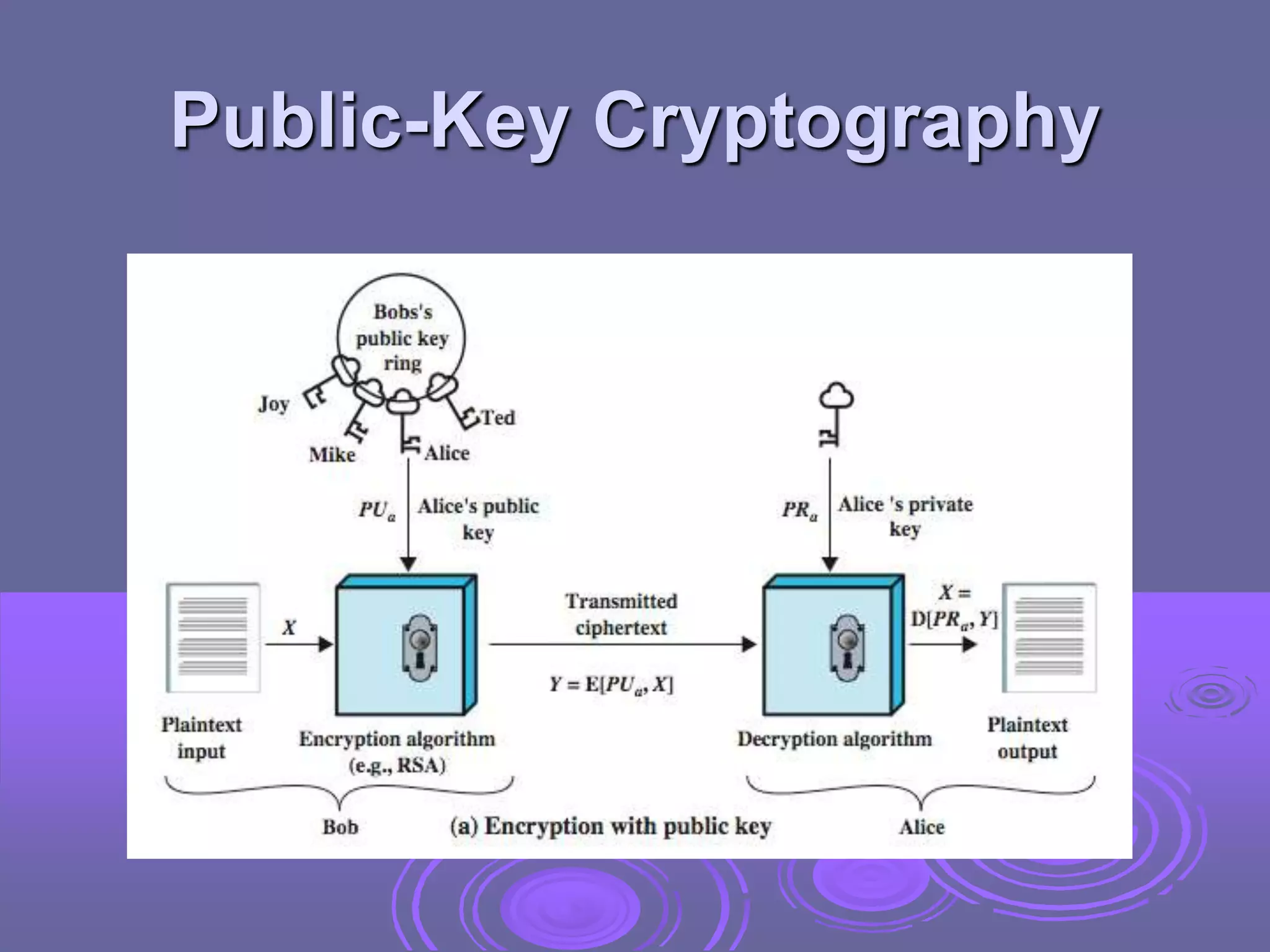
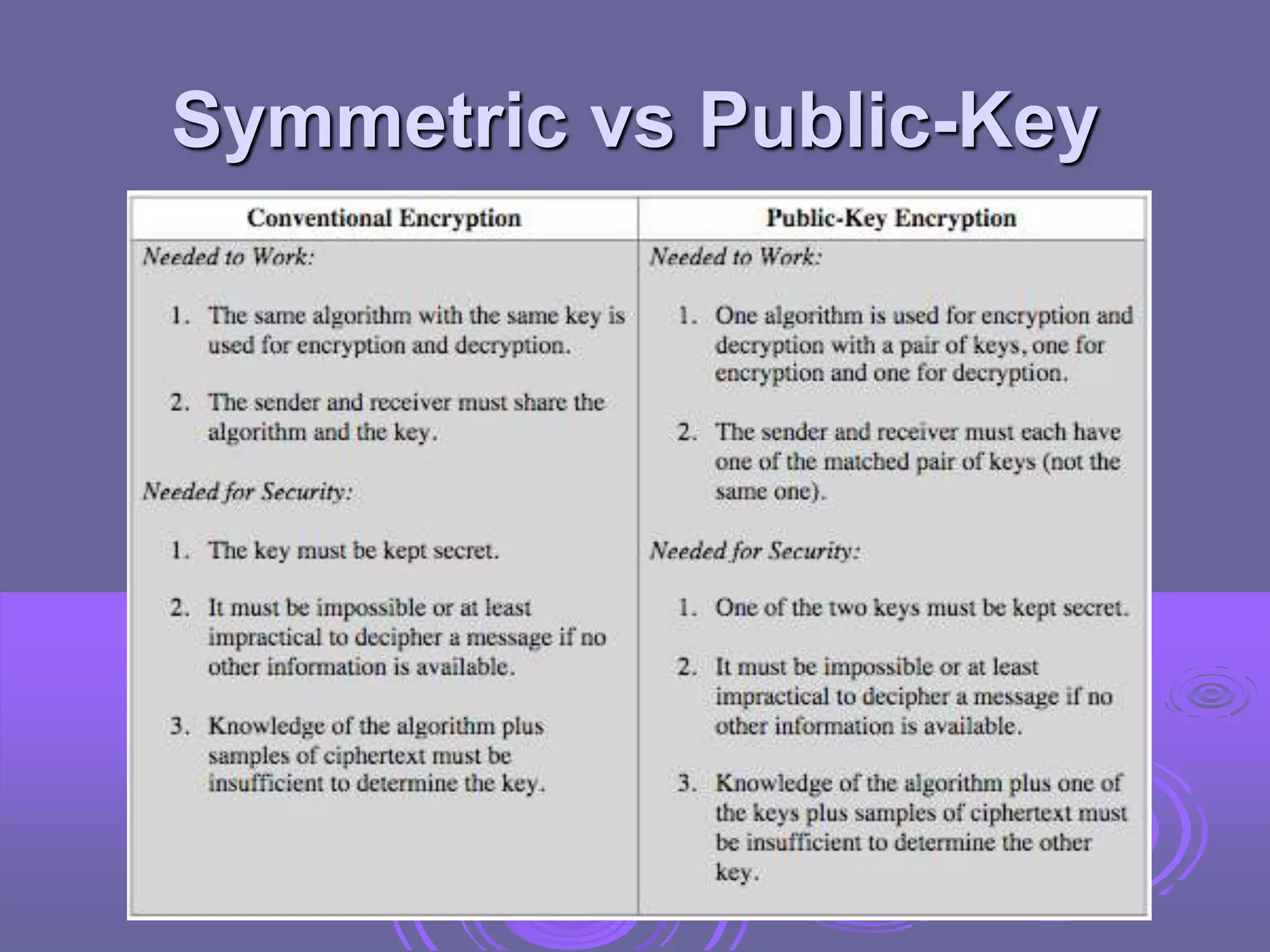
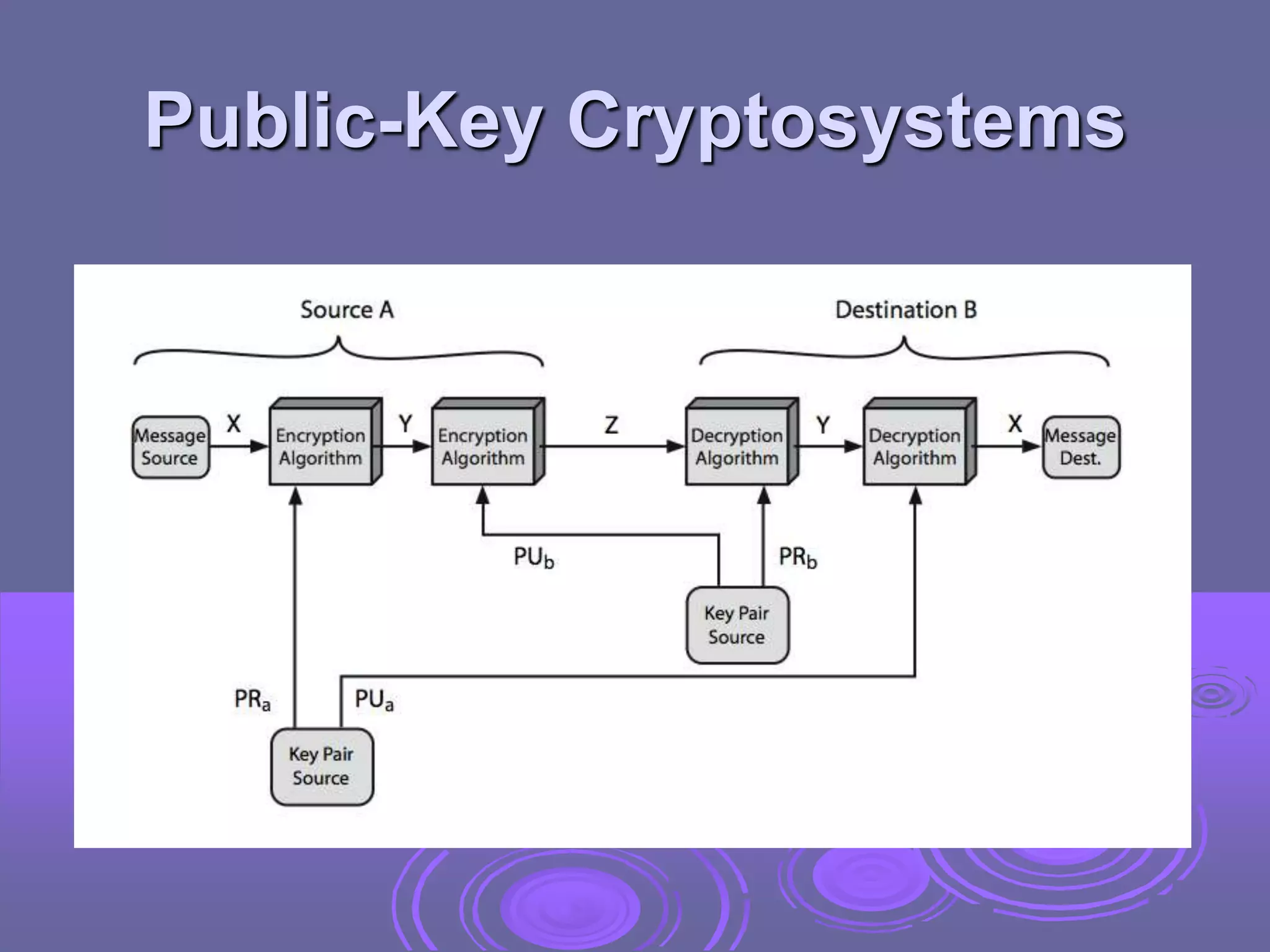
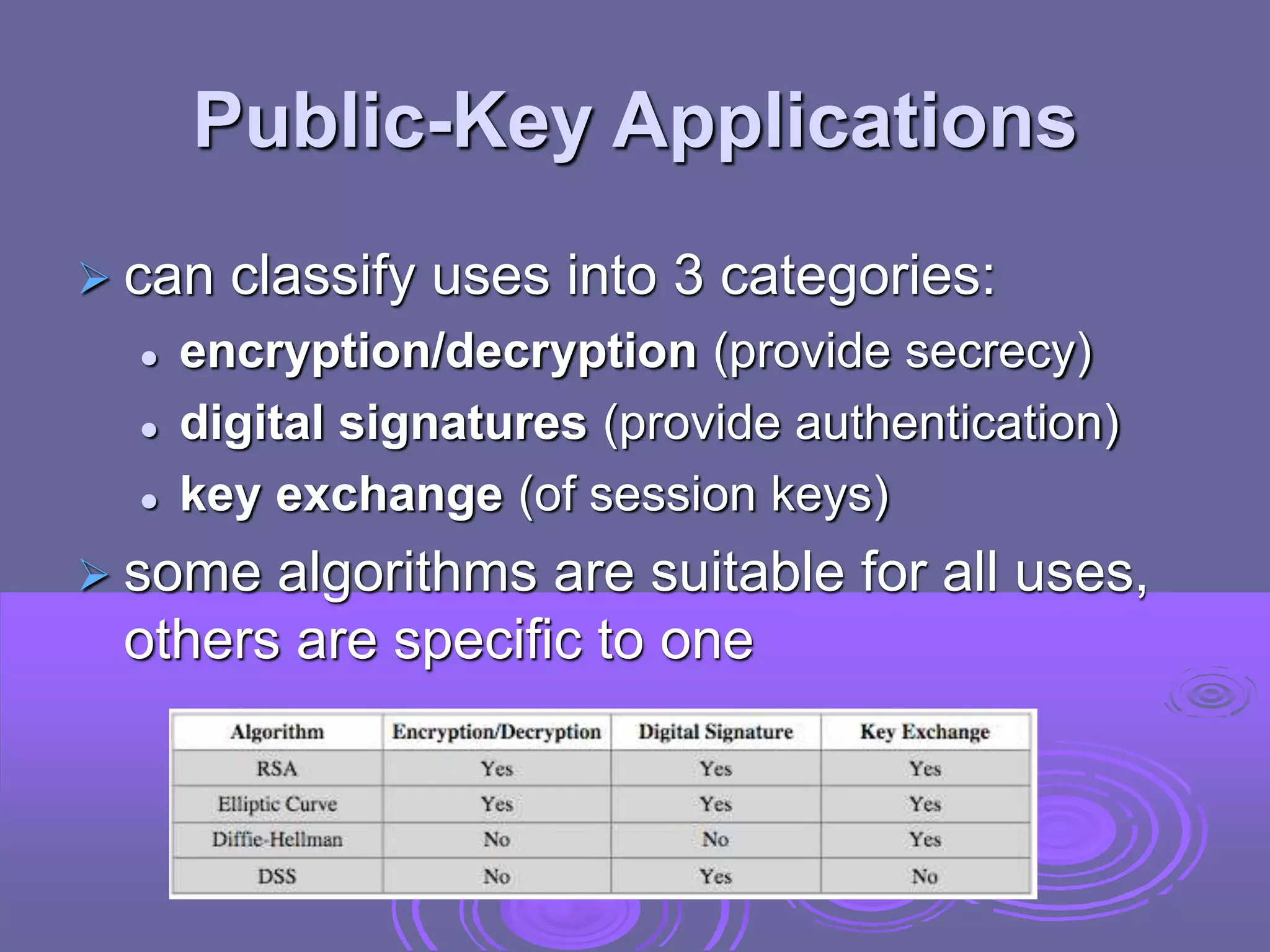
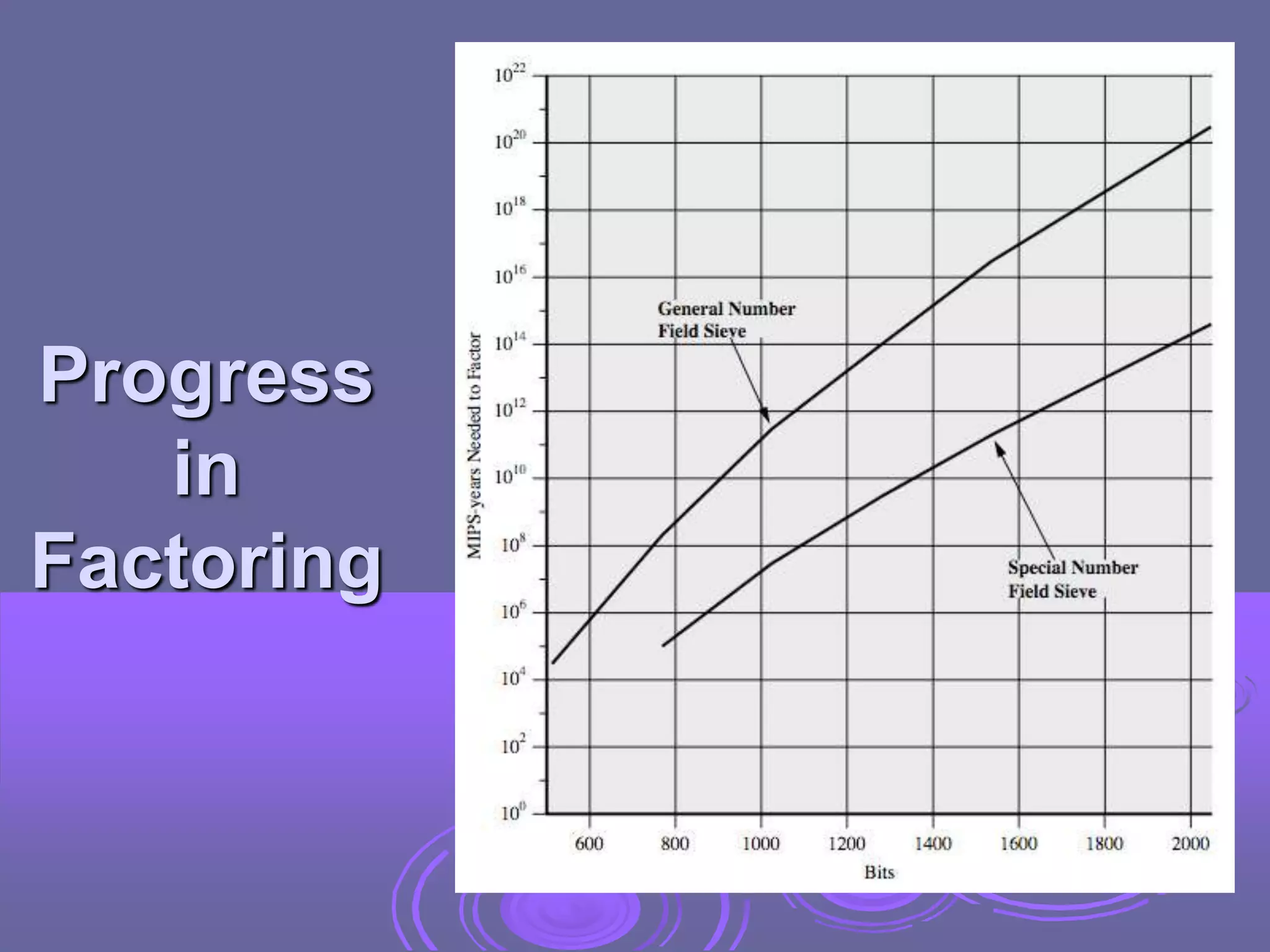
Public-key cryptography uses two keys: a public key for encryption and digital signatures, and a private key for decryption and signature verification. RSA is the most widely used public-key cryptosystem, using large prime factorization and modular exponentiation. It allows secure communication without prior key exchange. While brute force attacks on RSA are infeasible due to large key sizes, its security relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers.