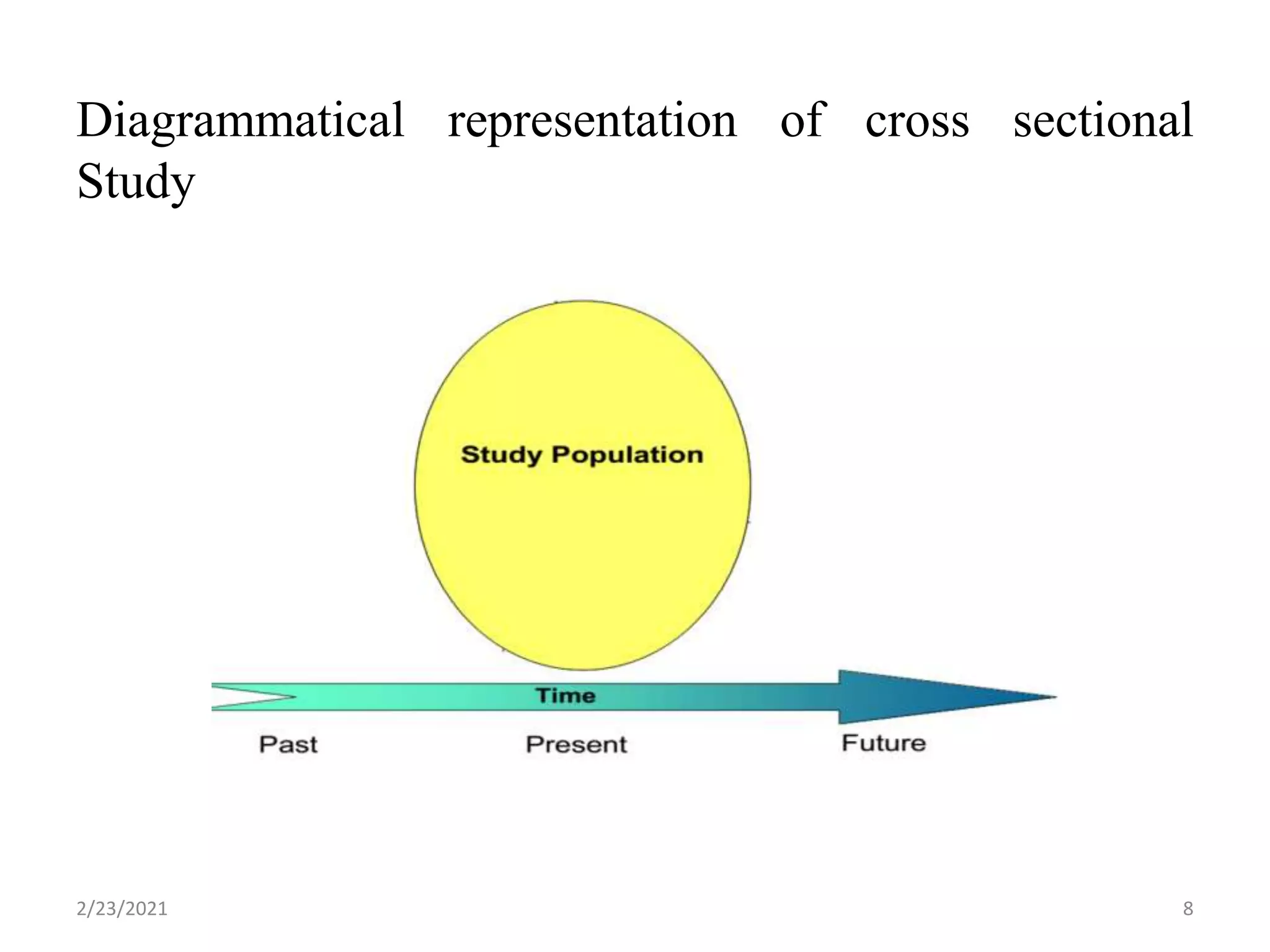
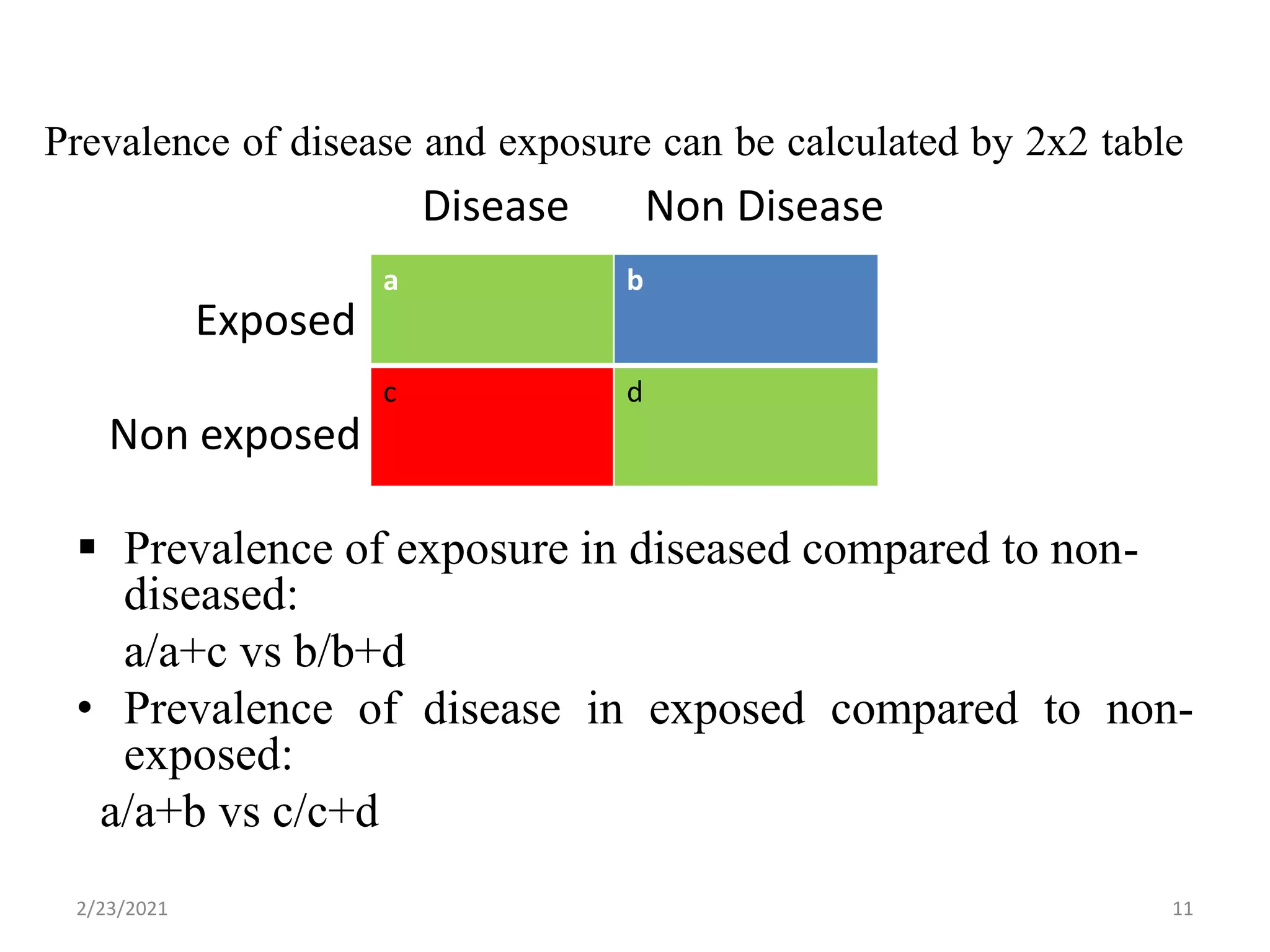
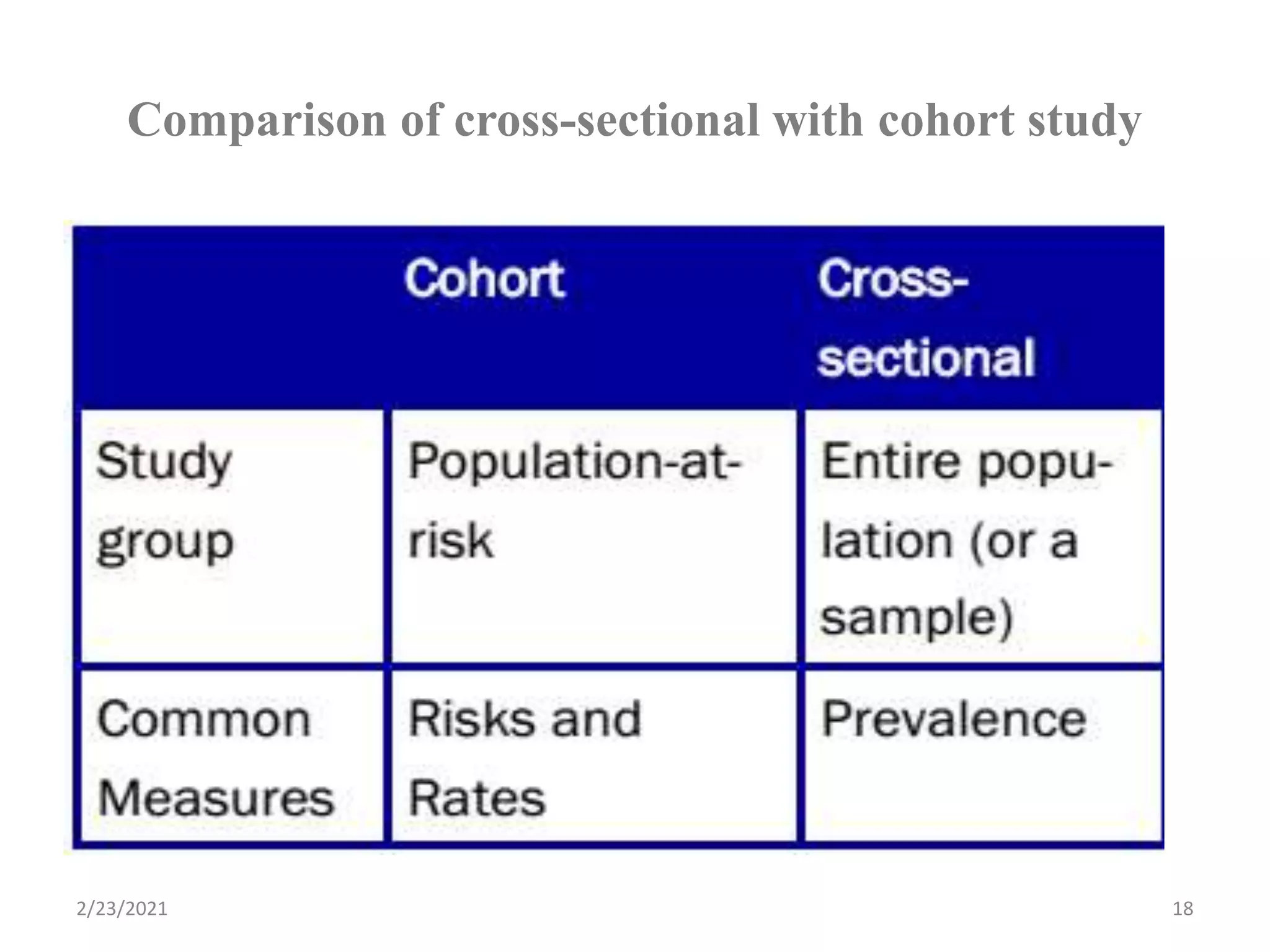
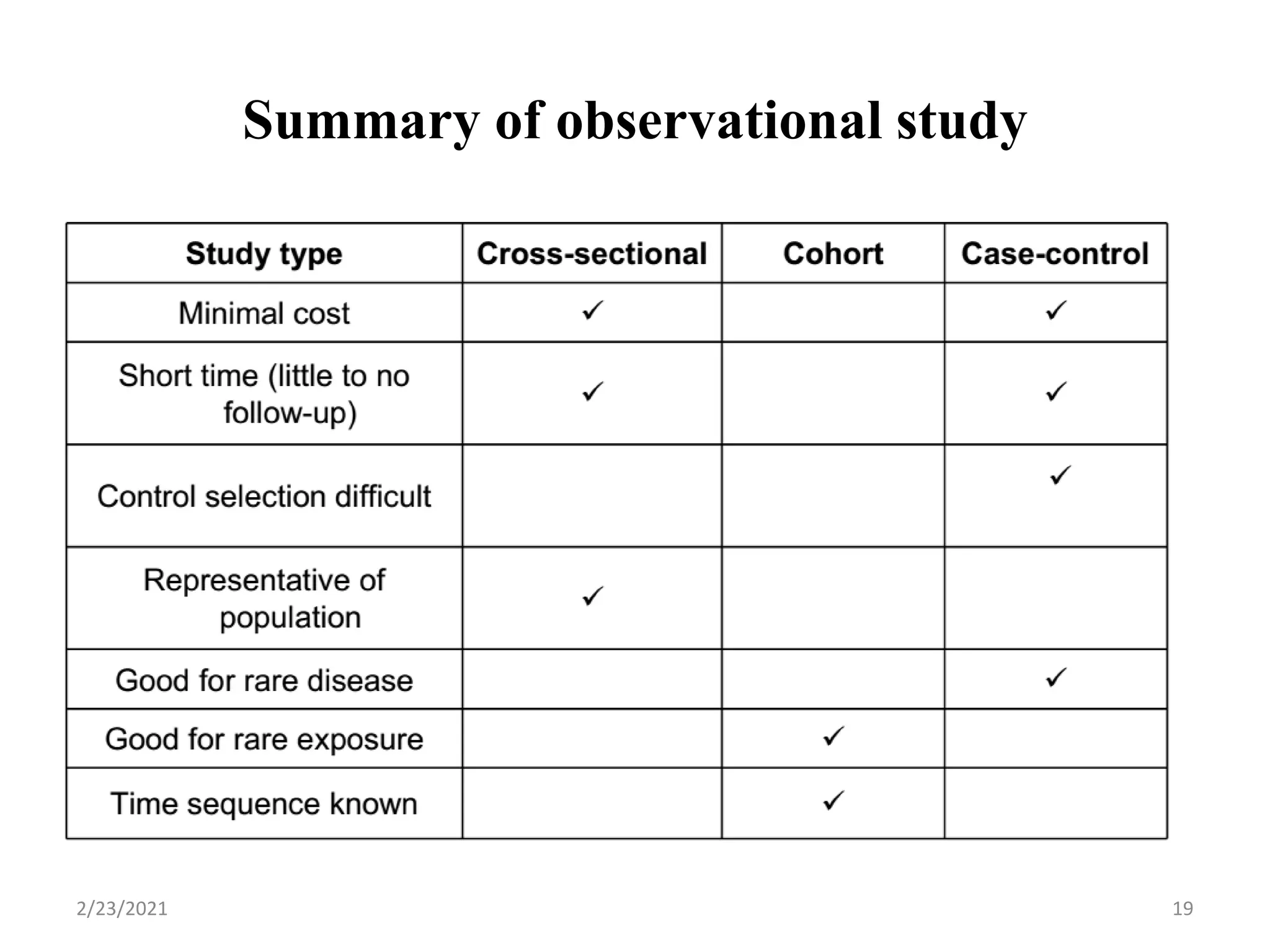
This document discusses cross-sectional studies. It defines a cross-sectional study as an observational study that measures exposure and health outcomes in a population at a single point in time, providing a "snapshot" of prevalence. It describes key characteristics, including simultaneously collecting exposure and outcome data, estimating prevalence rather than incidence, and inability to determine temporal relationships between variables. The document outlines advantages as being quick and inexpensive but also limitations such as inability to establish causation.