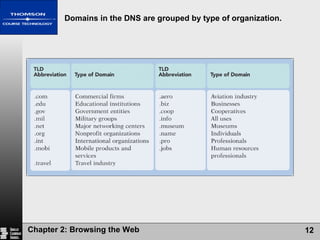
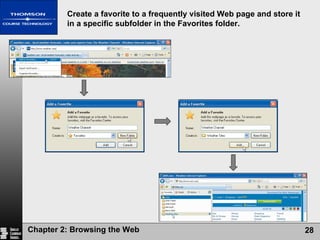
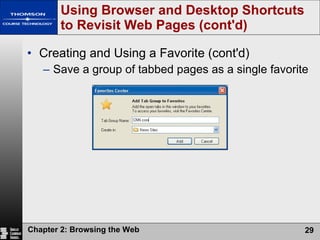
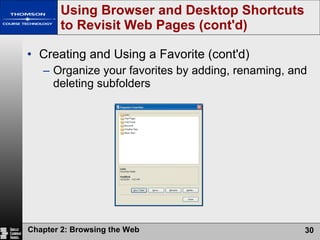
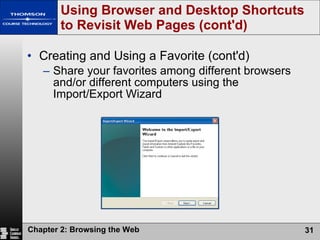
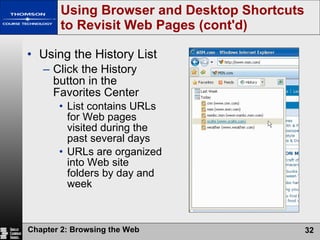
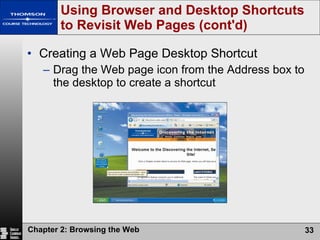
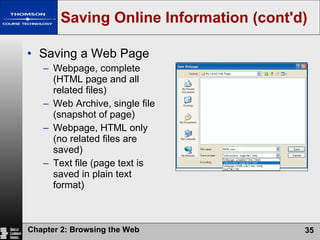
The document summarizes key concepts about browsing the web, including describing web sites and pages, explaining how IP addresses and URLs locate web content, and outlining how to navigate and customize a web browser. It also discusses risks of using the web like viruses and privacy concerns, emphasizing the importance of installing protection software and understanding sites' privacy policies.