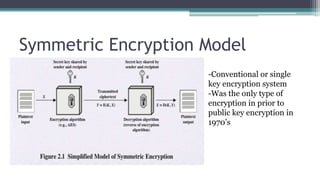
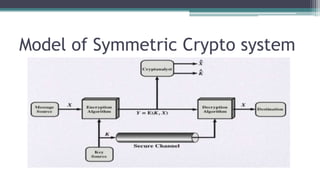
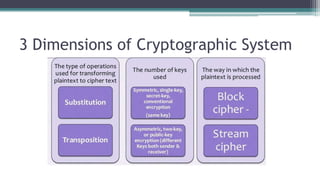
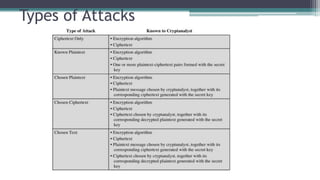
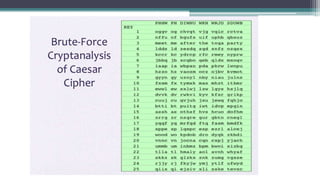
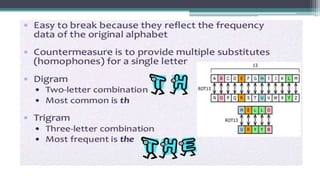
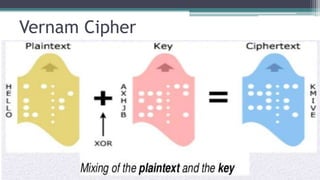
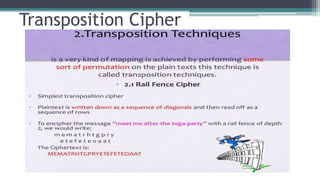
The document discusses classical encryption techniques such as substitution ciphers (Caesar cipher, monoalphabetic cipher, polyalphabetic cipher like the Vigenere cipher), transposition ciphers (rail fence, row-column transposition), and the Playfair and Hill ciphers. It covers basic terminology in cryptography, the symmetric encryption model involving a single encryption key, and types of attacks like brute force attacks.