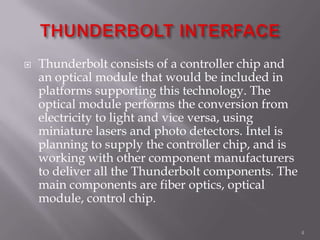
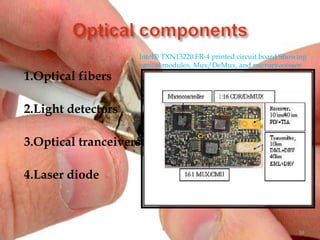
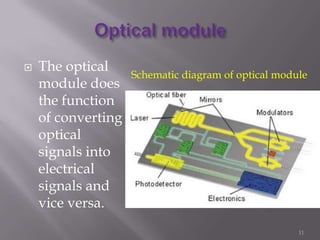
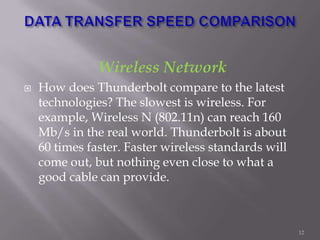
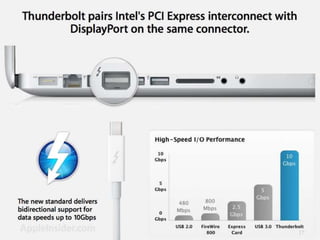
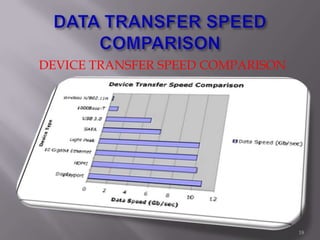
Thunderbolt is a new high-speed optical cable technology developed by Intel to connect devices using a single port. It uses fiber optics and can transfer data at 10 Gbps with potential for 100 Gbps. Thunderbolt allows multiple protocols to run simultaneously over a single cable, providing higher bandwidth and fewer connectors than existing standards. The technology consists of a controller chip and optical module for converting signals between electrical and optical. Intel plans to supply the controller chip and work with manufacturers to deliver Thunderbolt components for use starting in 2010.