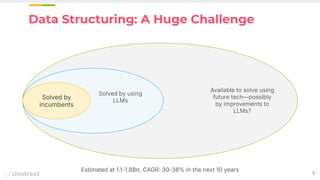
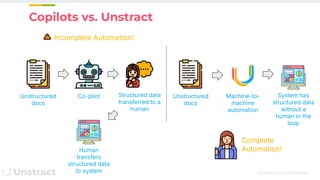
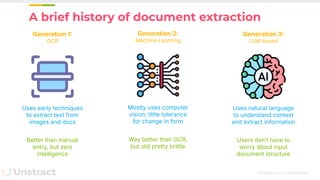
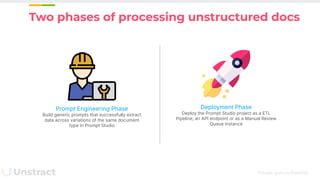
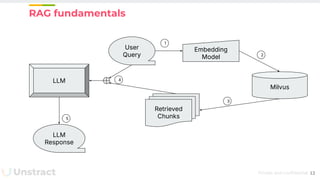
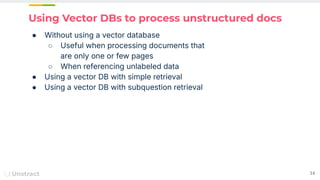
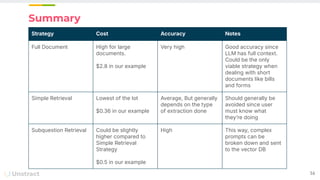
The document discusses challenges and advancements in extracting structured data from unstructured documents, highlighting the role of large language models (LLMs) in addressing these issues. It introduces Unstract, a startup focused on automated data extraction, and compares various approaches to processing documents, including the use of vector databases. Additionally, it explores the evolution of document extraction technologies, from OCR to LLM-based methods, emphasizing the importance of prompt engineering and the potential for future improvements.