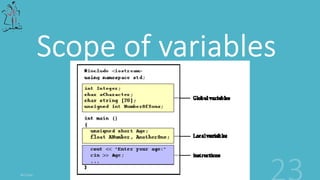
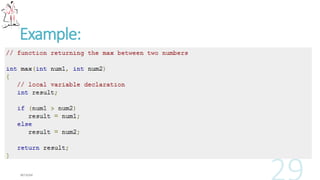
The document provides information about C++ programming concepts including functions, parameters, arrays, pointers, and recursion. It includes code examples for defining and calling functions, initializing and accessing arrays, declaring pointers, and the basic concept of recursion. The document covers fundamental C++ topics for a beginner learning the language.











































![Code
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<i;j++)
{
if(array[i]>array[j])
{
int temp=array[i]; //swap
array[i]=array[j];
array[j]=temp;
}}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ccoursestart-130524162302-phpapp01/85/C-course-start-49-320.jpg)

![Declaring Arrays
fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type.
type arrayName [ arraySize ];
double balance[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ccoursestart-130524162302-phpapp01/85/C-course-start-51-320.jpg)
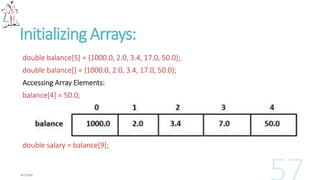
![Initializing Arrays:
double balance[5] = {1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 17.0, 50.0};.
double balance[] = {1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 17.0, 50.0};
Accessing Array Elements:
balance[4] = 50.0;
double salary = balance[9];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ccoursestart-130524162302-phpapp01/85/C-course-start-52-320.jpg)

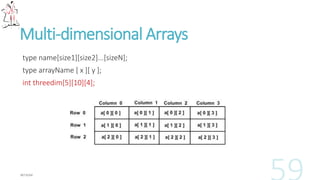
![Multi-dimensional Arrays
type name[size1][size2]...[sizeN];
type arrayName [ x ][ y ];
int threedim[5][10][4];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ccoursestart-130524162302-phpapp01/85/C-course-start-54-320.jpg)
![AccessingTwo-DimensionalArrayElements:
int val = a[2][3];
Initializing Two-Dimensional Arrays:
int a[3][4] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ccoursestart-130524162302-phpapp01/85/C-course-start-55-320.jpg)