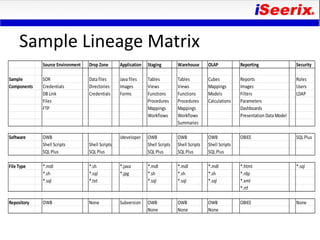
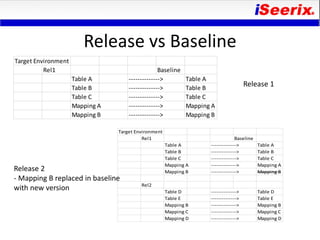
This document discusses best practices for release management of business intelligence software. It defines release management and outlines key challenges with managing releases across multiple BI tools. It then describes the typical steps in a release management process - define, build, deploy, and manage. Specific examples are provided for managing Oracle Warehouse Builder (OWB) releases. The importance of version control and separating releases from the baseline configuration is also covered.