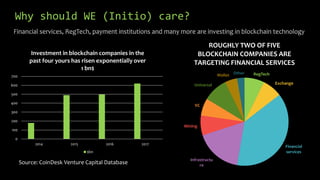
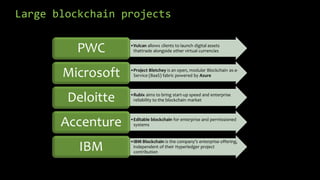
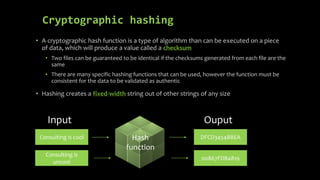
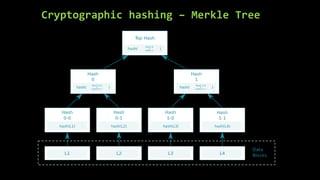
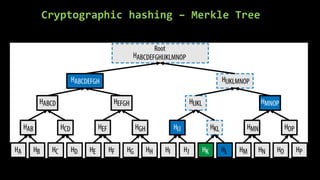
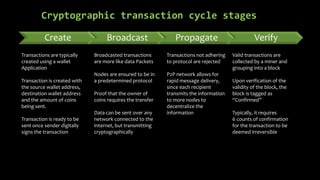
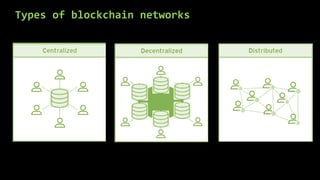
This document provides an overview of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, highlighting their foundational concepts such as decentralization, cryptography, and various protocols. It discusses the significance of blockchain for industries like financial services and outlines major projects like Ethereum, Bitcoin, and Hyperledger. Additionally, it explains the mechanics of transactions, mining, and the security principles underlying cryptographic methods used in these digital platforms.