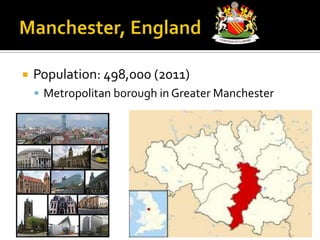
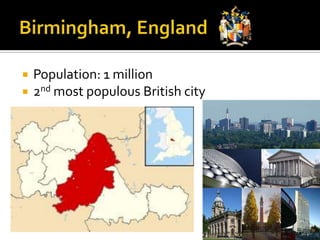
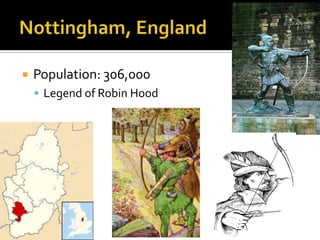
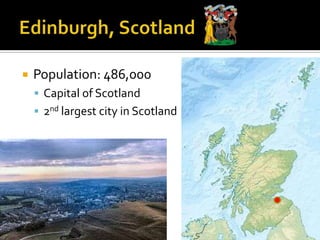
This document provides information about several major cities in England and Scotland. It details the populations and notable landmarks, industries or cultural aspects of London, Manchester, Birmingham, Stratford-upon-Avon, Edinburgh, and Glasgow. London is highlighted as the capital of England and UK, located on the River Thames with a population of over 7 million people. Key landmarks mentioned include Buckingham Palace, Palace of Westminster, Westminster Abbey, Kew Gardens, St. Paul's Cathedral, Tower Bridge, and various parks.