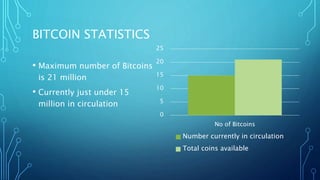
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that allows transactions without a central bank, first introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. It operates on a public ledger called the blockchain, which verifies transactions and maintains transparency while users control their own bitcoin addresses. Users can obtain bitcoins by purchasing them or accepting them in exchange for goods and services, and transactions are recorded and verified by miners who add them to the blockchain.