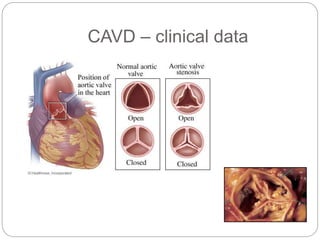
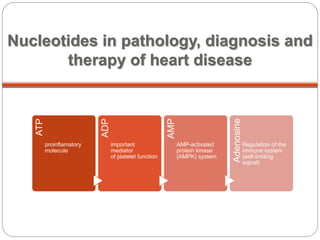
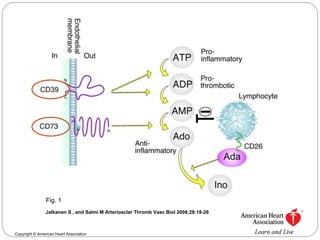
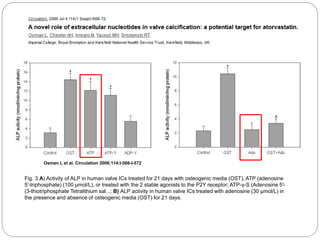
This document discusses the potential roles of CD39 and CD73 in valve calcification and the role of shear stress in this process. It notes that ATP is a proinflammatory molecule while ADP is an important mediator of platelet function. It also discusses how adenosine regulates the immune system. The document includes figures showing the activity of alkaline phosphatase in human valve cells treated with various compounds like ATP, adenosine, and osteogenic media.