More Related Content
PPT
Chapter 5 Risk and Return from Fundamental of financial Management PPTX
Risk and RetEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEurn.pptx PDF
PPT
PPTX
PDF
PPT
Unit Two Risk and Return Accounting Finance.ppt PDF
Risk & Return Basic Framework Similar to BF Risk hhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhand Return.pptx
PPT
risk and return student.ppt PPT
Financial Management Slides Ch 05 PPT
PPT
PDF
Investment_chapter-1-2020.pdf PPTX
1. introduction basics of investments.ppt PPT
PPTX
Week 5.pptxfgggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggg PPT
PPTX
Risk and return analysis.pptx PPTX
Invt Chapter 2 ppt.pptx best presentation PPTX
Risk & Return of the stock and calculation of risk PPT
Risk and return. Chapter 8- Principles of Managerial Finance PPTX
PPT
Fin254-ch08_nnh-Risk-return.pptvweveverververv PPT
PPT
PPTX
Financial Management: Introduction, Scope, Functions PPTX
Brigham_EFM5_ch08_Risk and Rates of Return.pptx PPT
More from sairayamin2
PPTX
BF RisFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFk Return.pptx PPT
BF Cost of Capkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkital.ppt PPTX
Business and Cohhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhmpany LAW.pptx PPTX
bcl 1uuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuu3.pptx PPTX
BCL 1eeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee1 B.pptx PPT
BF 9 lkklkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk2.ppt PPTX
NPpppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppV.pptx PPT
BCL 11 INDEppppppppppppppppppppppppppppMINITY.ppt PPT
BCL 10 A Contraoooooooooooooooooooct of SALE.ppt PPTX
BCL 5 A PERFORMGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGANCE OF CONTRACTS.pptx PPTX
Company cases i LLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLn Pakistan.pptx PPT
Foreclorrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrsures.ppt PPTX
Mr. Aqib Abbasi Prettttttttttttttttttttttttsentation.pptx PPTX
uuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuWE (1) (1).pptx PPTX
uuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuQUIZ - Copy.pptx PPTX
BCL 8 PARNuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuI.P 2pptx PPTX
QUIeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeZ.pptx PPT
ttyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyT.ppt PPT
qqqqqwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwww.ppt PPT
ratiouuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuus.ppt Recently uploaded
PDF
How to Buy Old Gmail Accounts – Verified & Secure.pdf DOCX
_18 Buying USA LinkedIn Accounts Can Boost Your Social.docx PDF
RFI Responses for Govt Contracting Tips. PDF
_Top 7 Mistakes to Avoid When Buying Google Ads Accounts.pdf PDF
BendelPuertoRicoCubaGuyanaVenezuelaPetroleumRefineryPetrochemicalPetroAgroInd... DOCX
Podcast Promotion Schedule for Turntable News PDF
Nicky Oppenheimer World Economic Forum Jan 2000 PDF
_The Ultimate Guide to Buying Twitter Accounts Safely.pdf PDF
OIL CHECK 500 Portable - Air Quality Monitoring System DOCX
How to Buy Verified OnlyFans Accounts Work in 2026.docx PDF
The threat to financial insitutions of quantum computing breaking all encrypt... PDF
enterprise software is not dead and here is why PDF
How to Buy Twitter Accounts_ A Step-by-Step Guide (2).pdf DOCX
Best Top 7 sites to Buy Old Gmail Accounts (PVA & Aged).docx PPTX
Explore Hubspot’s Customer Agent for B2B PPTX
REVIEWER-3rd-quarter-exam-mathematics.pptx PDF
17 Guide to Buying Verified Binance Accounts in the US.pdf PDF
Camil Institutional Presentation_Jan26.pdf PDF
Equinox Gold - Corporate Presentation - Jan 2026 PDF
Kirill Klip GEM Royalty TNR Gold Lithium Presentation BF Risk hhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhand Return.pptx
- 1.
Principles of Finance5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May
not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Chapter 5
Risks and
Rates of
Return
1
- 2.
Chapter 11 –Learning Objectives
Explain what it means to take risk when investing.
Compute the risk and return of an investment, and explain how the risk
and return of an investment are related.
Identify relevant and irrelevant risk, and explain how irrelevant risk can
be reduced.
Describe how to determine the appropriate reward—that is, risk
premium—that investors should earn for purchasing a risky
investment.
Describe actions that investors take when the return they require to
purchase an investment is different from the return they expect the
investment to produce.
Identify different types of risk and classify each as relevant or
irrelevant with respect to determining an investment’s required rate of
return.
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2
- 3.
Defining and MeasuringRisk
Risk is the chance that an outcome other
than expected will occur
Probability distribution is a listing of all
possible outcomes with a probability
assigned to each
Probabilities must sum to 1.0 (100%)
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 3
- 4.
Probability Distributions
It eitherwill rain, or it will not
Only two possible outcomes
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 4
Outcome (1) Probability (2)
Rain 0.40 = 40%
No Rain 0.60 = 60%
1.00 100%
- 5.
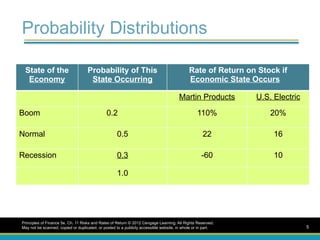
Probability Distributions
Principles ofFinance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 5
State of the
Economy
Probability of This
State Occurring
Rate of Return on Stock if
Economic State Occurs
Martin Products U.S. Electric
Boom 0.2 110% 20%
Normal 0.5 22 16
Recession 0.3 -60 10
1.0
- 6.
Expected Rate ofReturn
The rate of return expected to be realized from
an investment over a long period of time
The mean value of the probability distribution
of possible returns
The weighted average of the outcomes, where
the weights are the probabilities
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 6
- 7.
Expected Rate ofReturn
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 7
- 8.
Measuring Risk: TheStandard Deviation
A measure of the tightness, or variability,
of a set of outcomes
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 8
- 9.
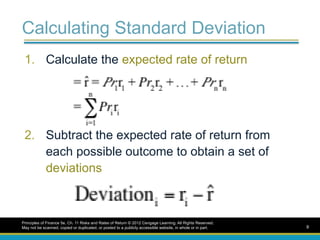
Calculating Standard Deviation
1.Calculate the expected rate of return
2. Subtract the expected rate of return from
each possible outcome to obtain a set of
deviations
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 9
- 10.
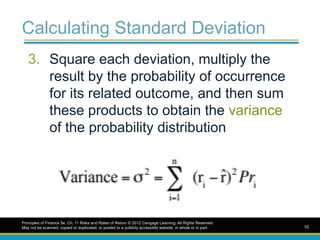
Calculating Standard Deviation
3.Square each deviation, multiply the
result by the probability of occurrence
for its related outcome, and then sum
these products to obtain the variance
of the probability distribution
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 10
- 11.
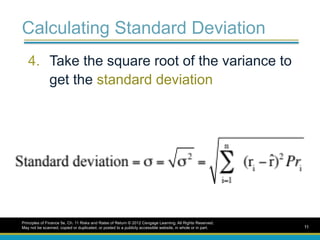
Calculating Standard Deviation
4.Take the square root of the variance to
get the standard deviation
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 11
- 12.
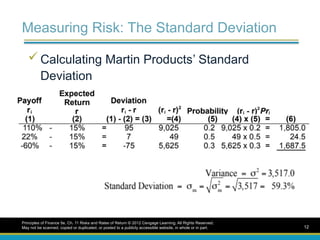
Measuring Risk: TheStandard Deviation
Calculating Martin Products’ Standard
Deviation
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 12
- 13.
Measuring Risk: Coefficientof Variation
Standardized measure of risk per unit of
return
Calculated as the standard deviation
divided by the expected return
Useful where investments differ in risk
and expected returns
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 13
- 14.
Principles of Finance5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved
. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 14
Using Historical Data to Measure Risk
- 15.
Risk Aversion
Risk-averse investorsrequire higher
rates of return to invest in higher-risk
securities
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 15
- 16.
Risk Aversion andRequired Returns
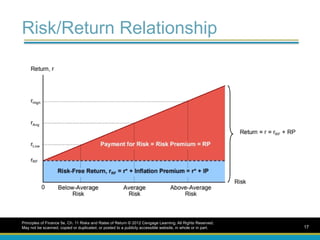
Risk premium (RP)
The portion of the expected return that can
be attributed to the additional risk of an
investment
The difference between the expected rate
of return on a given risky asset and that on
a less risky asset
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 16
- 17.
Risk/Return Relationship
Principles ofFinance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 17
- 18.
Risk and Returnin a Portfolio
Context
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights
Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in
whole or in part.
18
- 19.
Risk and Returnin a Portfolio Context
Portfolio
A collection of investment securities
A combination of two or more securities or
assets.
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 19
- 20.
Portfolio Returns
Expected returnon a portfolio
The weighted average expected return on
the stocks held in the portfolio
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 20
- 21.
Portfolio Risk andthe Importance of
Covariance
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 21
- 22.
Portfolio Risk
Correlation coefficient
A measure of the degree of relationship
between two variables
Positively correlated stocks have rates of
return that move in the same direction
Negatively correlated stocks have rates of
return that move in opposite directions
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 22
- 23.
Portfolio Risk
Risk reductionthrough diversification
The concept of diversification makes
such common sense that our language
even contains everyday expressions that
exhort us to diversify (“Don’t put all your
eggs in one basket”). The idea is to
spread your risk across a number of
assets or investments.
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 23
- 24.
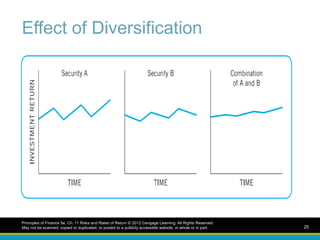
Risk reduction throughdiversification
Combining stocks that are not perfectly
positively correlated will reduce the portfolio
risk through diversification
The riskiness of a portfolio is reduced as
the number of stocks in the portfolio
increases
The smaller the positive correlation, the
greater the reduction of risk from adding
another investment
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 24
- 25.
Effect of Diversification
Principlesof Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 25
- 26.
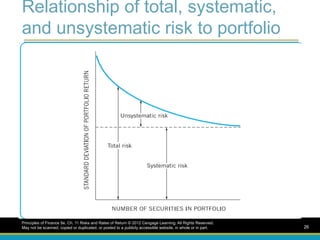
Relationship of total,systematic,
and unsystematic risk to portfolio
size
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 26
- 27.
Systematic risk
Systematic riskThe variability of return
on stocks or portfolios associated with
changes in return on the market as a
whole such as changes in the nation’s
economy, tax reform by Congress, or a
change in the world energy situation.
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 27
- 28.
Different Types ofRisk
Systematic Risks
Interest rate risk
Inflation risk
Maturity risk
Liquidity risk
Exchange rate risk
Political risk
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 28
- 29.
Un Systematic Risk
Thevariability of return on stocks or
portfolios not explained by general
market movements. It is avoidable
through diversification such as a new
competitor may begin to produce
essentially the same product; or a
technological breakthrough may make
an existing product obsolete.
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 29
- 30.
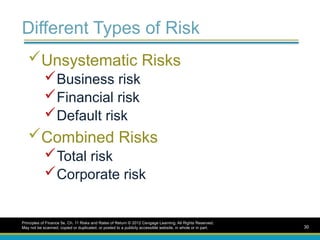
Different Types ofRisk
Unsystematic Risks
Business risk
Financial risk
Default risk
Combined Risks
Total risk
Corporate risk
Principles of Finance 5e, Ch. 11 Risks and Rates of Return © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 30