An array is a collection of similar data elements stored in contiguous memory locations that can be accessed using an index number. For example, to store marks of a student in 5 subjects, an array called "marks" could be used where marks[0] stores the mark of the first subject and so on. Arrays make it easier to store and access large amounts of data compared to individual variables. They allow direct access, easy traversal through elements using indexes and allocate contiguous memory for elements.

![An array is a collection of similar data elements stored at contiguous
memory locations. It is the simplest data structure where each data
element can be accessed directly by only using its index number.
For instance, if we want to store the marks scored by a student in 5
subjects, then there’s no need to define individual variables for each
subject. Rather, we can define an array which will store the data elements
at contiguous memory locations.
· array marks[5] defines the marks scored by a student in 5 different
subjects where each subject marks are located at a particular location in
the array i.e. marks[0] denotes the marks scored in first
subject, marks[1] denotes the marks scored in 2nd subject and so on.
What is Array ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carray-230514181342-df58c3f7/85/C-Array-pptx-2-320.jpg)


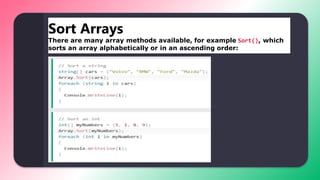
![C# ARRAY
string[] cars;
Data type 1D Name of Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carray-230514181342-df58c3f7/85/C-Array-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![To insert values to it, we can use an array literal - place the
values in a comma-separated list, inside curly braces:
string[] cars = {"Volvo", "BMW", "Ford", "Mazda"};
To create an array of integers, you could write:
int[] myNum = {10, 20, 30, 40};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carray-230514181342-df58c3f7/85/C-Array-pptx-6-320.jpg)
![Access the Elements of an Array
You access an array element by referring to the index number.
This statement accesses the value of the first element in cars:
string[] cars = {"Volvo", "BMW", "Ford", "Mazda"};
Console.WriteLine(cars[0]);
Change an Array Element
To change the value of a specific element, refer to the index number:
cars[0] = "Opel";
Before change the value of zero index : Volvo
After output of zero-index = Opel](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carray-230514181342-df58c3f7/85/C-Array-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![string[] cars = {"Volvo", "BMW", "Ford", "Mazda"};
Console.WriteLine(cars.Length);
Array Length
Return number of elements in the array
Output
3
Note : index start from zero](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carray-230514181342-df58c3f7/85/C-Array-pptx-8-320.jpg)