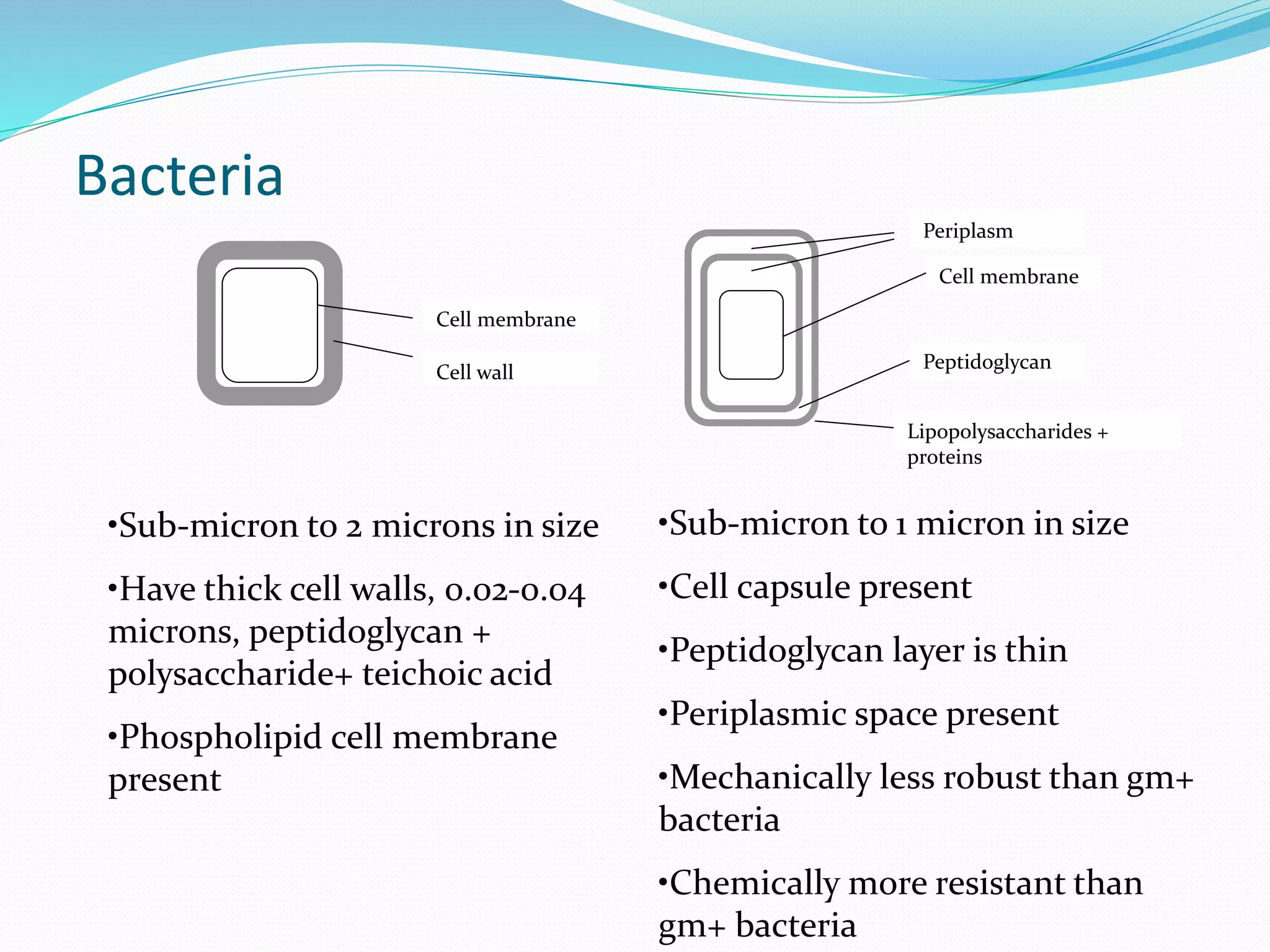
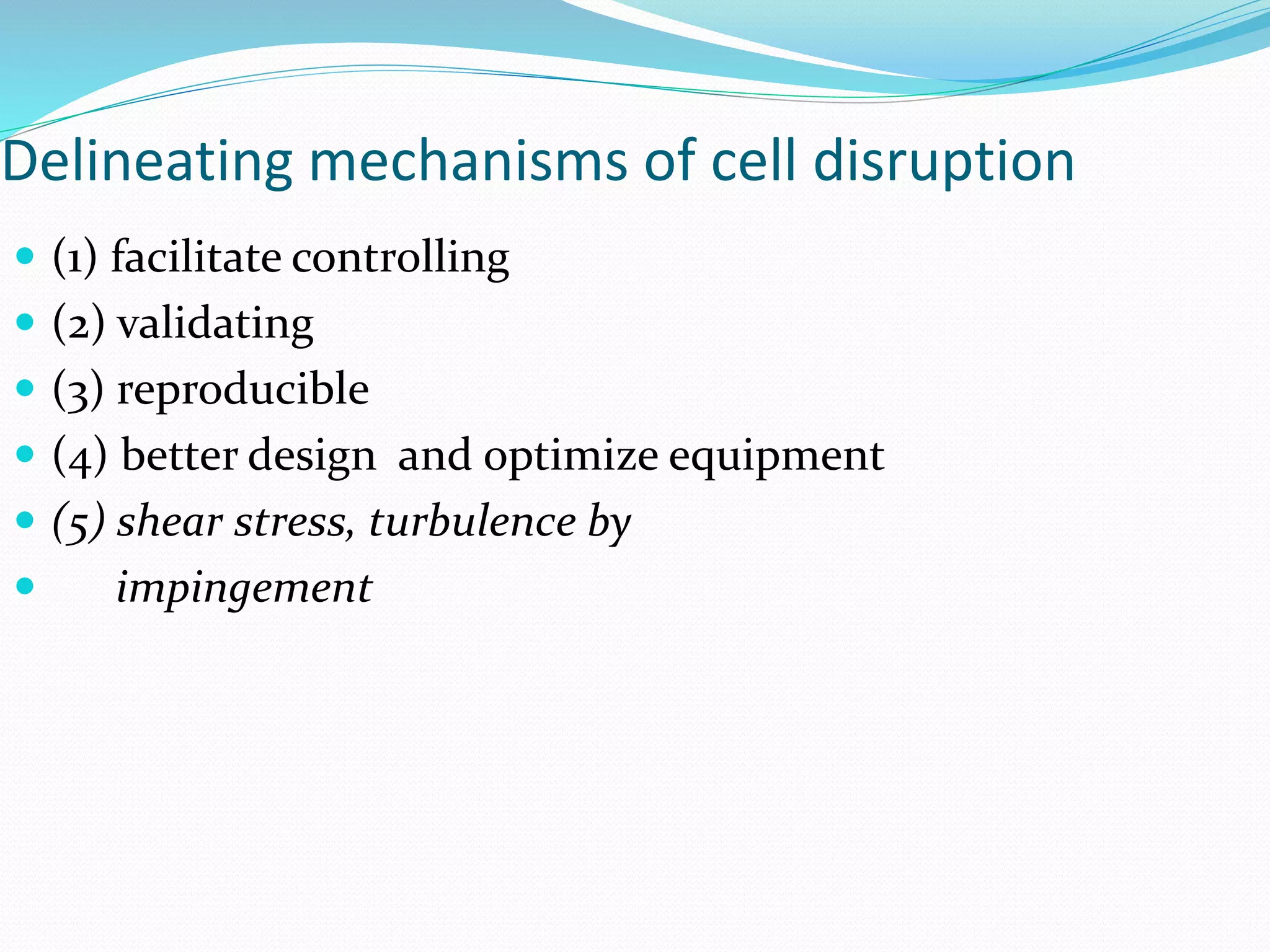
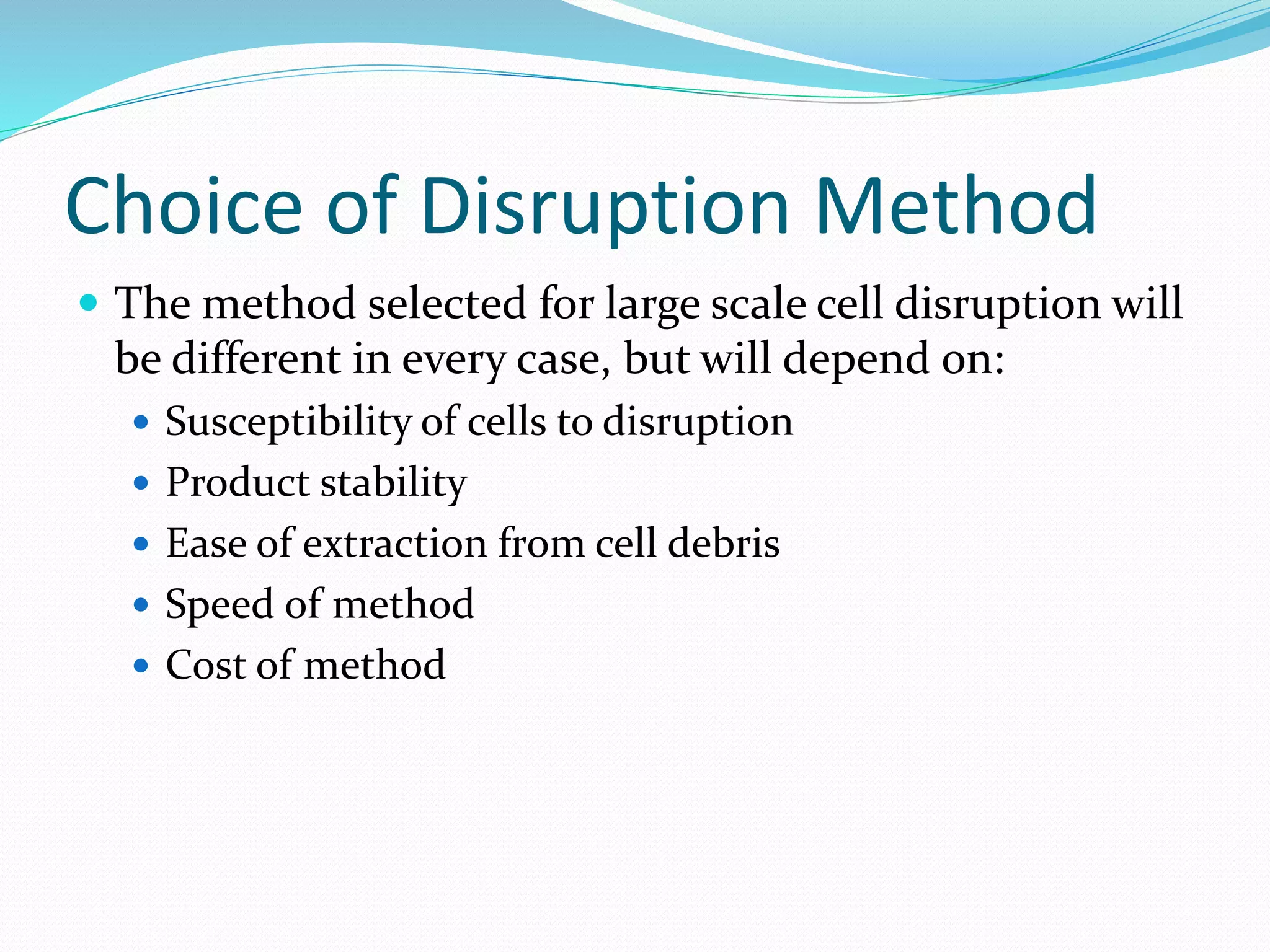
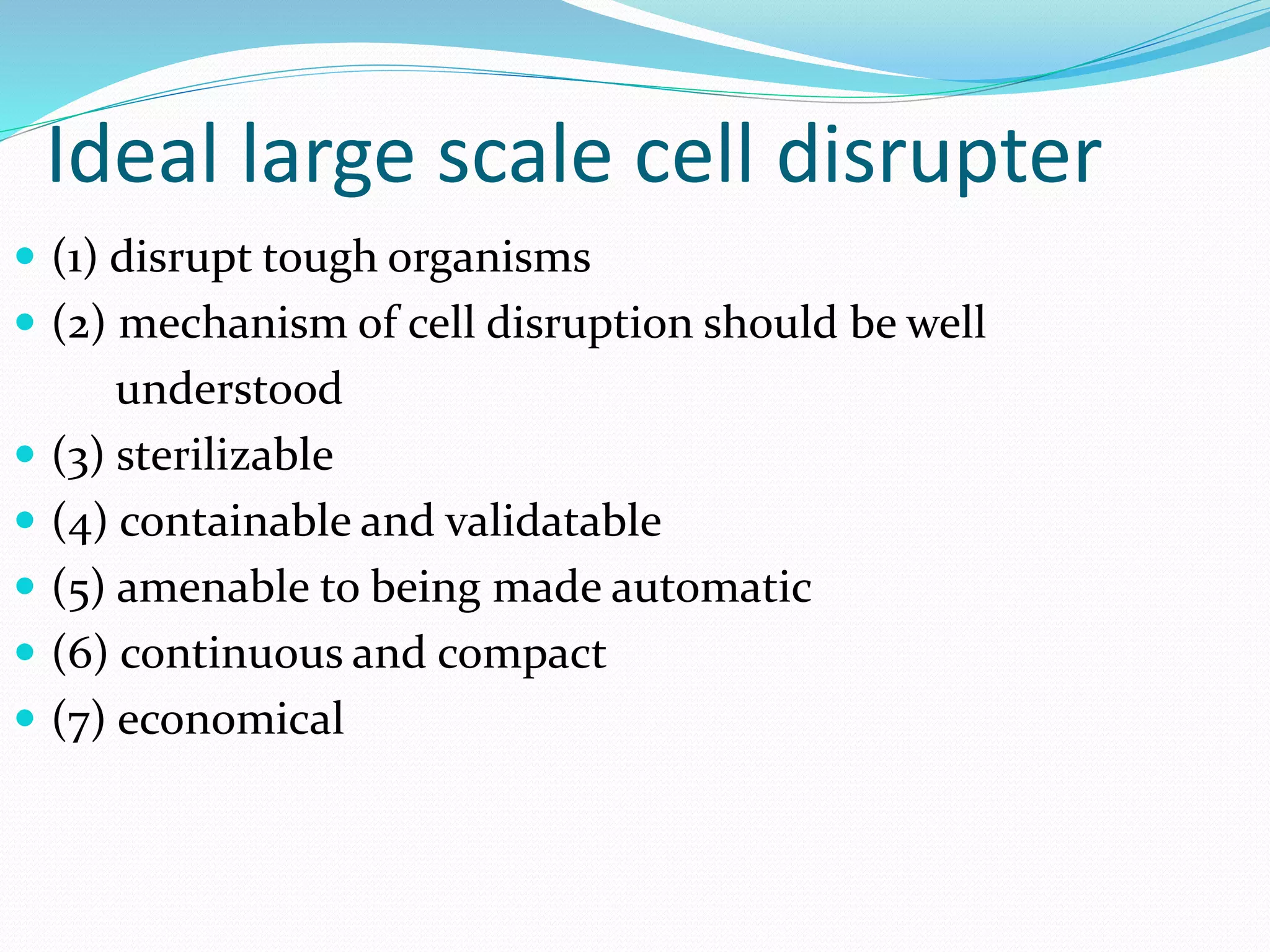
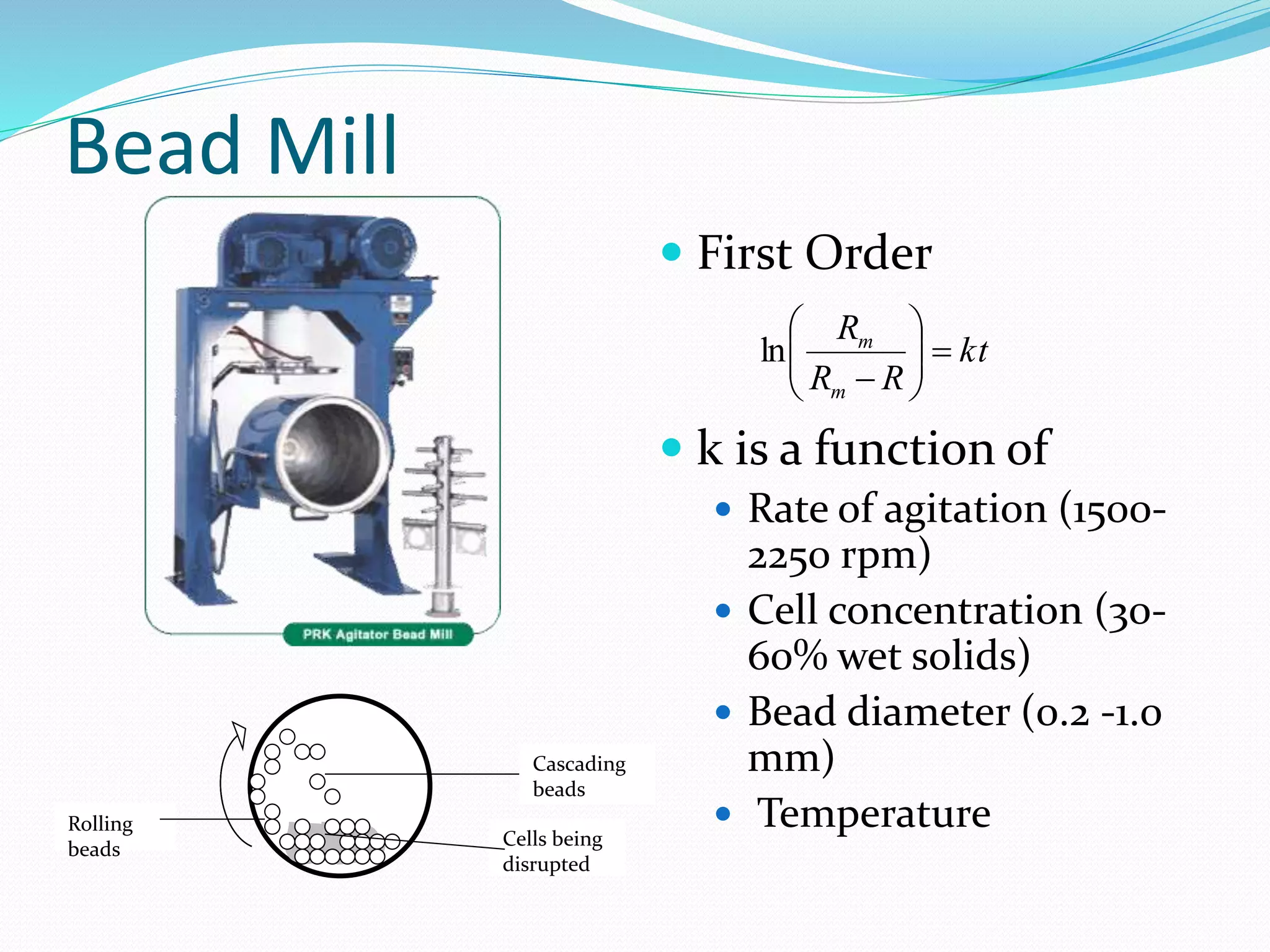
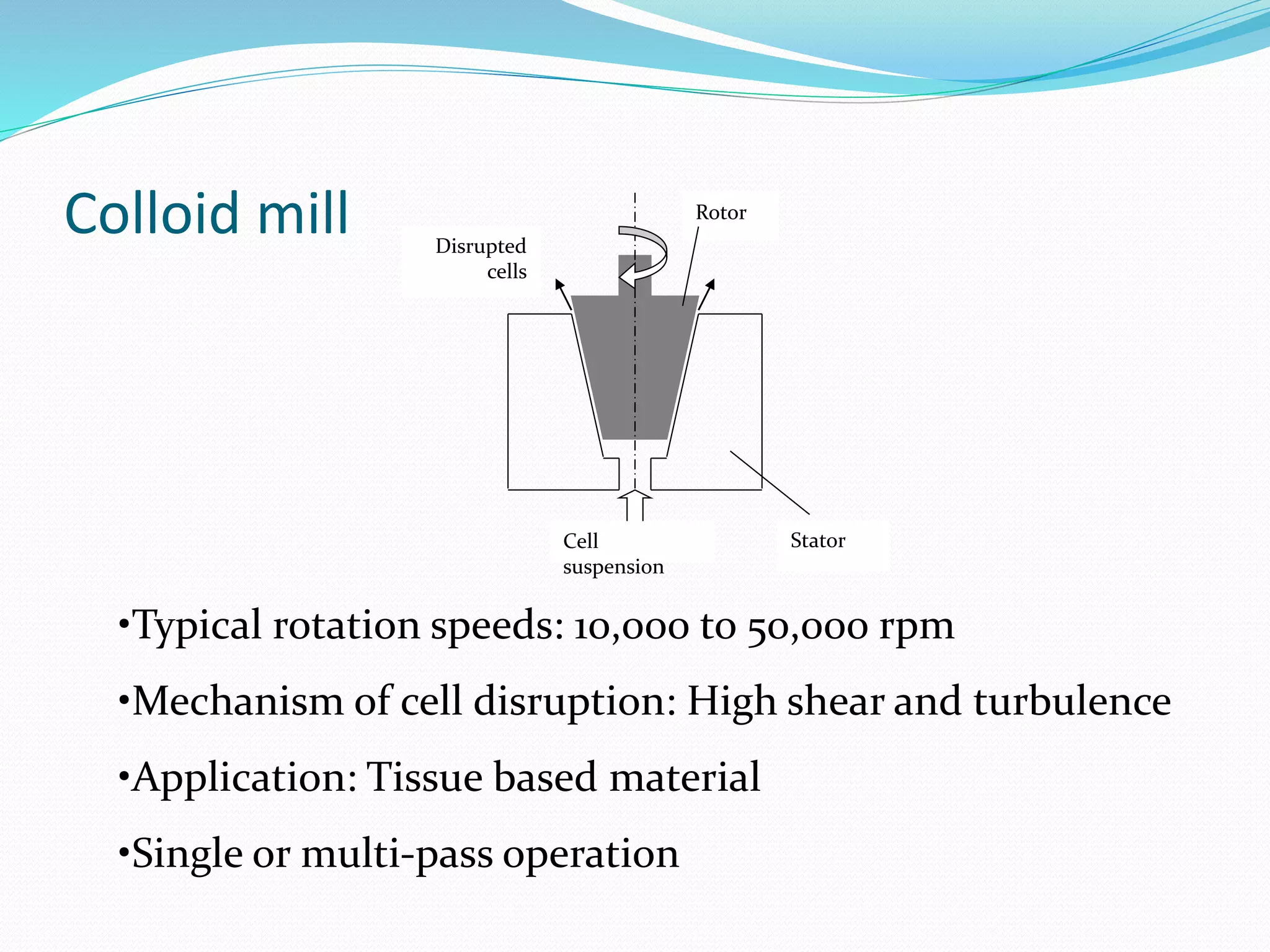
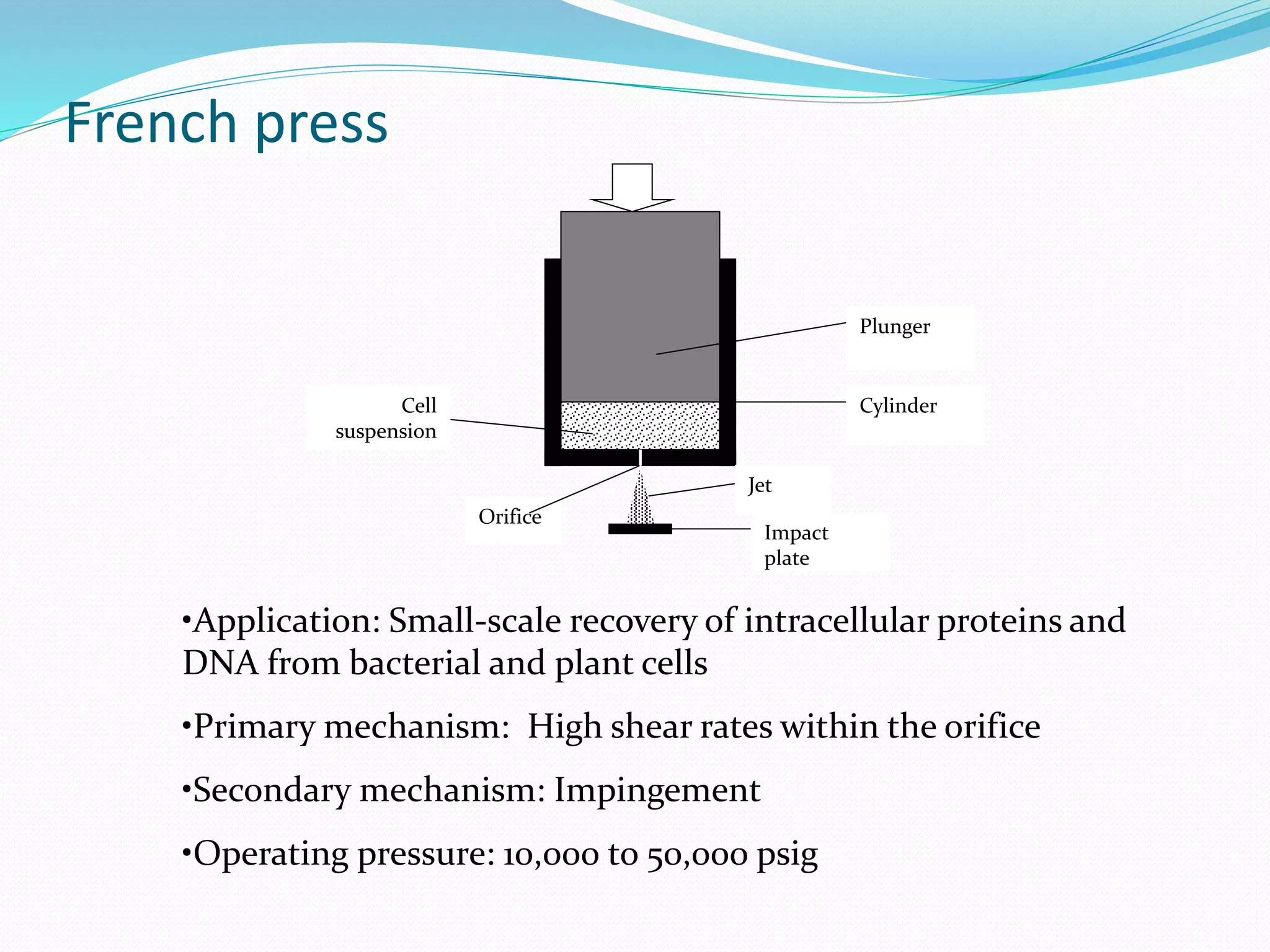
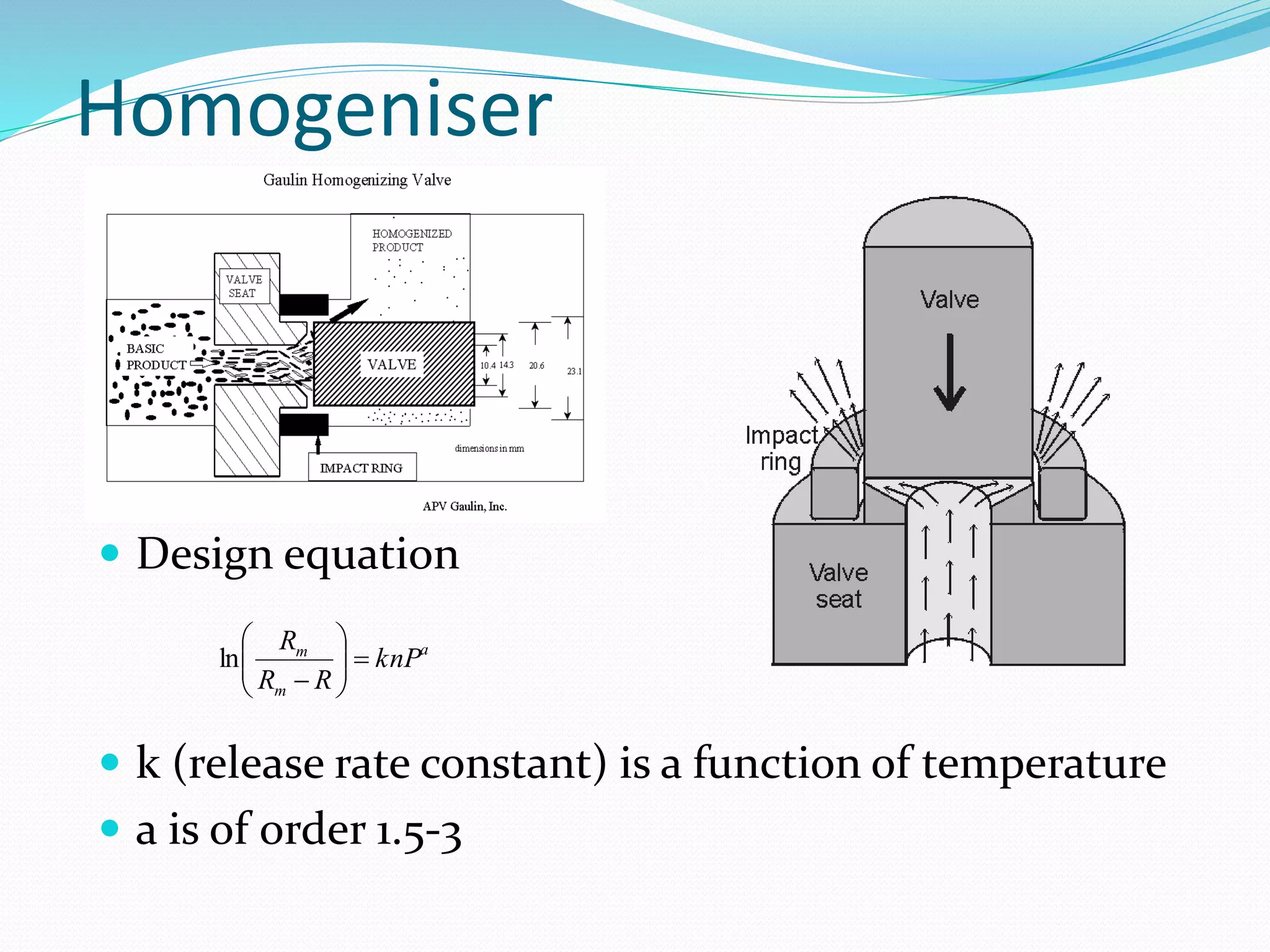
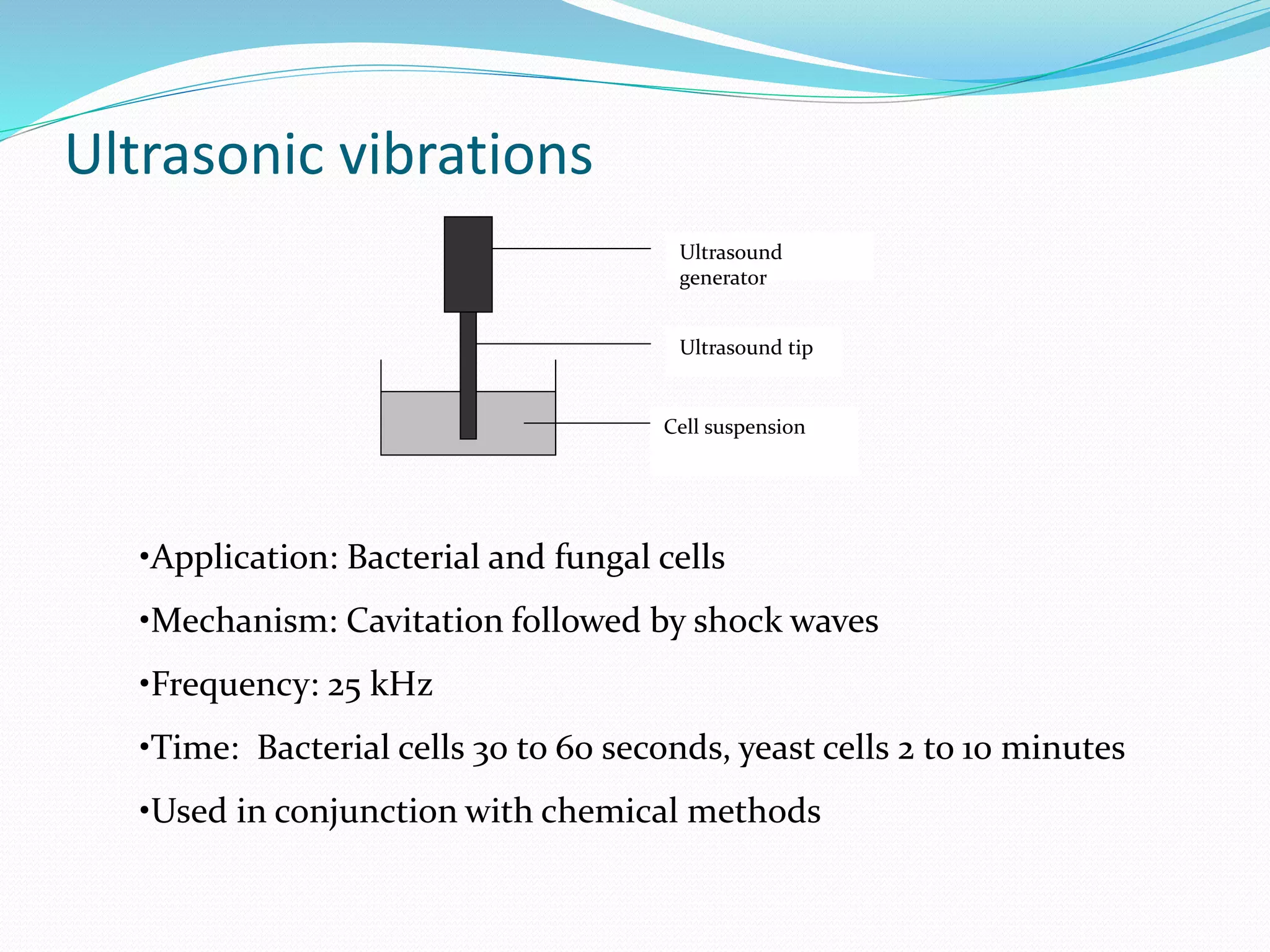
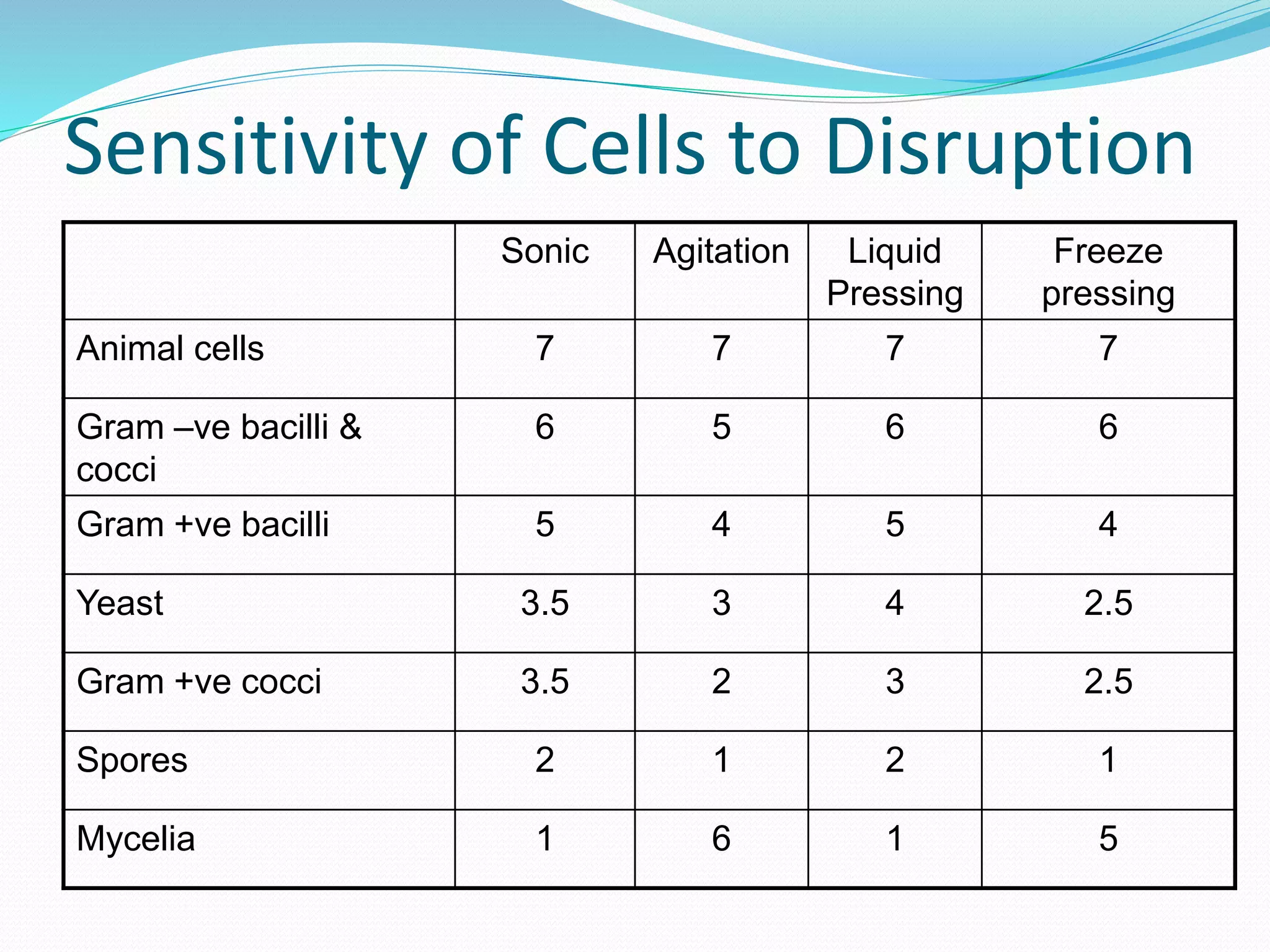
The document discusses various methods for cell disruption, which is the process of breaking open cells to release intracellular components. It describes both physical methods like bead mills, homogenizers, and ultrasonication as well as chemical/enzymatic methods like using detergents or osmotic shock. The ideal large-scale cell disrupter must disrupt tough organisms, have a well-understood and controllable mechanism, be sterilizable, economical, and amenable to automation. The choice of disruption method depends on factors like the cell type, product stability, and desired scale of production. Understanding the mechanisms of disruption helps control and validate the process.