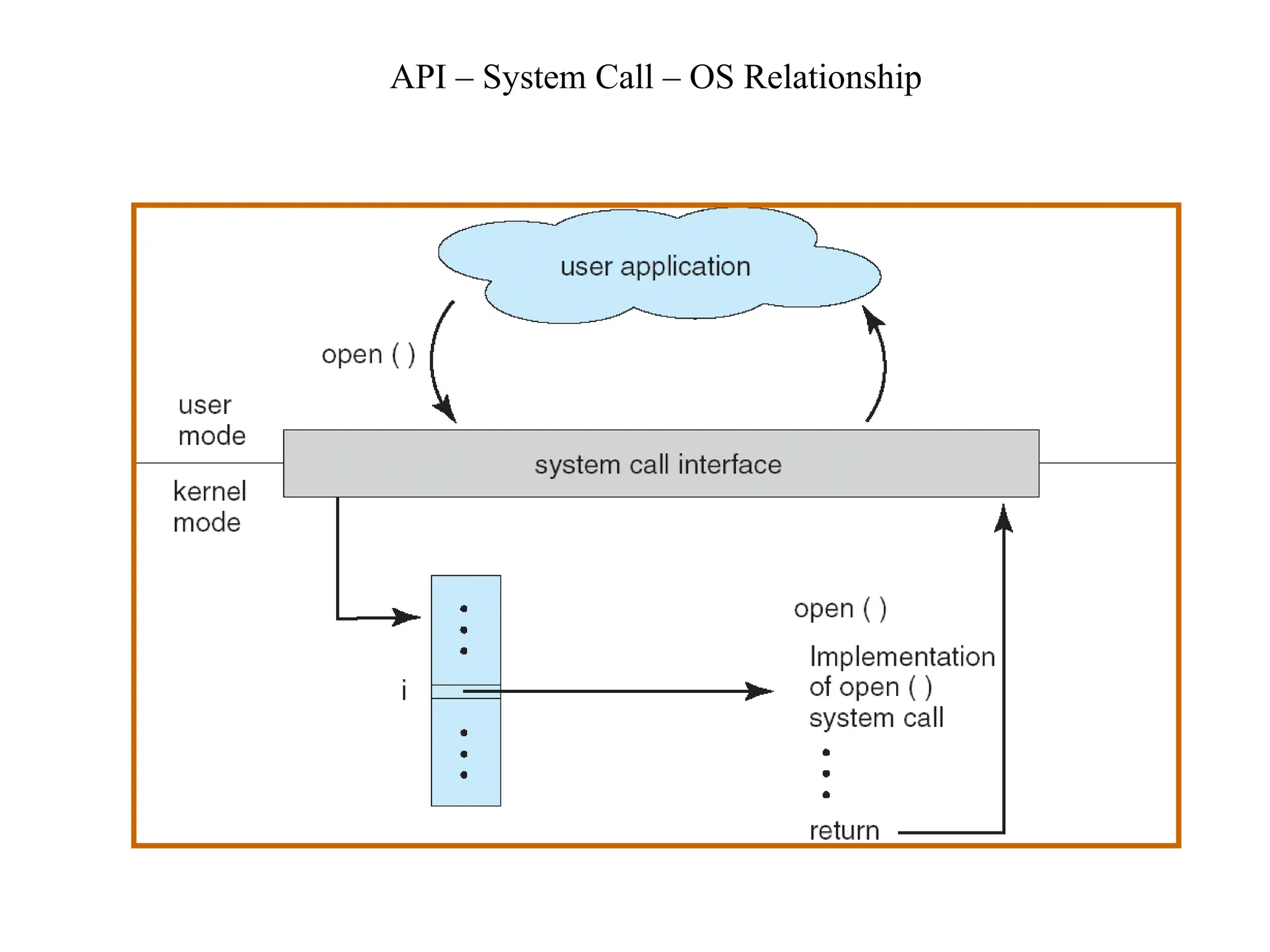
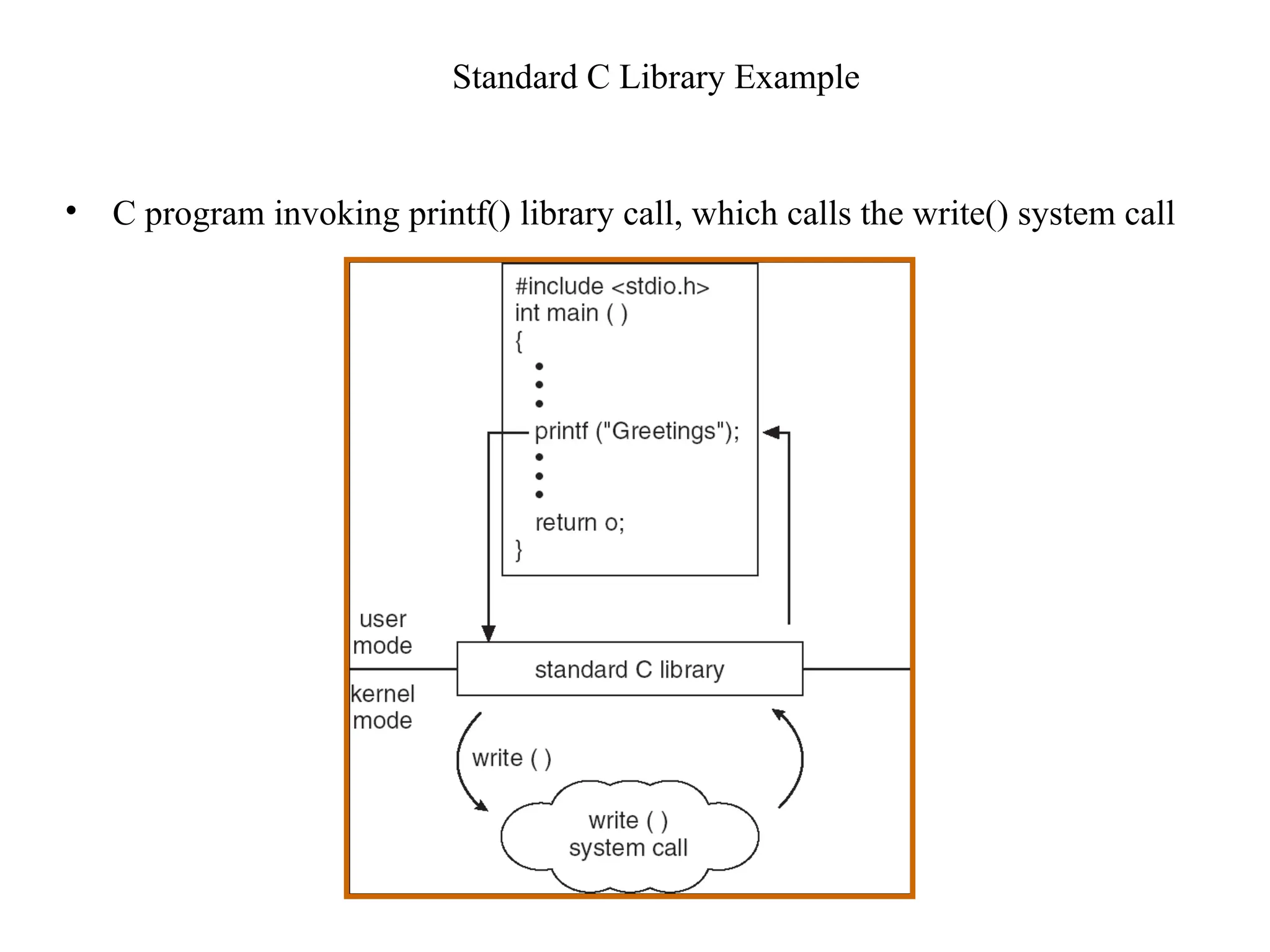
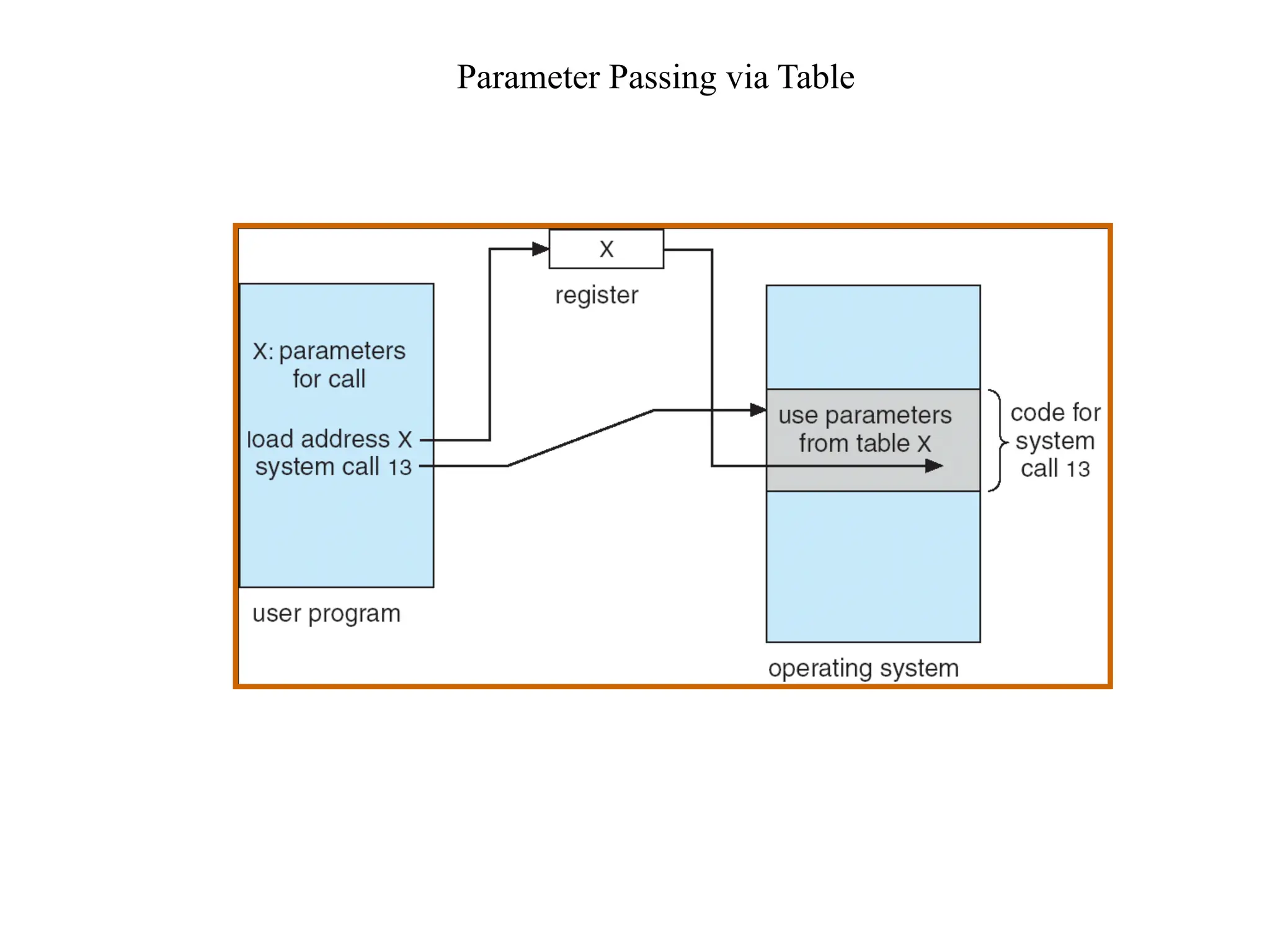
The document discusses the structure and services of operating systems, detailing services such as user interfaces, program execution, input/output operations, file system manipulation, communication, error detection, resource allocation, accounting, and security. It also covers system calls and their implementation, including process control, file management, device management, information maintenance, and communications. Furthermore, it outlines the components of operating systems, specifically focusing on process, memory, file, I/O, and secondary storage management.