The document provides information on the BSc (Hons) Computer Science program at Birmingham City University, including:
- The program aims to develop competence in computer systems solutions from a mathematical and scientific base while appreciating professional responsibilities.
- Students will gain knowledge of programming, software design, databases, web technologies, and social factors related to IT. Intellectual skills include system modeling, specification, analysis and evaluation. Practical skills include system construction, tools/methodologies, and teamwork.
- Learning is through lectures, seminars, practical activities and independent study. Assessment includes coursework, projects, presentations and exams. Students complete a major final year project applying research.
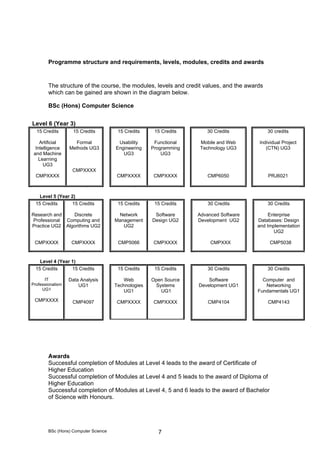
- The program structure