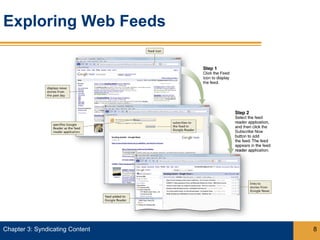
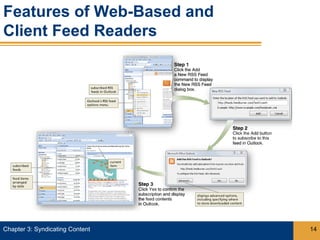
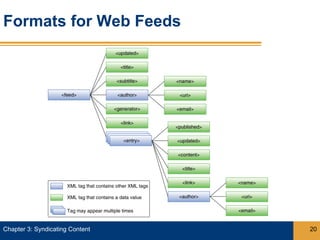
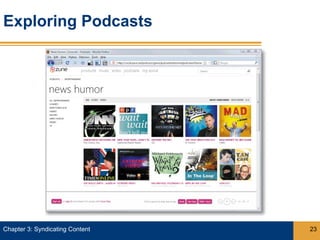
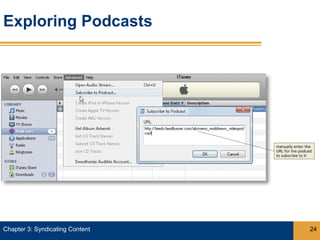
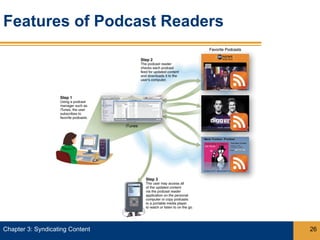
Syndication allows content from websites to be shared through web feeds. Web feeds represent lists of updated content items that can be accessed by feed readers and subscriber devices. Common types of syndicated content include blog posts, news headlines, job listings, and photos. RSS and Atom are popular formats for web feeds, which are written in XML. Podcasts are a type of web feed that distributes audio or video files.