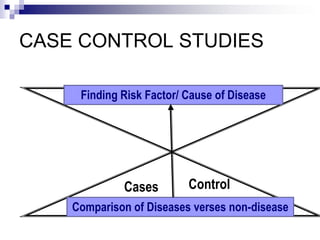
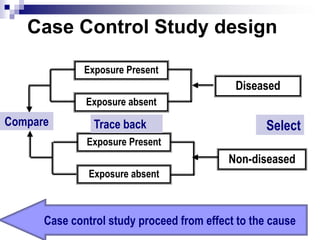
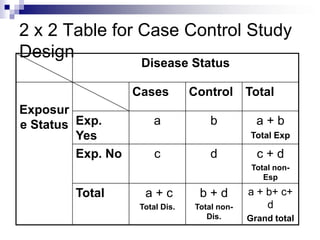
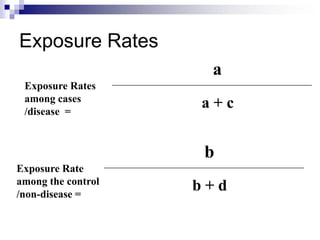
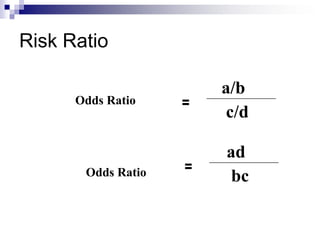
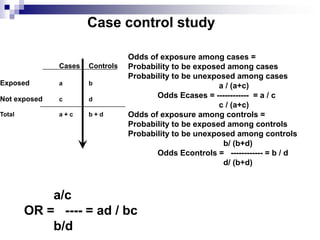
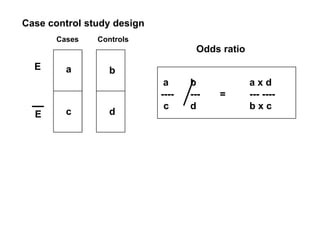
Case control studies compare exposures in individuals with a disease (cases) to individuals without the disease (controls) to identify potential risk factors for the disease. The study involves selecting cases and controls, ascertaining their exposure status, analyzing differences in exposure rates using odds ratios, and interpreting results to determine if an exposure is associated with the disease. Key limitations are that it cannot estimate incidence rates or time relationships between exposure and disease.