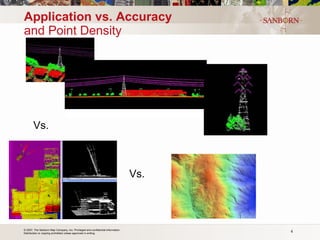
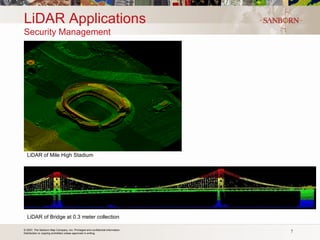
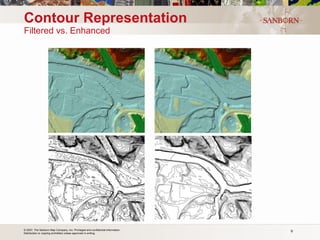
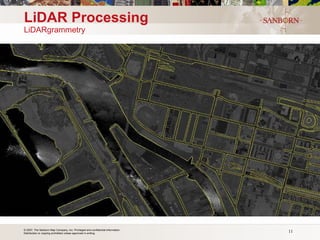
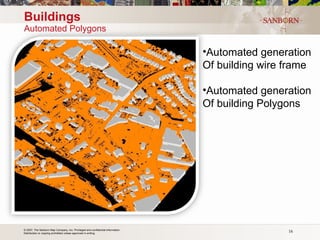
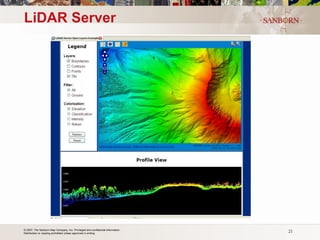
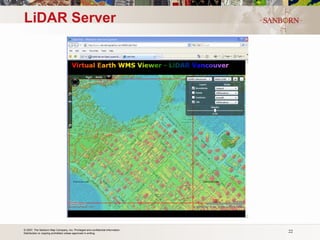
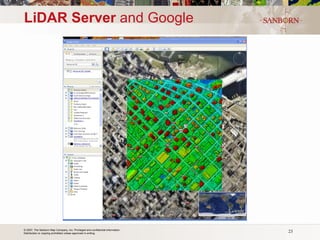
The document discusses the use of LiDAR (light detection and ranging) technology for various applications such as flood plain mapping, transportation infrastructure, forestry management, and more. It provides details on LiDAR accuracy standards, processing methods, and deliverable data formats. The presentation aims to help audiences understand how LiDAR data can aid in decision-making processes.