Embed presentation
Download to read offline



![https://www.lucidchart.com/
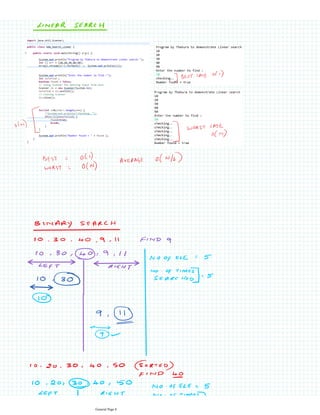
BinarySearchAlgorithm(A,x,size){
//A = Sorted array, "x"=element to be searched and "size" = size of array
Low:=0, high:=size-1
while low<=end
mid:=(low+high)/2
If a[mid]= x
return mid
then
Else
If a[mid]<x
low=mid+1
else
endif
high=mid-1
EndWhile
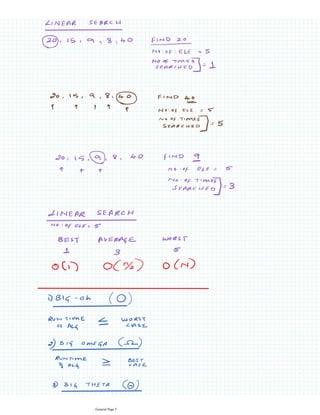
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Input Sorted array in "a[]" and element to be searched in "x" and size of array in "size"
Step 3: Initialize low=0, high=size-1
Step 4: Repeat until start>=end
Step 4.1: mid=(low+high)/2
Step 4.2: If a[mid] is equal to x , then xis found.print index value of mid and exit
Step 4.3: Else check if x is less than a[mid] search left of array by adjusting the array index as high=mid-1
Step 4.5 : else, search right of array by adjusting the array index as low=mid+1
Step 5: Print x not found in the list
Stop 6: Stop
General Page 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/betada1timespacecomplexity-220219150521/85/Time-and-Space-complexity-of-Algorithms-9-320.jpg)
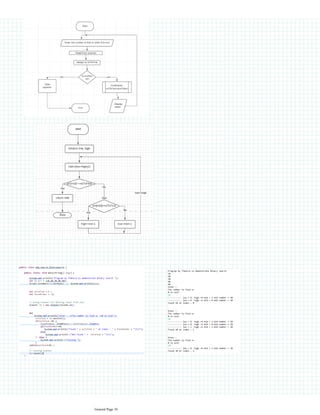


This document provides an overview of the binary search algorithm. It begins with 12 pages of general information before explaining the steps to perform a binary search on a sorted array. It outlines 6 steps: 1) Start, 2) Input sorted array and search element, 3) Initialize low and high indexes, 4) Repeat search until indexes meet, 4.1) Calculate mid-index, 4.2) Check if mid element equals search element, 4.3/4.5) Adjust low/high index to search left or right side, 5) Element not found message, 6) Stop. Pseudocode is provided to demonstrate how to implement the binary search algorithm.








![https://www.lucidchart.com/
BinarySearchAlgorithm(A,x,size){
//A = Sorted array, "x"=element to be searched and "size" = size of array
Low:=0, high:=size-1
while low<=end
mid:=(low+high)/2
If a[mid]= x
return mid
then
Else
If a[mid]<x
low=mid+1
else
endif
high=mid-1
EndWhile
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Input Sorted array in "a[]" and element to be searched in "x" and size of array in "size"
Step 3: Initialize low=0, high=size-1
Step 4: Repeat until start>=end
Step 4.1: mid=(low+high)/2
Step 4.2: If a[mid] is equal to x , then xis found.print index value of mid and exit
Step 4.3: Else check if x is less than a[mid] search left of array by adjusting the array index as high=mid-1
Step 4.5 : else, search right of array by adjusting the array index as low=mid+1
Step 5: Print x not found in the list
Stop 6: Stop
General Page 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/betada1timespacecomplexity-220219150521/85/Time-and-Space-complexity-of-Algorithms-9-320.jpg)


