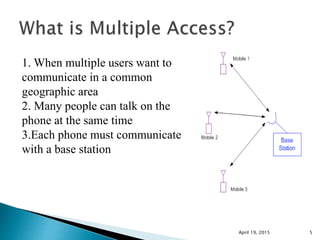
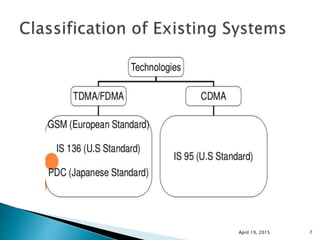
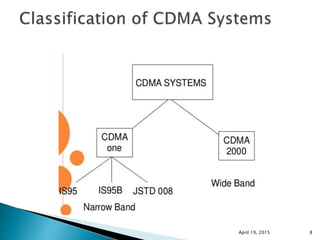
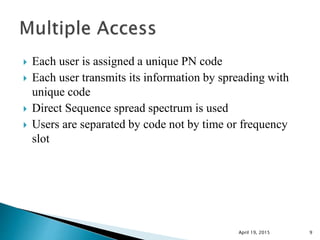
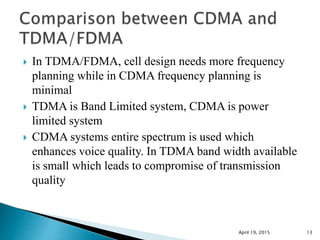
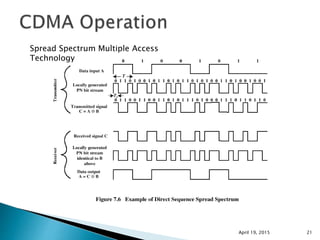
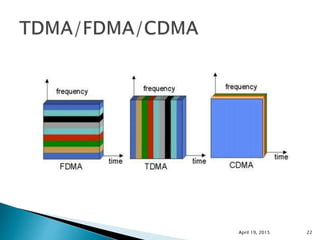
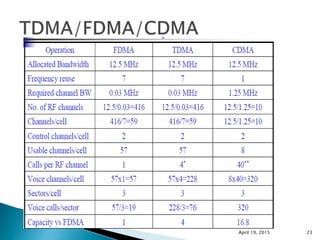
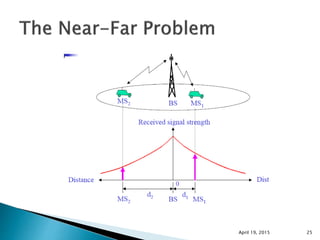
This document discusses Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) wireless communication technology. It provides an overview of CDMA, including that it uses unique digital codes to allow multiple users to access the same radio channel simultaneously. The document also covers CDMA specifications and standards like IS-95, as well as comparing CDMA to other multiple access technologies like TDMA and FDMA. It addresses topics such as the near-far problem and how CDMA provides advantages like increased network capacity but also challenges like potential self-interference.