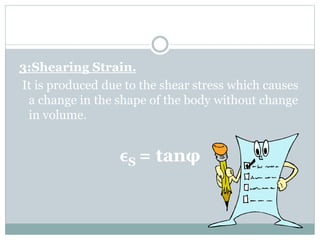
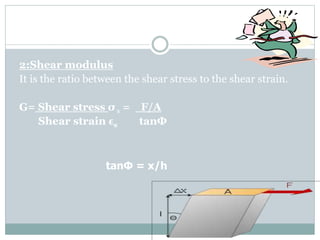
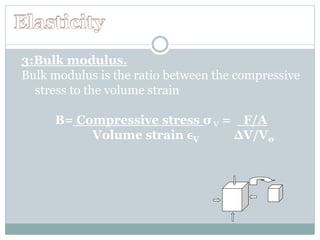
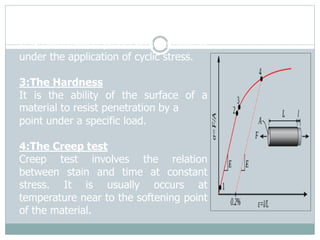
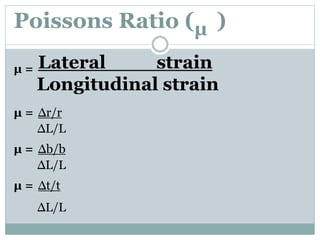
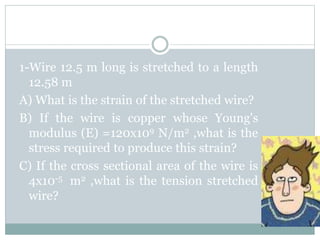
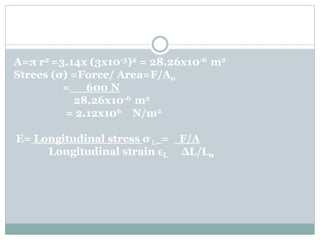
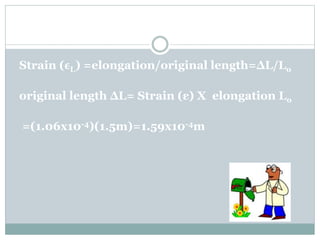
This chapter discusses elasticity and mechanical properties of materials. It defines stress as force per unit area and strain as deformation produced due to stress. It describes different types of stresses like tensile, compressive, and shear stress. It also describes different types of strains like longitudinal, volume, and shear strains. Hooke's law states that stress is directly proportional to strain. The chapter outlines various mechanical tests to study material properties including stress-strain tests, fatigue tests, hardness tests, and creep tests. It defines elastic coefficients like Young's modulus, shear modulus, and Poisson's ratio.