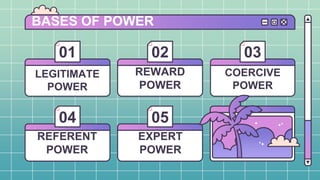
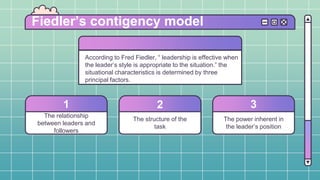
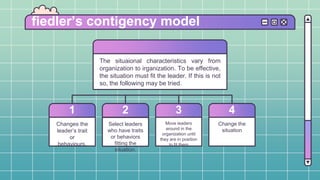
This document discusses different approaches to leadership. It begins by defining leadership as influencing others to achieve organizational goals and discusses the various bases of power leaders can have, such as legitimate, reward, coercive, referent, and expert power. It then examines traits of effective leaders, leadership skills, and behavioral and contingency approaches to leadership styles. The contingency approaches discussed include Fiedler's contingency model, Hersey and Blanchard's situational leadership model, the path-goal model, and Vroom's decision-making model.