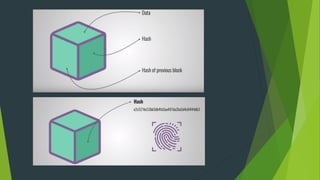
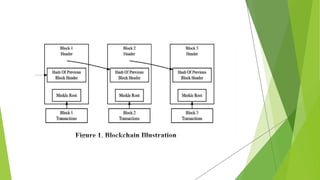
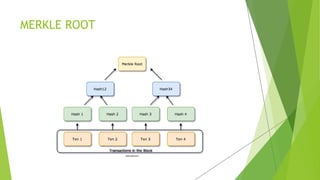
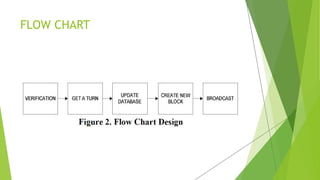
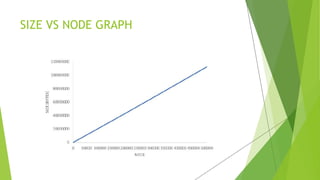
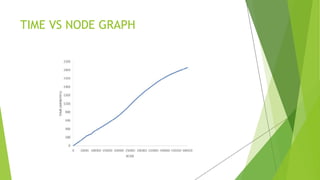
The document proposes a blockchain-based e-voting system designed to enhance security and transparency in elections by eliminating the risks associated with centralized control over the electoral database. It outlines the advantages of blockchain technology, including its distributed nature and use of cryptography, which help prevent data tampering and improve vote verification. The proposed system maintains privacy and integrity through a decentralized structure where each vote is recorded as a transaction on the blockchain, ensuring validation and security throughout the voting process.