More Related Content
PPT
Ch02:the economic problem scarcity and choice PPT
Chapter 2-the-economic-problems PPT
The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice PPT
PPT
The Economic Problem. Scarcity and Choice PPT
Principles of microeconomics PPT
Ppt econ 9e_one_click_ch02 PPT
Similar to Business administration microeconomics chap2
PPT
PPTX
PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCIAL PROBLEMS PDF
1.1. Scarcity, choice and opportunity cost.pdf PPTX
CFO_POE12_ppt_02 (1).pptx PPT
Economics : Unit 1 scarcity & choice PPT
PPT
APPLIED ECONOMICS and the types PPT.ppt PPTX
Econ. Wk1-2 PP Chapter 1(The basic Economic problem) G12.pptx PPTX
Chapter-2-The-fundamental-Economic-Problem-Scarcity.pptx PPTX
Scarcity and Opportunity Cost Summary.pptx PPT
production_possibility_curve PPT
PPTX
Scarcity, Choice and Opportunity Costs.pptx PPSX
PPT
PPTX
PPT
Ch02The Economic Problem economic and business.ppt PDF
PPSX
PPTX
Ma ch 02 economic tools and economic systems Recently uploaded
PDF
How to Buy Instagram accounts for professional brand ... (1).pdf PDF
LinkedIn Accounts in 2025_ Social Commerce, Trust Signals.pdf PDF
How to Buy Facebook accounts for professional brand ....pdf PDF
ActARion - The Future of Work with AI and Augmented Reality PDF
The safety revolution - Origins of workplace health and safety PDF
Institute for Public Relations 2025 Year in Review PDF
Step-by-Step Guide to Purchasing USA Facebook ....pdf PDF
What You in 2026 Buy Twitter Accounts_.pdf PDF
Top 10 Websites to Buy Facebook Accounts Tone.pdf PDF
Mobile and Online Banking_ Open an Account Today.pdf PDF
Juniper Research's Top 10 Trends for Fintech in 2026 PDF
How to Buy Twitter Accounts in 2026 (1).pdf PDF
How to Master Any Skill for Free with AI: The 4-Step Roadmap to $1,000/Month PPTX
CMMI Consulting & Implementation Services.pptx DOCX
How to Buy Old Gmail Accounts Smartly_ 5 Easy Methods (2025) (1).docx PPTX
DeFi Passive Income: From definitions to practical examples PDF
Best Platforms to Buy Verified Wise Accounts in the USA.pdf PDF
growth-approach-pm-letter-december-2025 (1).pdf PDF
Buy Verified PayPal Accounts Search Intent Analysis for 2025–26.pdf PDF
Equinox Gold - Corporate Presentation.pdf Business administration microeconomics chap2
- 1.
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
C
H
A
P
T
E
R 2
Prepared by:Fernando Quijano
Prepared by: Fernando Quijano
and Yvonn Quijano
and Yvonn Quijano
© 2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing
© 2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics, 7/e
Principles of Economics, 7/e Karl Case, Ray Fair
Karl Case, Ray Fair
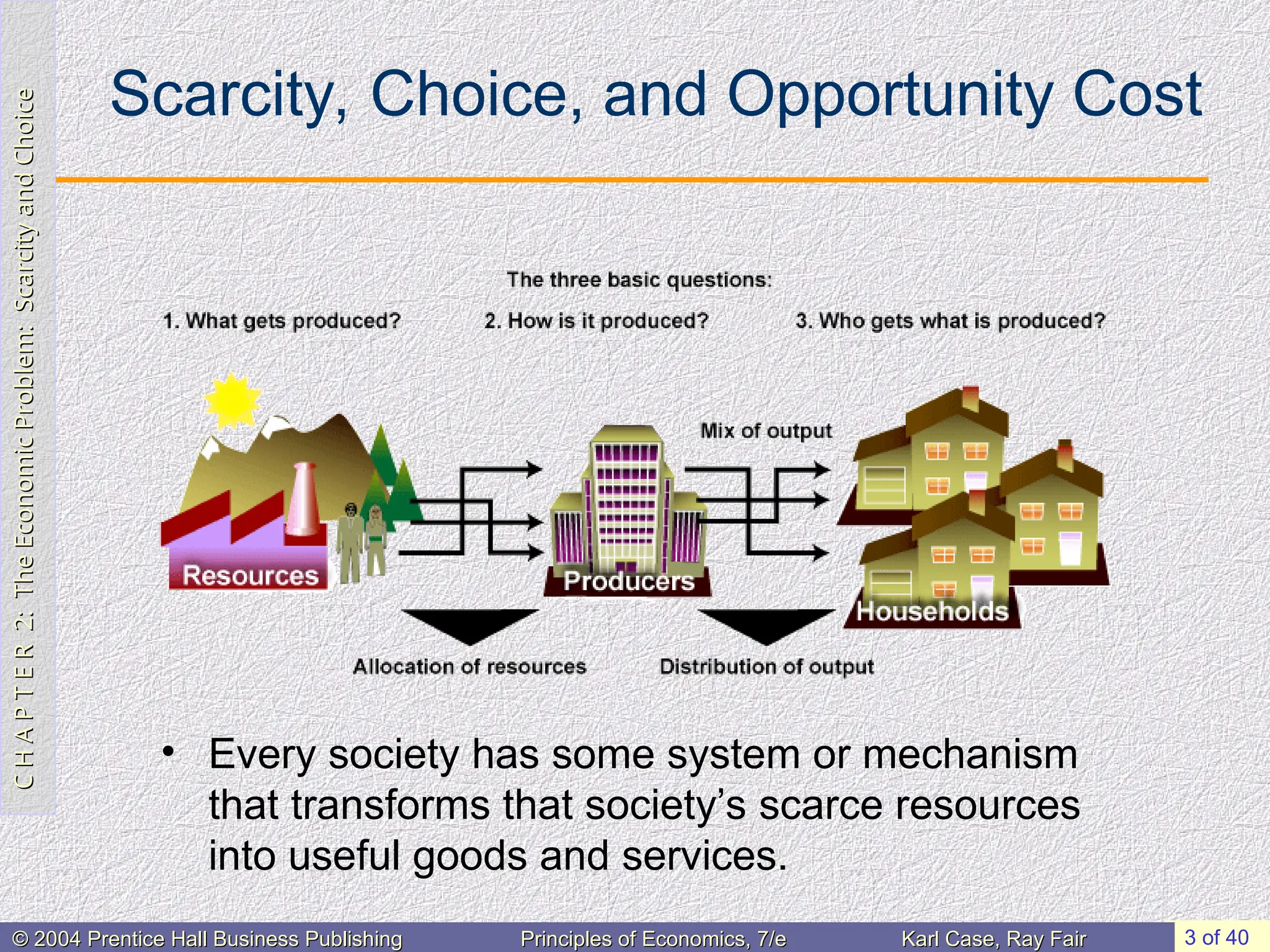
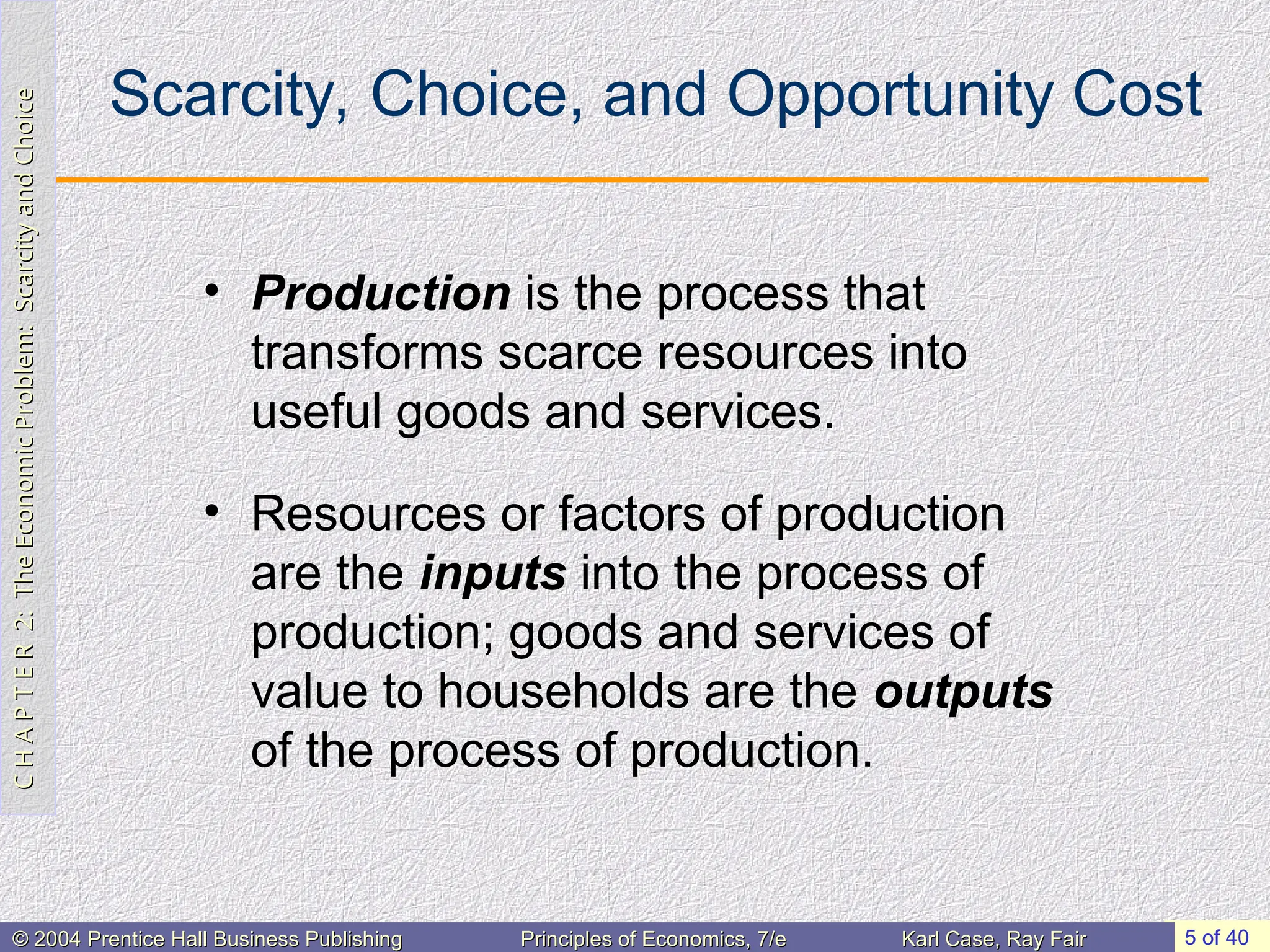
The Economic Problem:
Scarcity and Choice
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
11 of 40
©2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing
© 2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics, 7/e
Principles of Economics, 7/e Karl Case, Ray Fair
Karl Case, Ray Fair
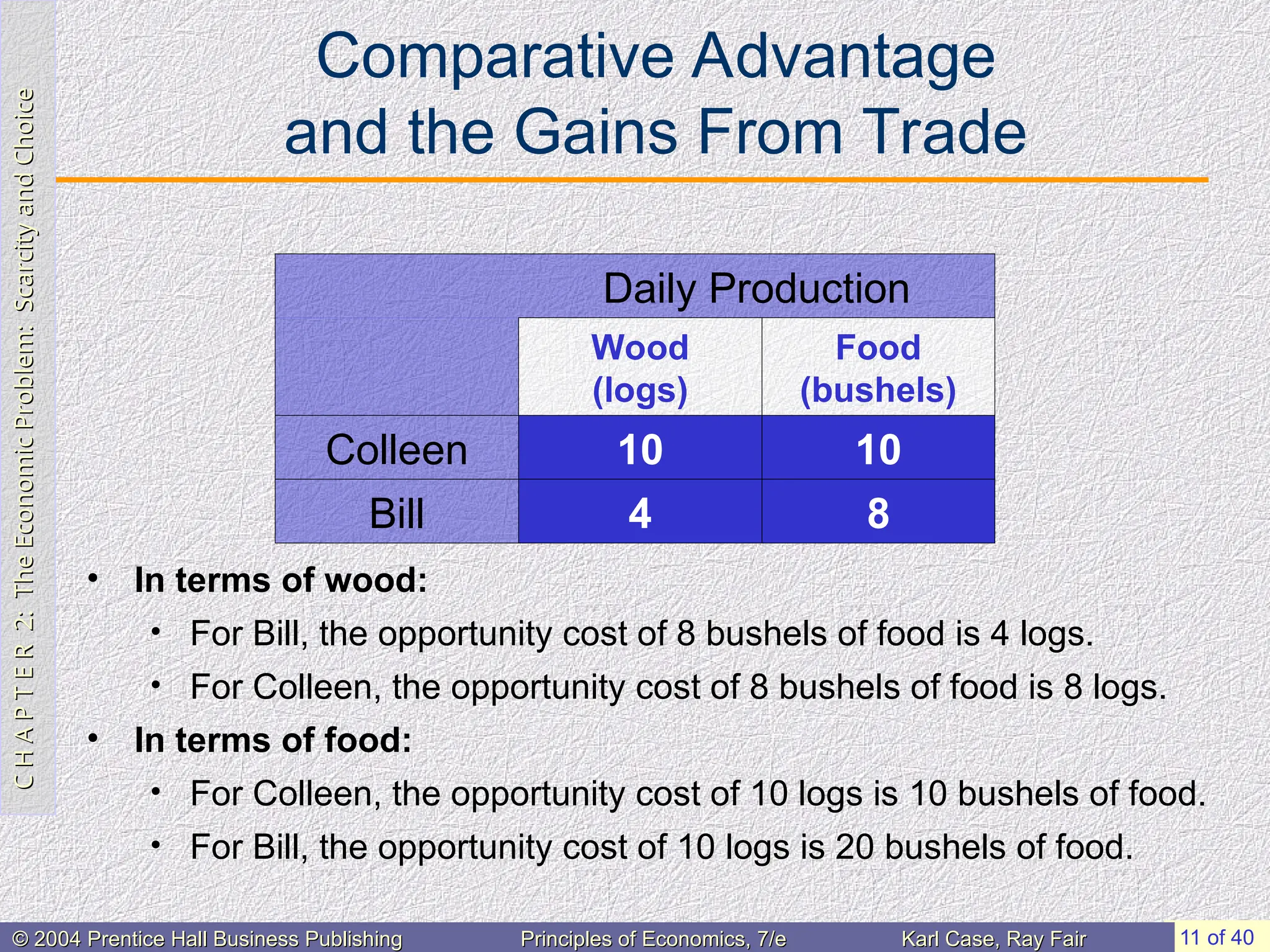
Comparative Advantage
and the Gains From Trade
• In terms of wood:
• For Bill, the opportunity cost of 8 bushels of food is 4 logs.
• For Colleen, the opportunity cost of 8 bushels of food is 8 logs.
• In terms of food:
• For Colleen, the opportunity cost of 10 logs is 10 bushels of food.
• For Bill, the opportunity cost of 10 logs is 20 bushels of food.
Daily Production
Wood
(logs)
Food
(bushels)
Colleen 10 10
Bill 4 8
- 12.
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
12 of 40
©2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing
© 2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics, 7/e
Principles of Economics, 7/e Karl Case, Ray Fair
Karl Case, Ray Fair
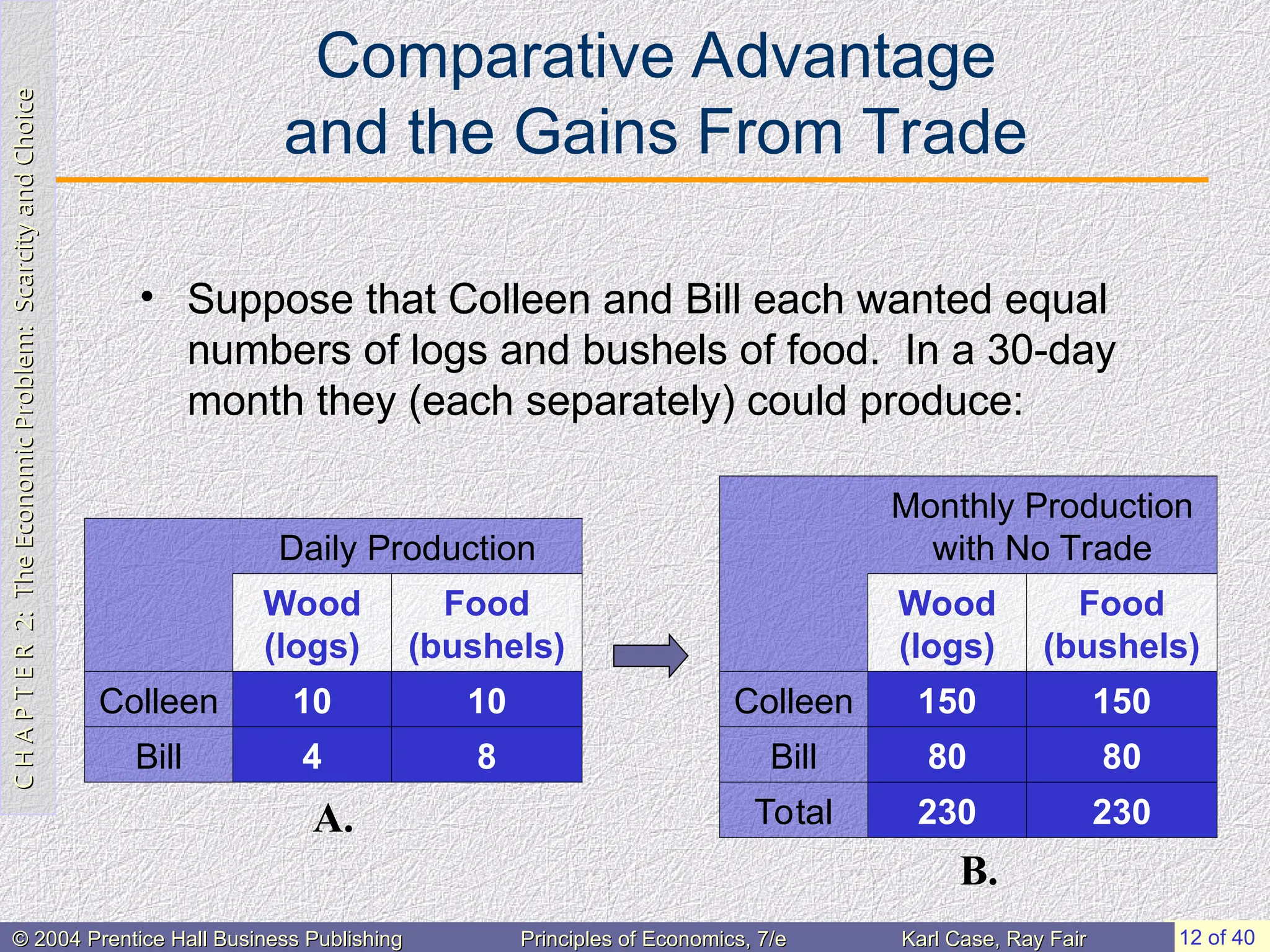
Comparative Advantage
and the Gains From Trade
• Suppose that Colleen and Bill each wanted equal
numbers of logs and bushels of food. In a 30-day
month they (each separately) could produce:
Daily Production
Wood
(logs)
Food
(bushels)
Colleen 10 10
Bill 4 8
Monthly Production
with No Trade
Wood
(logs)
Food
(bushels)
Colleen 150 150
Bill 80 80
Total 230 230
A.
B.
- 13.
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
13 of 40
©2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing
© 2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics, 7/e
Principles of Economics, 7/e Karl Case, Ray Fair
Karl Case, Ray Fair
Comparative Advantage
and the Gains From Trade
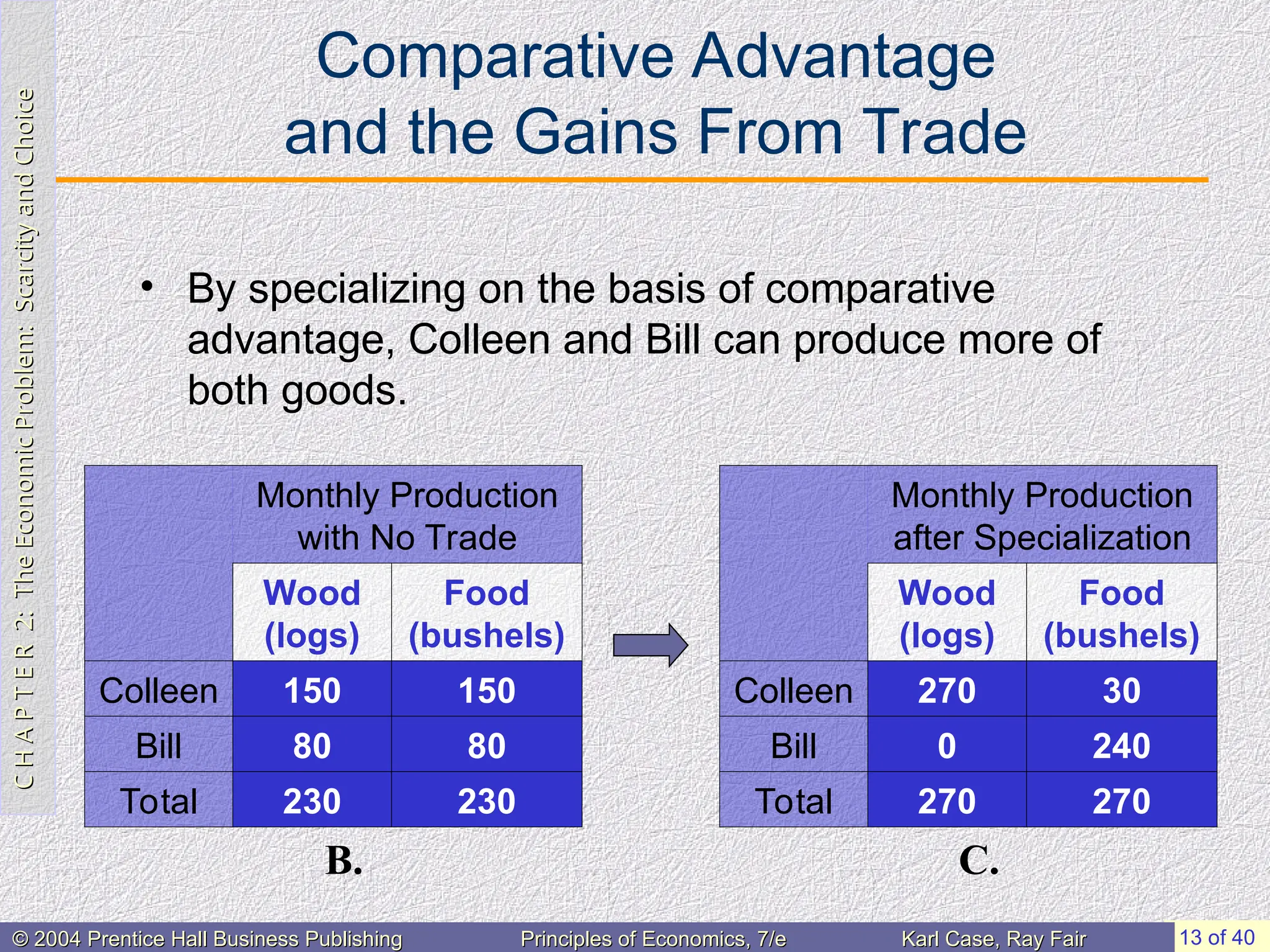
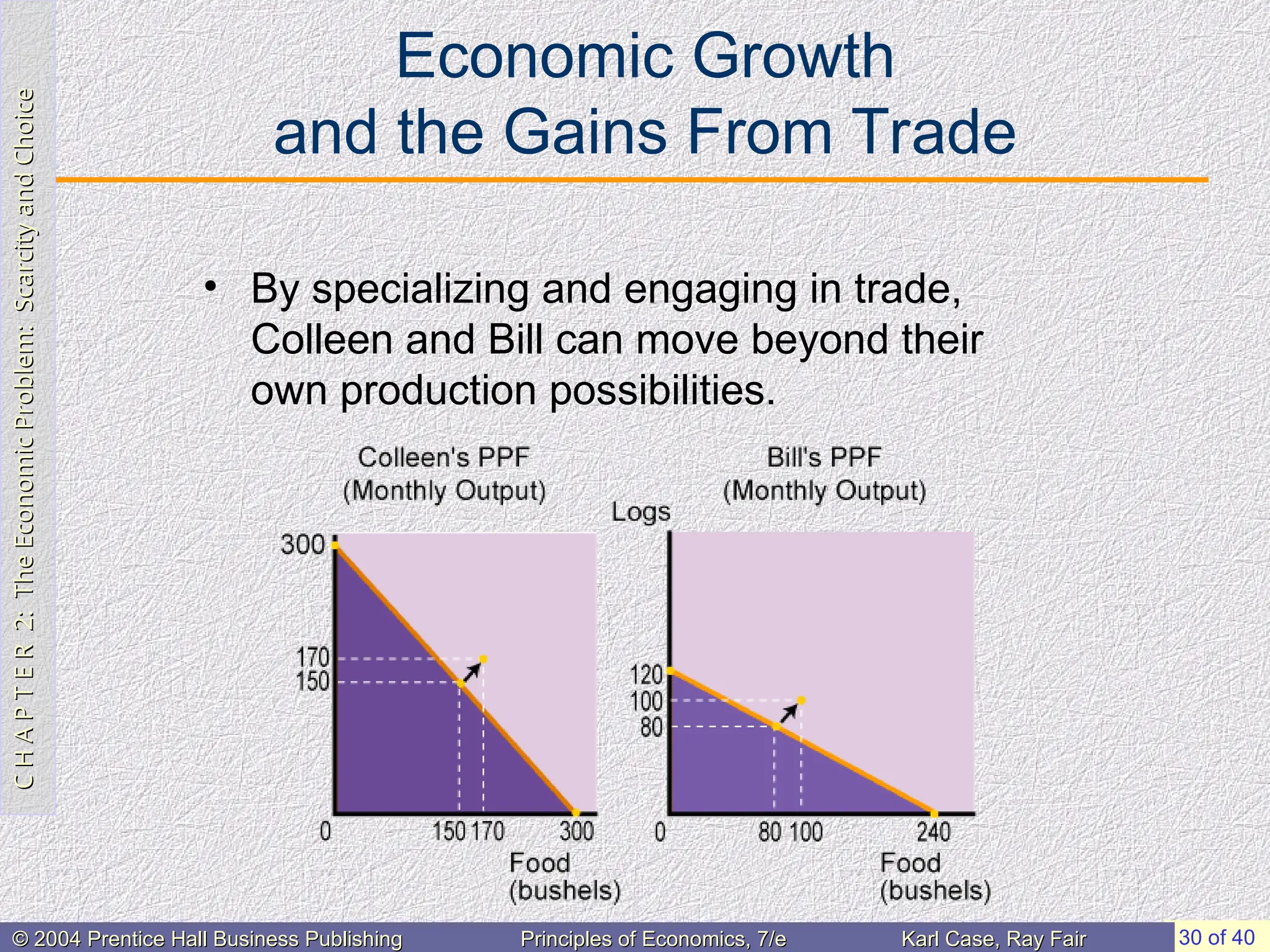
• By specializing on the basis of comparative
advantage, Colleen and Bill can produce more of
both goods.
Monthly Production
after Specialization
Wood
(logs)
Food
(bushels)
Colleen 270 30
Bill 0 240
Total 270 270
C.
Monthly Production
with No Trade
Wood
(logs)
Food
(bushels)
Colleen 150 150
Bill 80 80
Total 230 230
B.
- 14.
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
14 of 40
©2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing
© 2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics, 7/e
Principles of Economics, 7/e Karl Case, Ray Fair
Karl Case, Ray Fair
Comparative Advantage
and the Gains From Trade
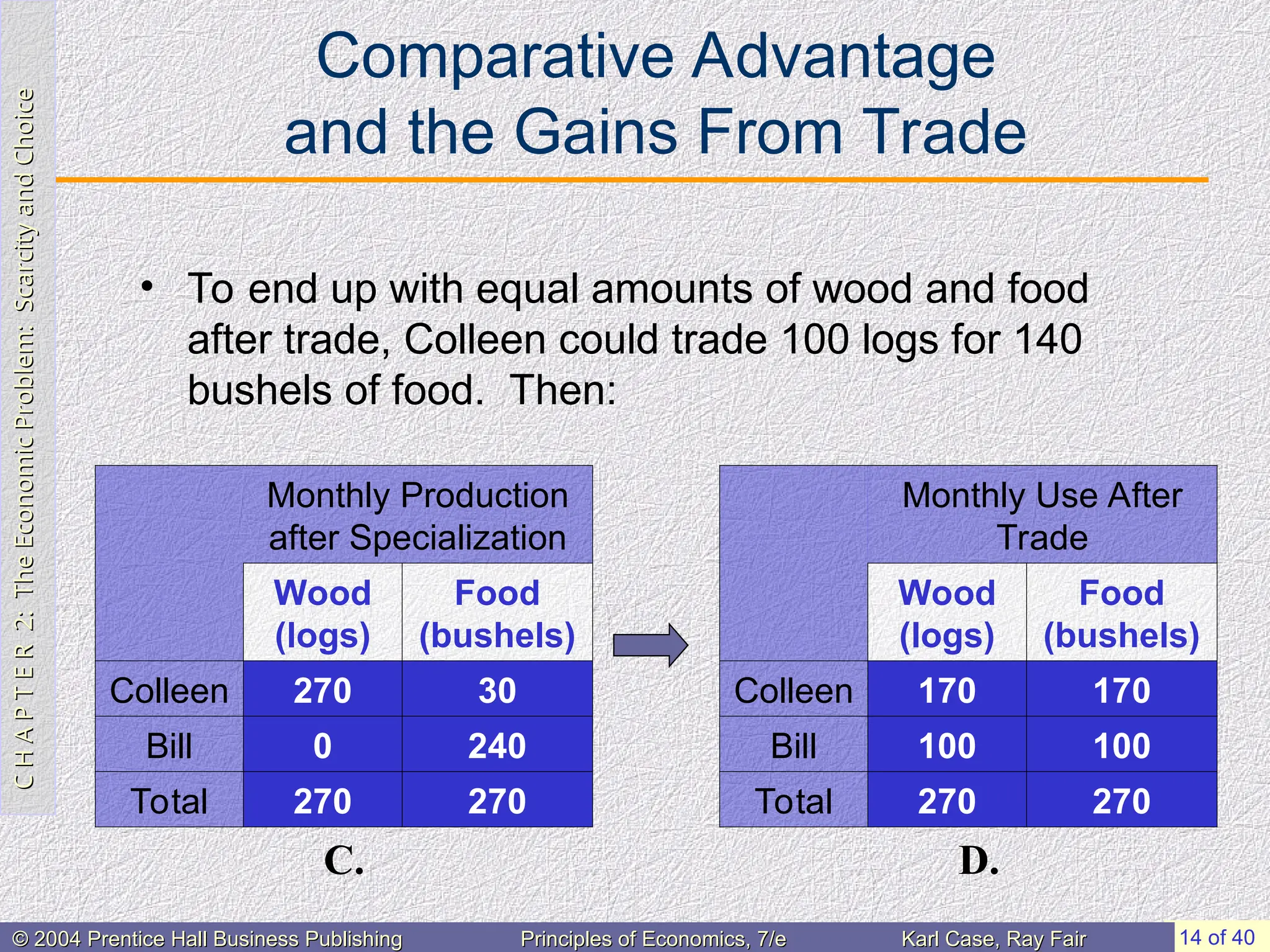
• To end up with equal amounts of wood and food
after trade, Colleen could trade 100 logs for 140
bushels of food. Then:
Monthly Production
after Specialization
Wood
(logs)
Food
(bushels)
Colleen 270 30
Bill 0 240
Total 270 270
D.
Monthly Use After
Trade
Wood
(logs)
Food
(bushels)
Colleen 170 170
Bill 100 100
Total 270 270
C.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
24 of 40
©2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing
© 2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics, 7/e
Principles of Economics, 7/e Karl Case, Ray Fair
Karl Case, Ray Fair
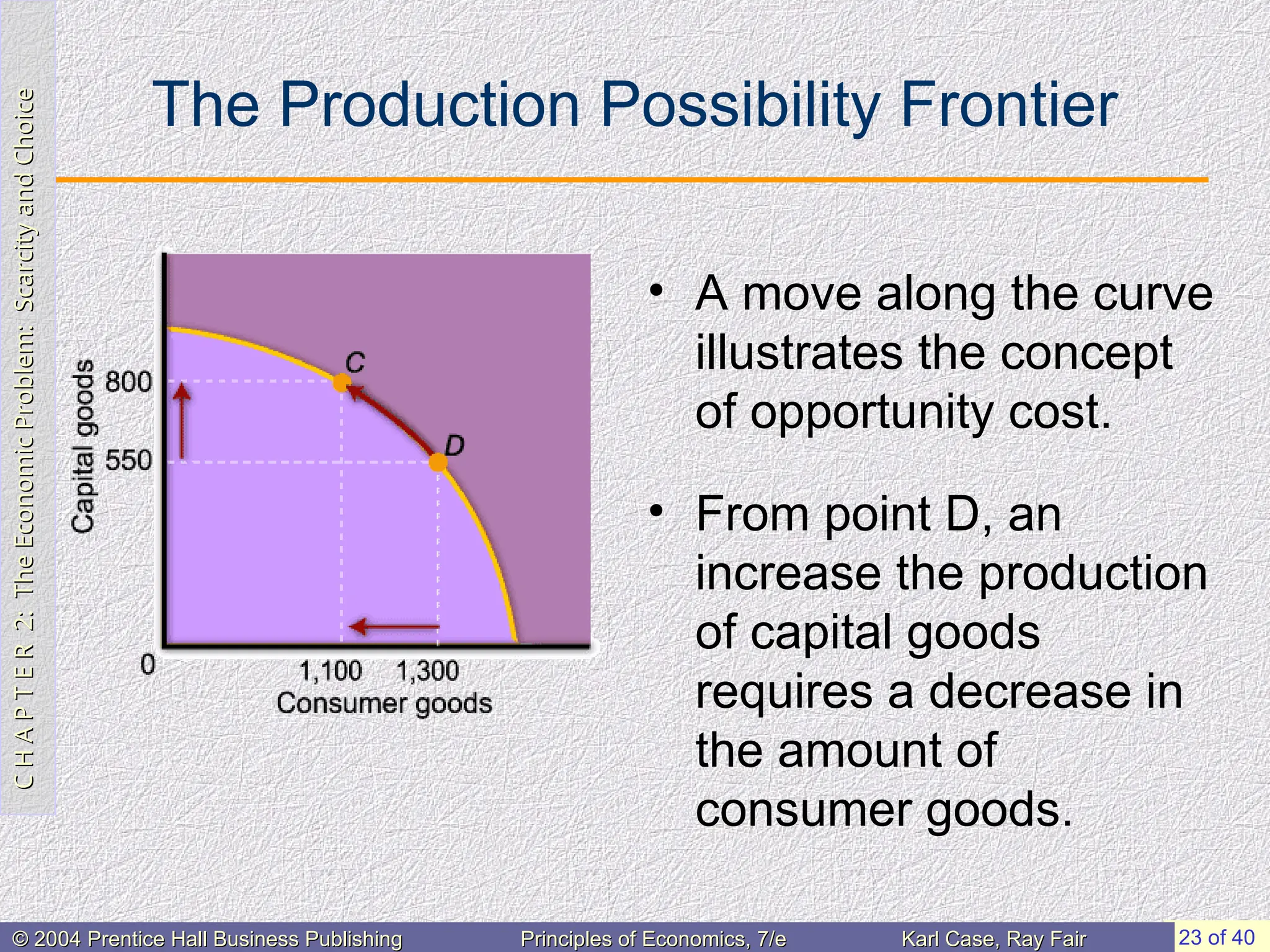
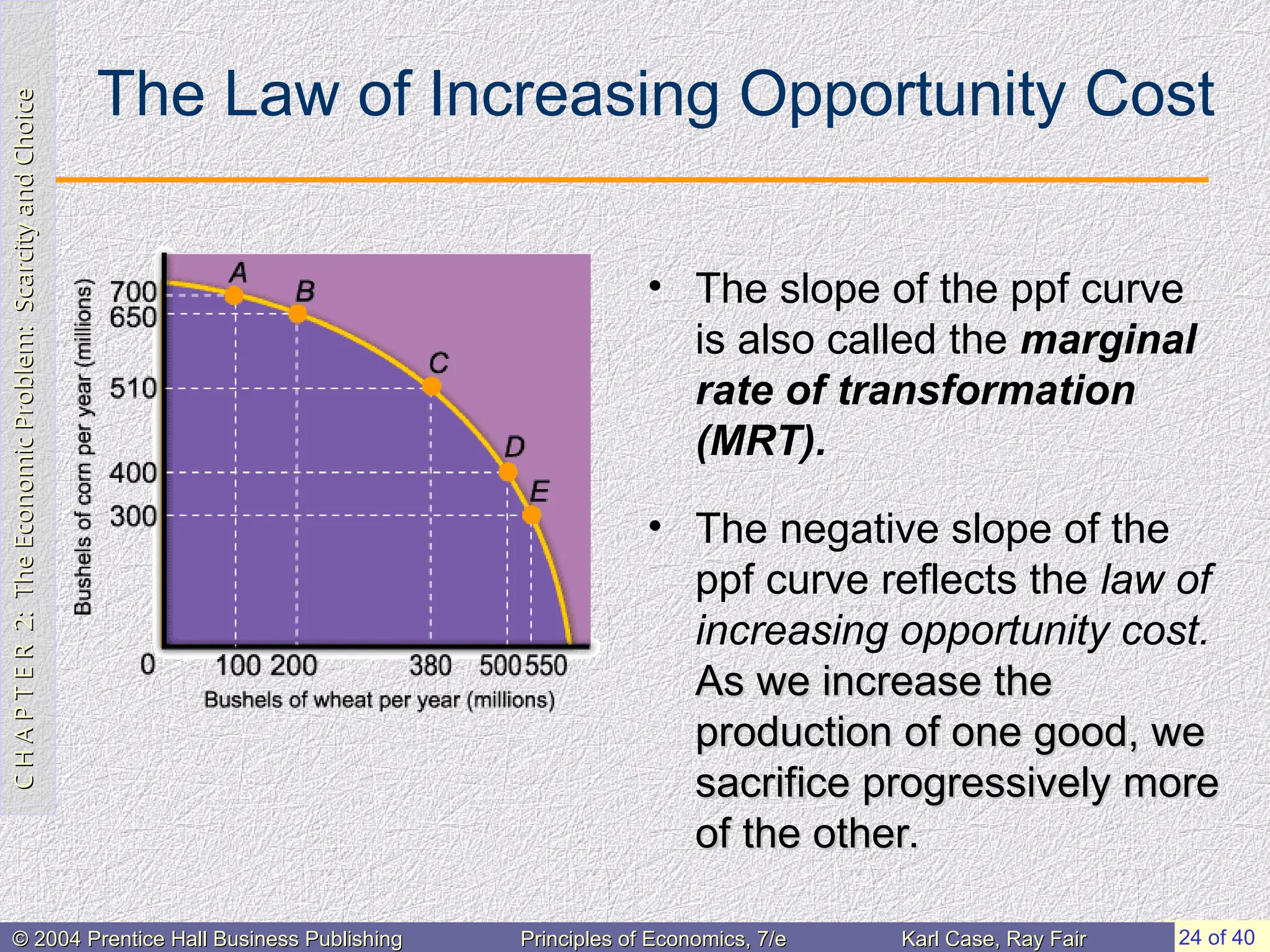
The Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost
• The slope of the ppf curve
is also called the marginal
rate of transformation
(MRT).
• The negative slope of the
ppf curve reflects the law of
increasing opportunity cost.
As we increase the
As we increase the
production of one good, we
production of one good, we
sacrifice progressively more
sacrifice progressively more
of the other.
of the other.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
39 of 40
©2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing
© 2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics, 7/e
Principles of Economics, 7/e Karl Case, Ray Fair
Karl Case, Ray Fair
Mixed Systems,
Markets, and Governments
Since markets are not perfect, governments
intervene and often play a major role in the
economy. Some of the goals of government are to:
• Minimize market inefficiencies
• Provide public goods
• Redistribute income
• Stabilize the macroeconomy:
• Promote low levels of unemployment
• Promote low levels of inflation
- 40.
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
C
H
A
P
T
E
R
2:
The
Economic
Problem:
Scarcity
and
Choice
40 of 40
©2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing
© 2004 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics, 7/e
Principles of Economics, 7/e Karl Case, Ray Fair
Karl Case, Ray Fair
Review Terms and Concepts
absolute advantage
capital
command economy
comparative advantage,
comparative advantage,
theory of
theory of
consumer goods
consumer goods
consumer sovereignty
consumer sovereignty
economic growth
economic growth
economic problem
economic problem
investment
investment
laissez-faire economy
laissez-faire economy
marginal rate of transformation (mrt)
marginal rate of transformation (mrt)
market
market
opportunity cost
opportunity cost
outputs
outputs
price
price
production
production
production possibility frontier (ppf)
production possibility frontier (ppf)
resources or inputs
resources or inputs
three basic questions
three basic questions