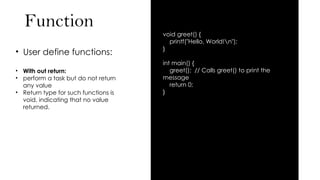
This PowerPoint presentation provides a clear and beginner-friendly explanation of functions in the C programming language. It covers both built-in functions and user-defined functions, including examples with and without return values. Topics also include recursion, prime number check, factorial program, and the use of global and static variables. Ideal for BCA students, beginners in C, or anyone preparing for programming exams.

![Function
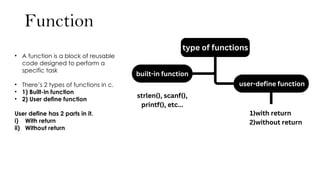
• Built-in functions:
• built-in functions (also known as
library functions) are pre-defined
functions provided by the C
Standard Library.
• These functions perform specific,
commonly-needed operations,
such as handling input and output,
manipulating strings
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char str[] = "Hello, World!";
printf("Length: %lun", strlen(str));
printf("First character: %cn", str[0]);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninc-250723045912-ac867f2d/85/C-Programming-Built-in-User-defined-Functions-With-Example-4-320.jpg)