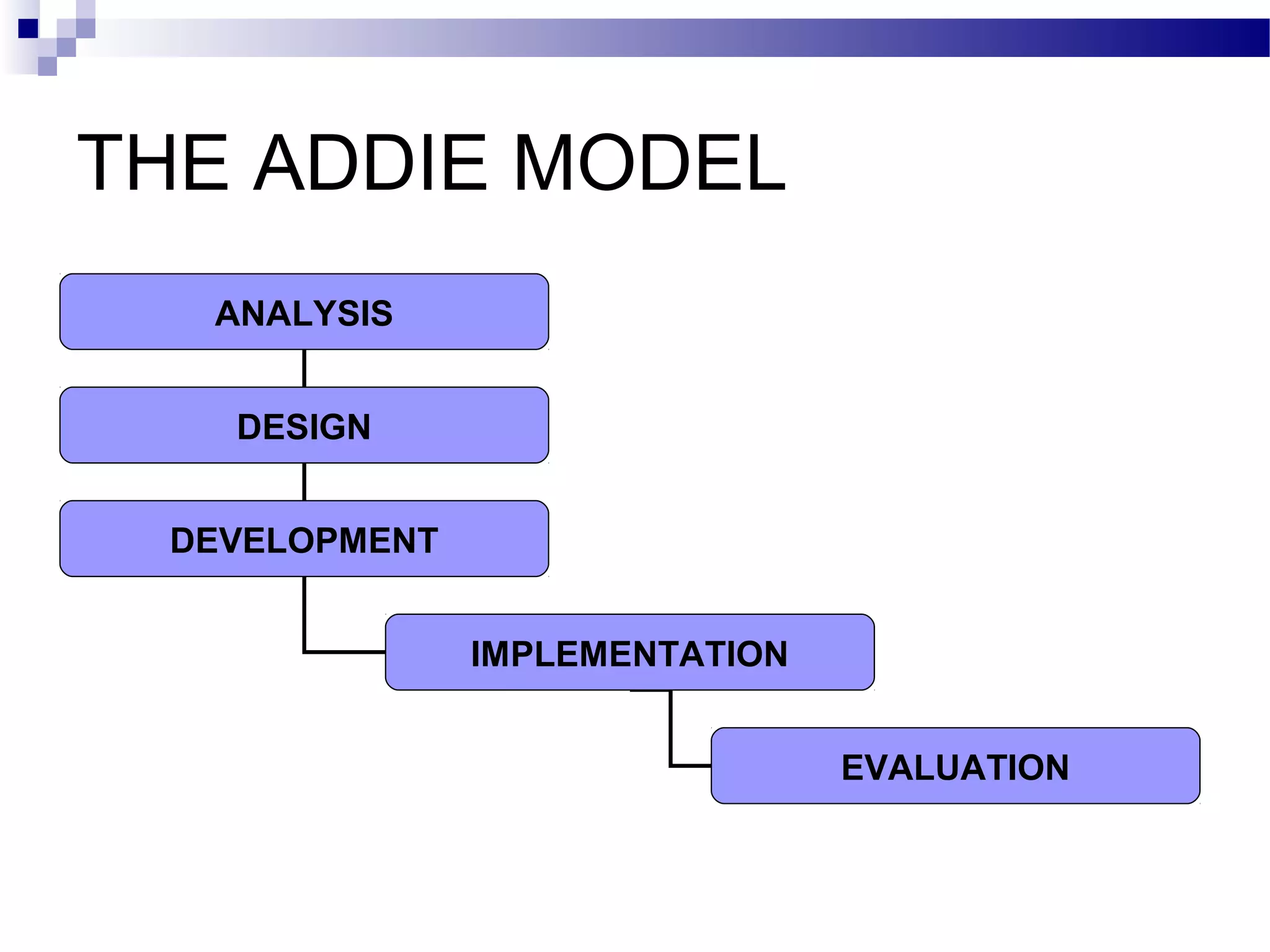
The document discusses multimedia systems and the process of designing systematic teaching. It defines multimedia systems as combining various elements like text, graphics, animation, sound and video to present information. The main elements are described as text, graphics, video, animation, audio and hypermedia. It then explains the ADDIE model of instructional design which consists of the five phases of analysis, design, development, implementation and evaluation. Each phase of the ADDIE model is described in one or two sentences.