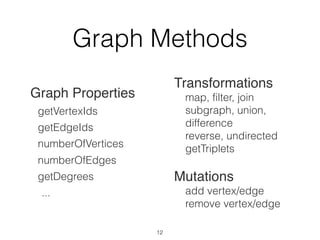
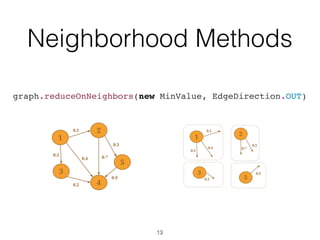
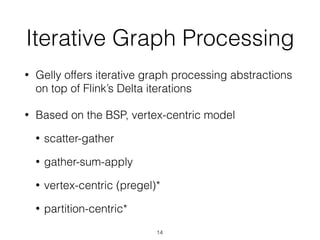
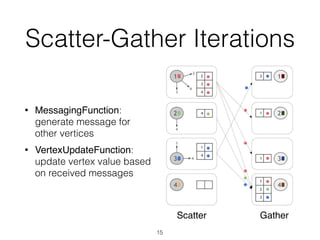
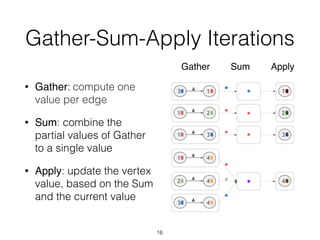
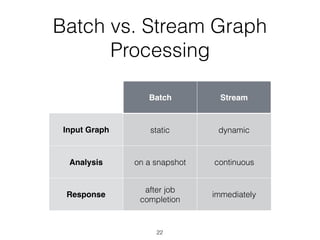
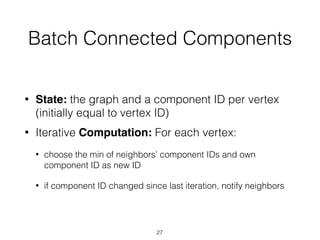
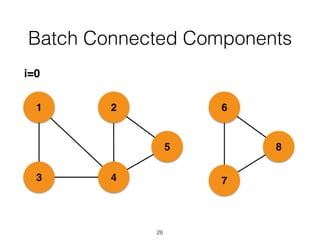
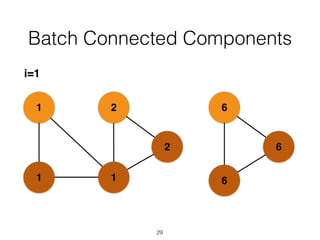
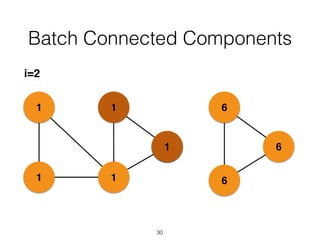
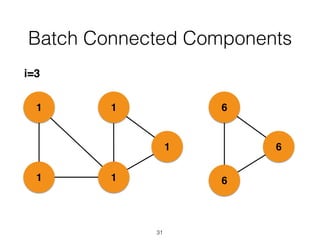
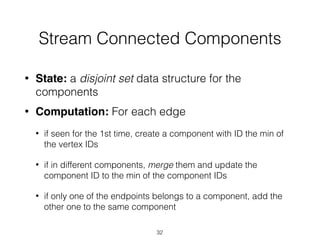
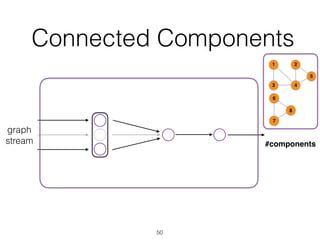
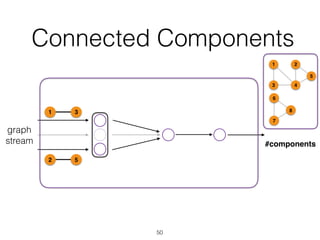
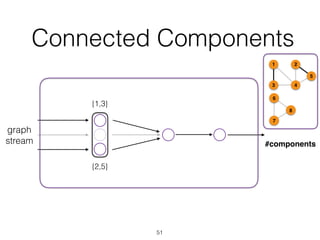
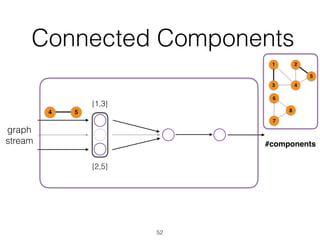
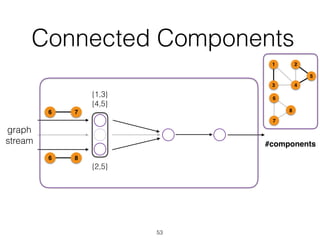
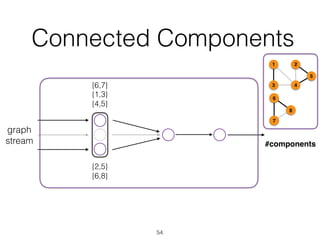
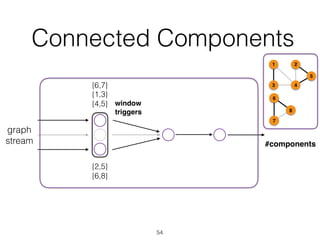
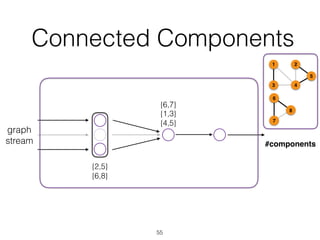
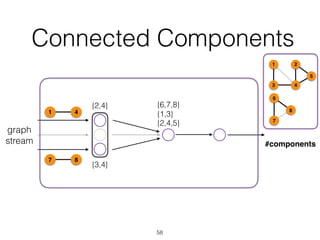
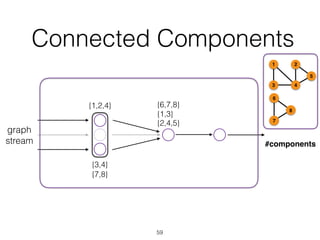
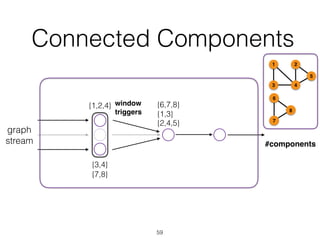
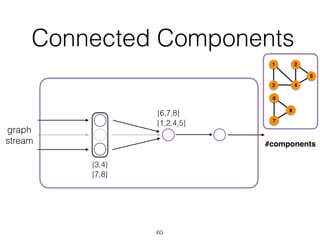
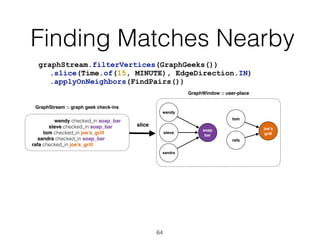
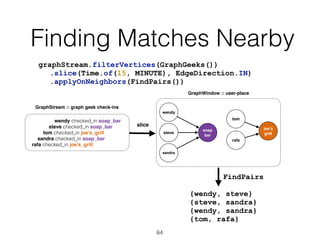
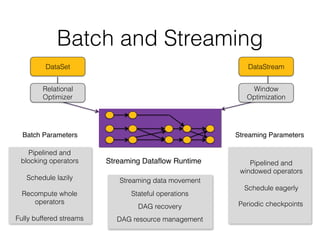
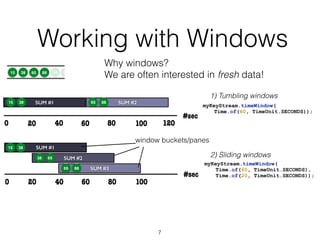
The document discusses batch and stream graph processing using Apache Flink, an open-source framework tailored for real-time data streaming and analysis. It highlights Flink's capabilities in handling both streaming and batch data through different APIs, introduces its graph processing library Gelly, and explains iterative graph processing and single-pass stream graph processing. Additionally, it covers key concepts like windowing, stateful operations, and challenges in maintaining graph structures during stream processing.
![Flink APIs
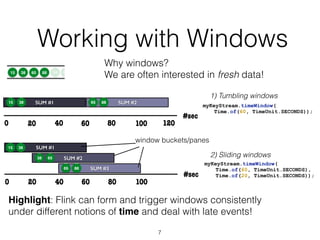
6
case class Word (word: String, frequency: Int)
val lines: DataStream[String] = env.readFromKafka(...)
lines.flatMap {line => line.split(" ").map(word => Word(word,1))}
.keyBy("word”).timeWindow(Time.of(5,SECONDS)).sum("frequency")
.print()
val lines: DataSet[String] = env.readTextFile(...)
lines.flatMap {line => line.split(" ").map(word => Word(word,1))}
.groupBy("word").sum("frequency”)
.print()
DataSet API (batch):
DataStream API (streaming):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4j-flink-meetup-160302233132/85/Batch-and-Stream-Graph-Processing-with-Apache-Flink-6-320.jpg)


![Hello, Gelly!
ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataSet<Edge<Long, NullValue>> edges = getEdgesDataSet(env);
Graph<Long, Long, NullValue> graph = Graph.fromDataSet(edges, env);
DataSet<Vertex<Long, Long>> verticesWithMinIds = graph.run(
new ConnectedComponents(maxIterations));
val env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val edges: DataSet[Edge[Long, NullValue]] = getEdgesDataSet(env)
val graph = Graph.fromDataSet(edges, env)
val components = graph.run(new ConnectedComponents(maxIterations))
Java
Scala
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4j-flink-meetup-160302233132/85/Batch-and-Stream-Graph-Processing-with-Apache-Flink-12-320.jpg)