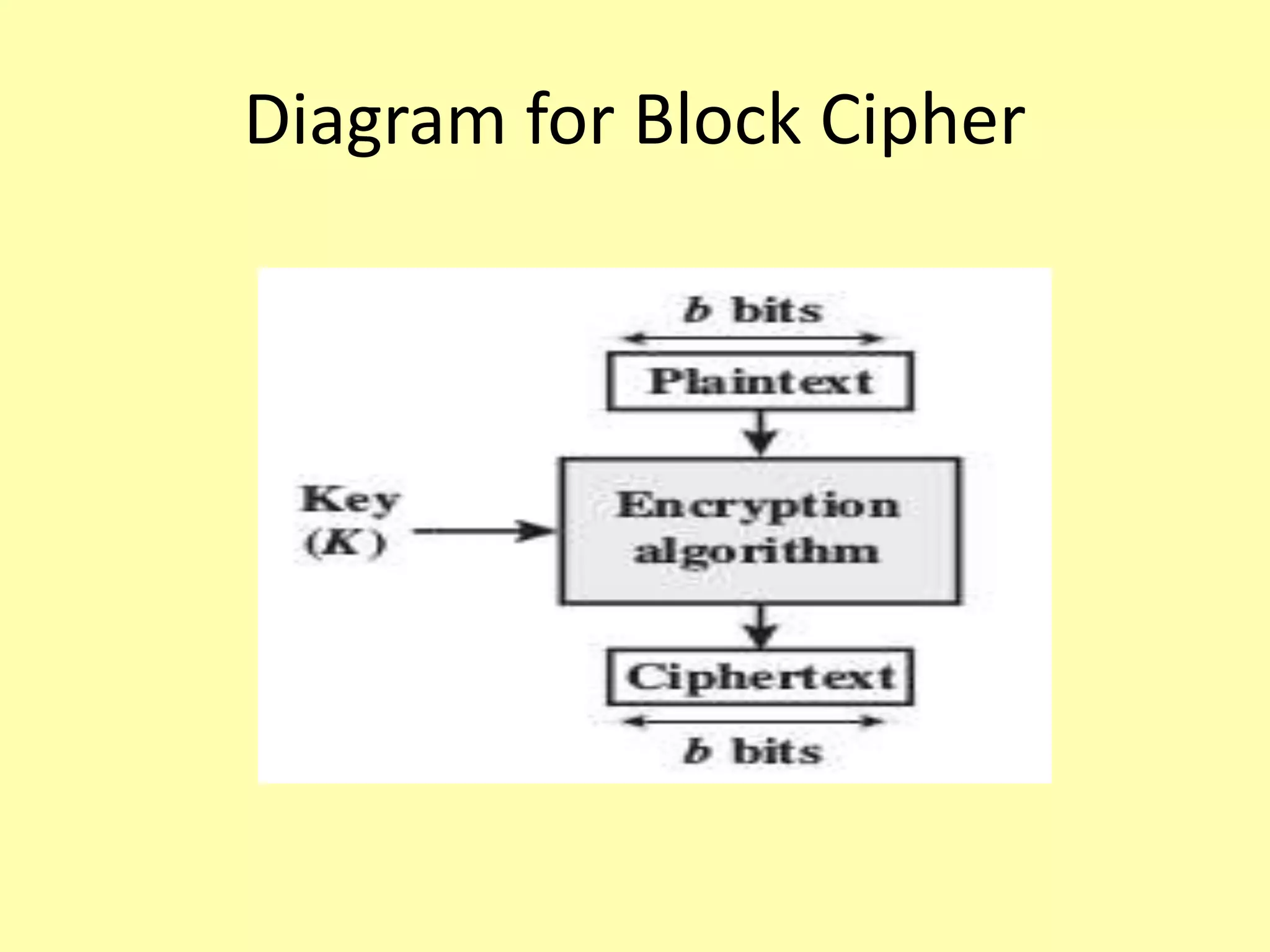
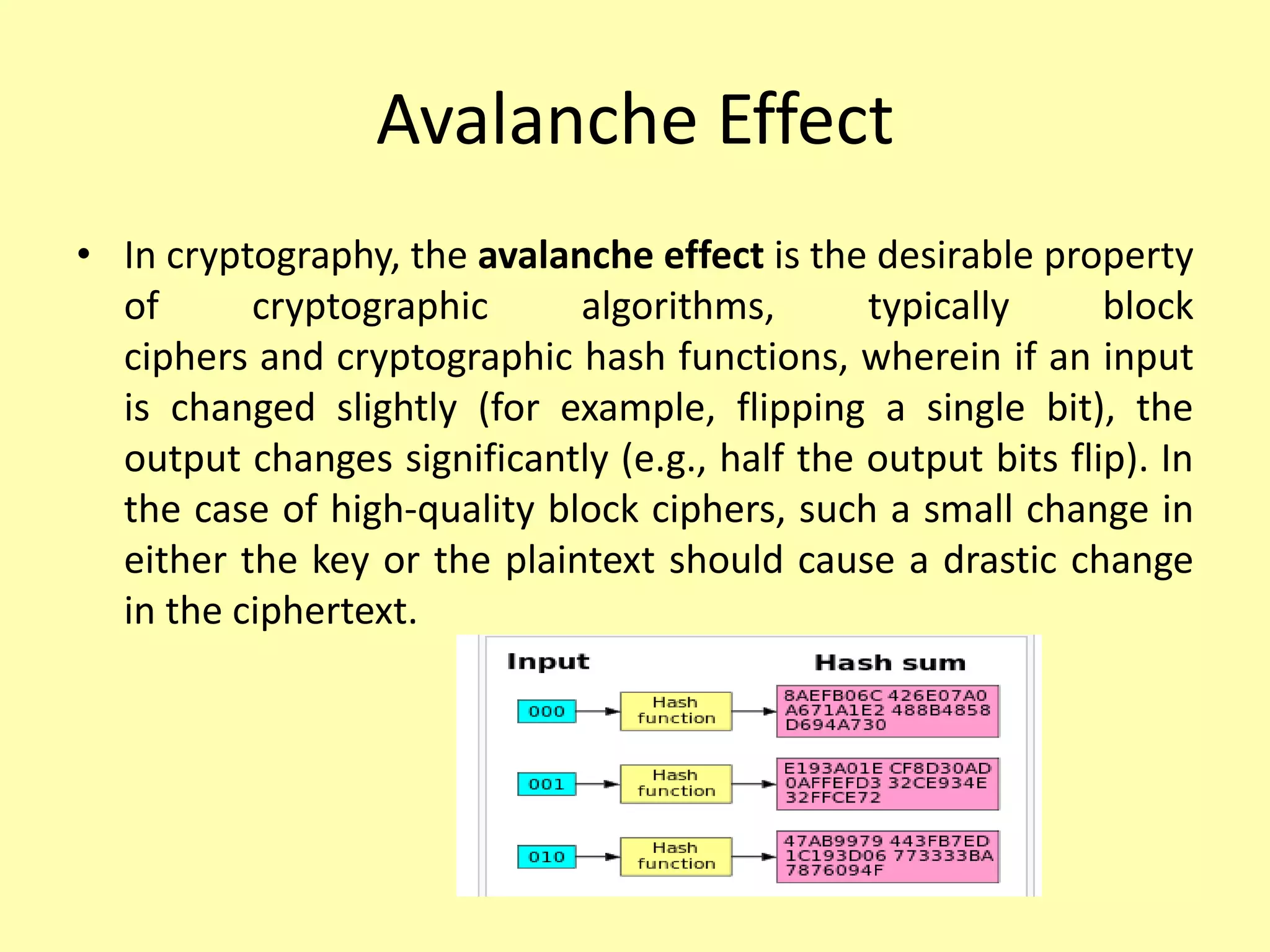
This document discusses block ciphers, including their definition, structure, design principles, and avalanche effect. A block cipher operates on fixed-length blocks of bits and uses a symmetric key. It encrypts bits in blocks rather than one by one. Block ciphers have advantages like high diffusion but are slower than stream ciphers. They are built using the Feistel cipher structure with a number of rounds and keys. Important design principles for block ciphers include the number of rounds, design of the round function, and key schedule algorithm. The avalanche effect causes a small input change to result in a significant output change.