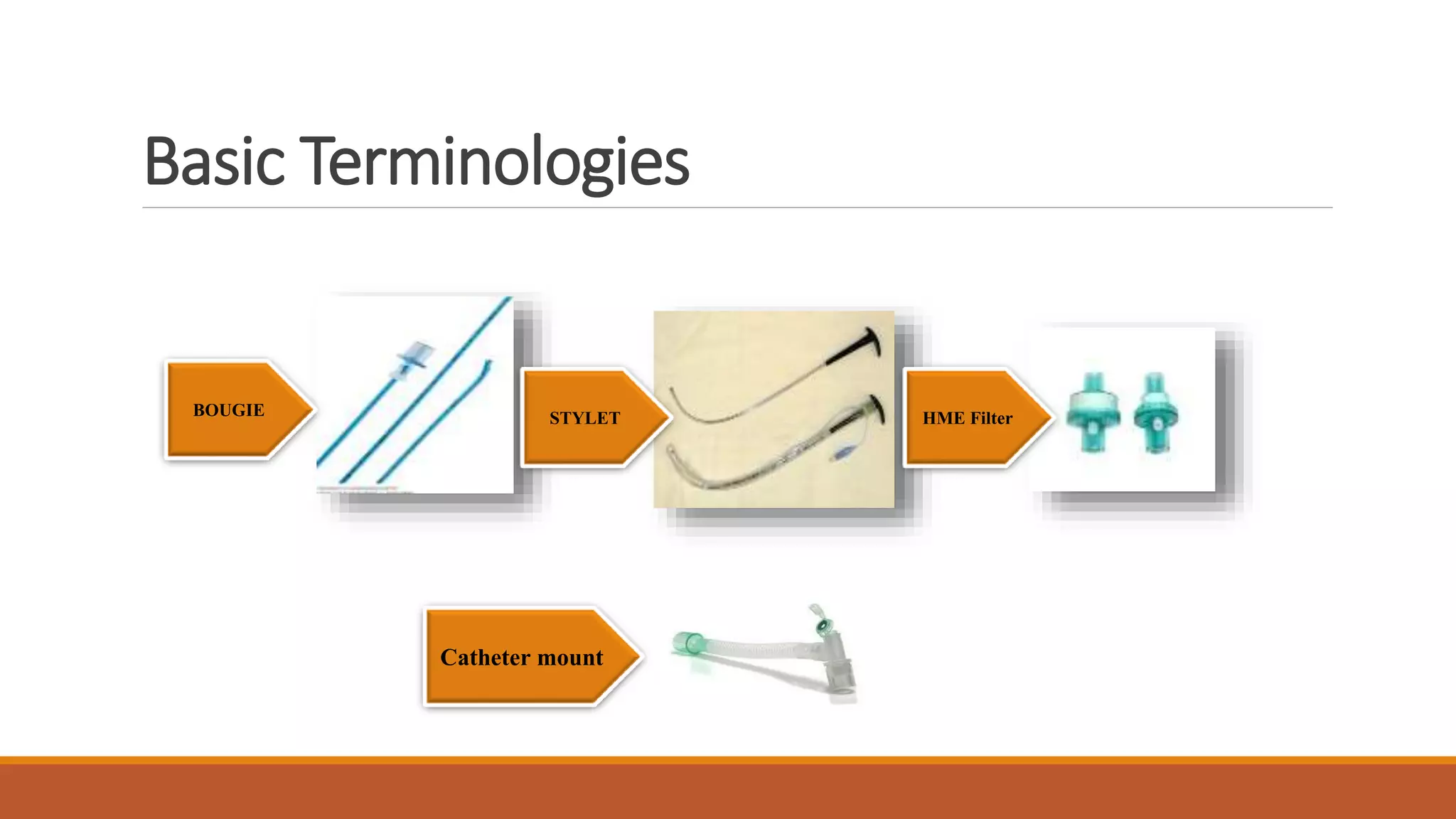
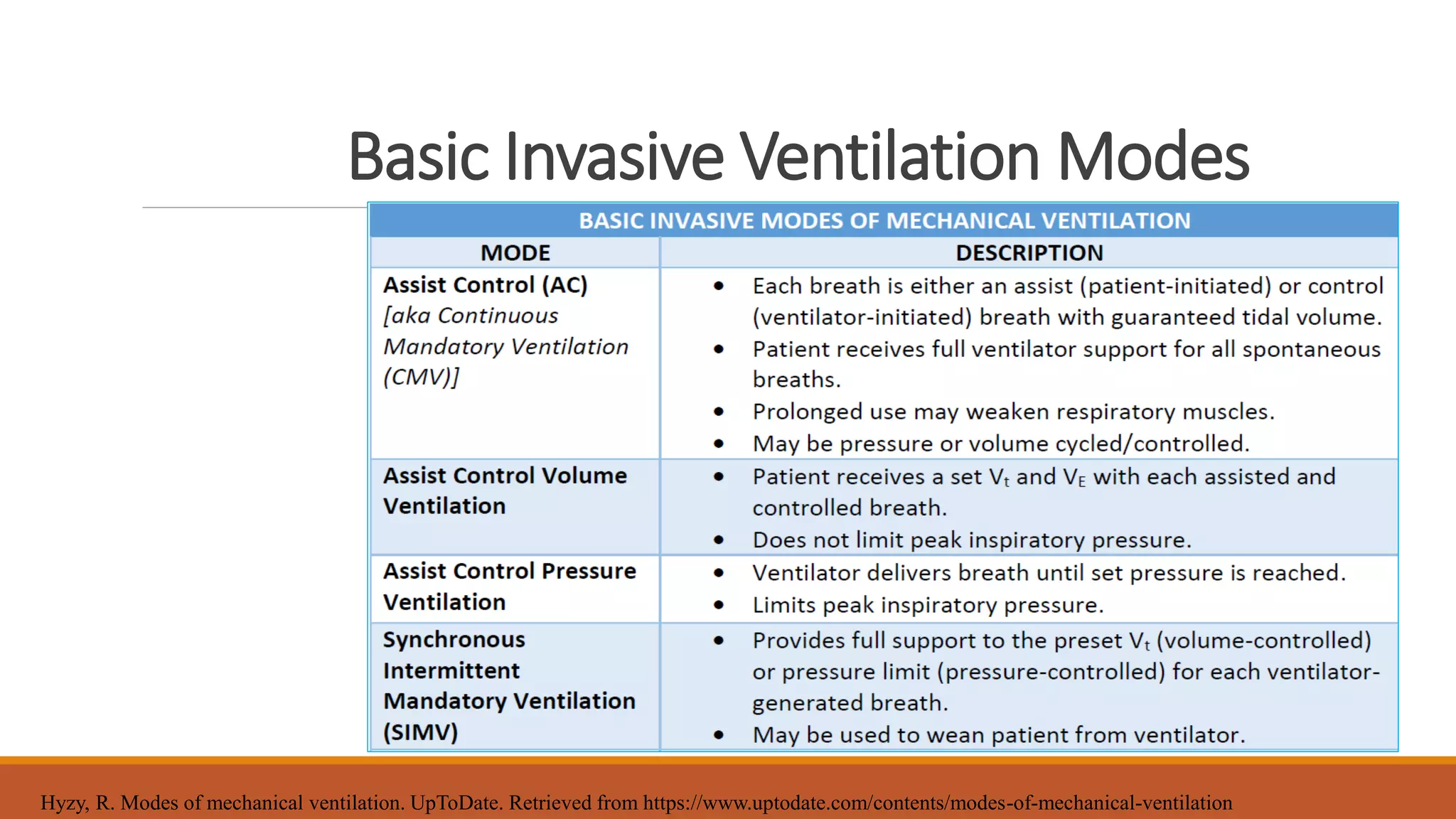
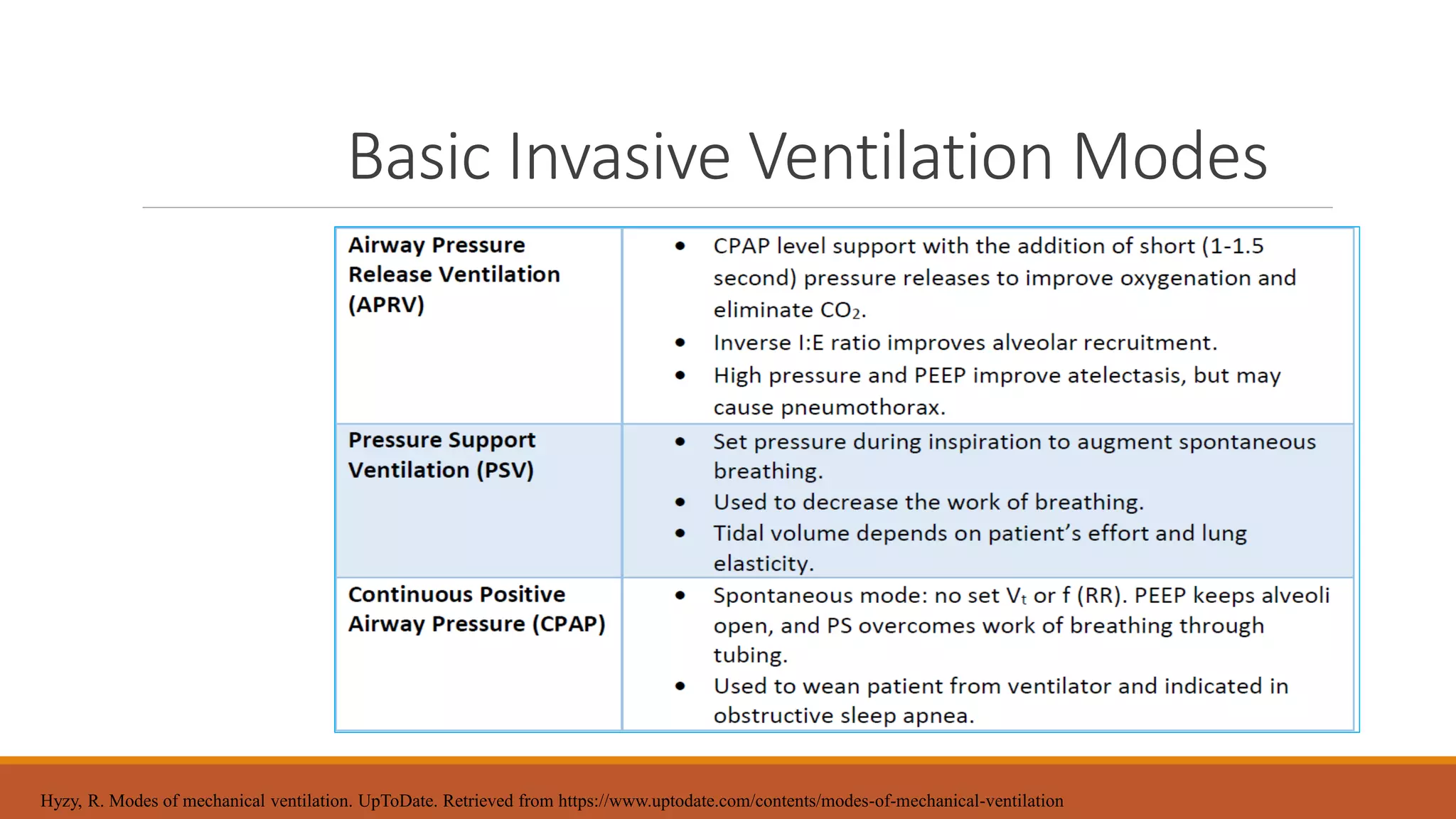
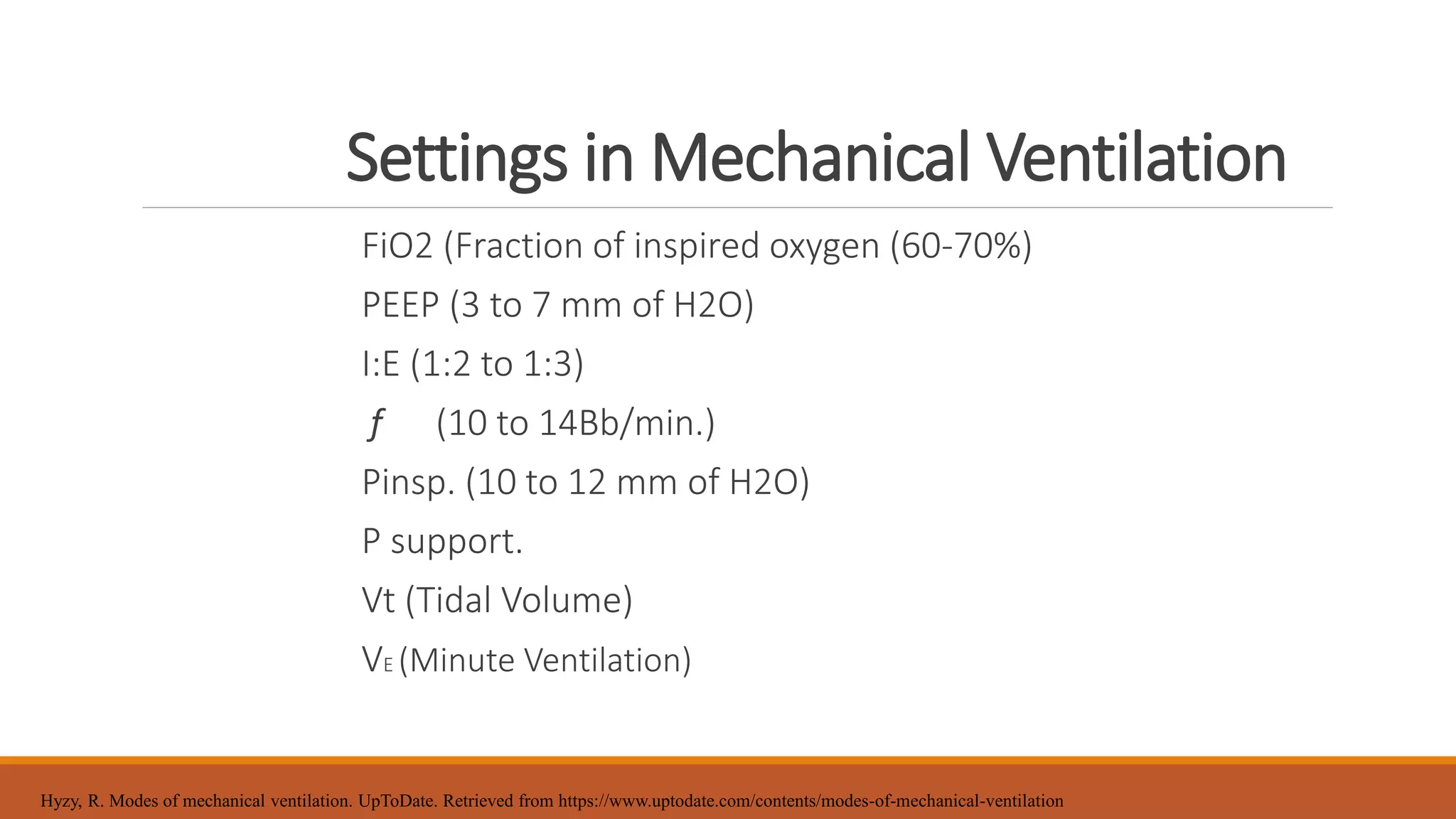
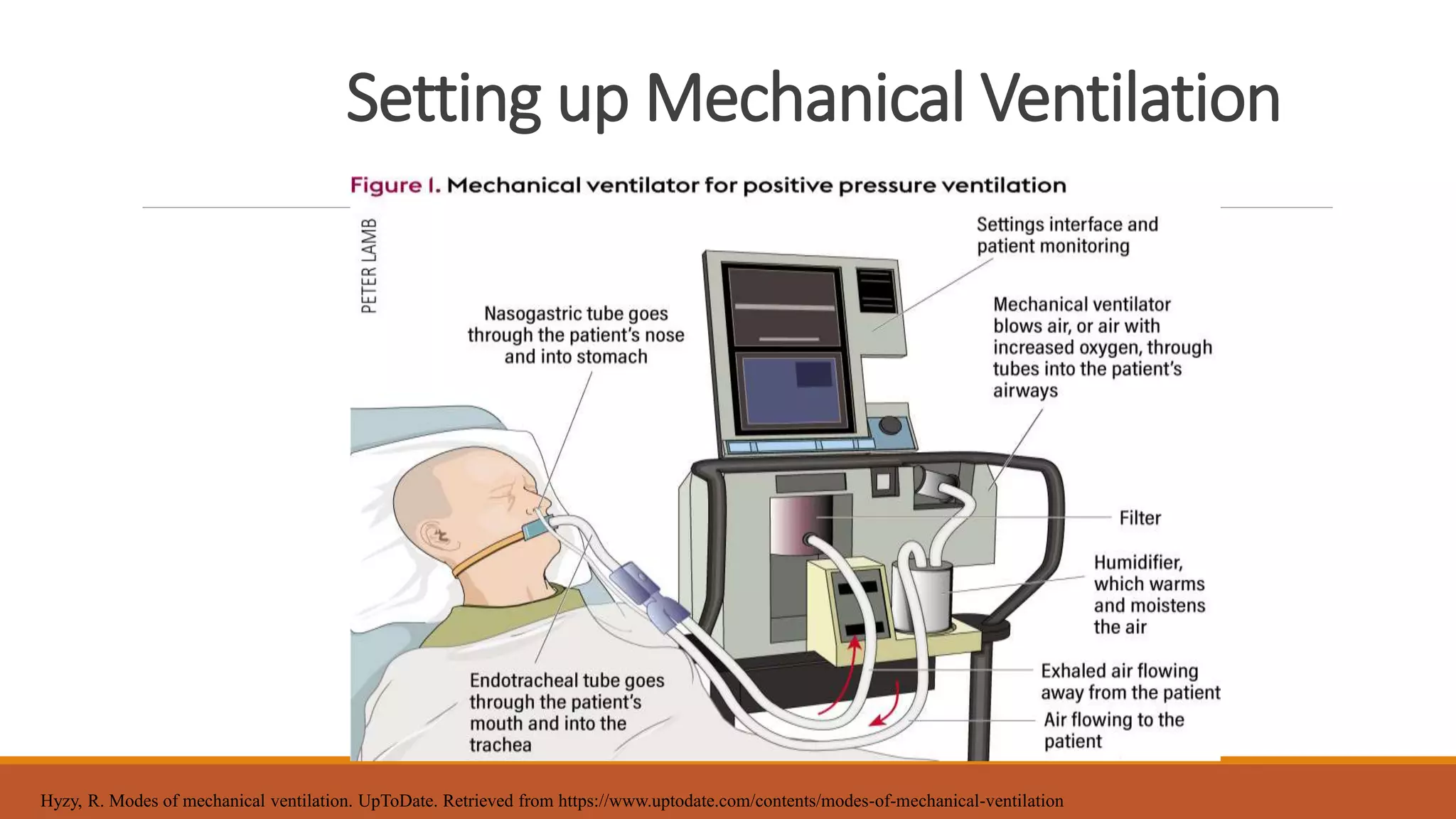
Mechanical ventilation provides respiratory support to patients who cannot breathe adequately on their own. It is used in intensive care and long-term care settings for conditions like acute or chronic respiratory failure. The benefits of mechanical ventilation include improved gas exchange and decreased work of breathing for the patient. Basic terminology includes endotracheal tubes, laryngoscopes, and filters. Common invasive ventilation modes are discussed, along with settings like tidal volume, minute ventilation, and oxygen levels. Proper care of patients on ventilators involves assessment, suctioning, and preventing infections through bundles. Troubleshooting helps address potential issues with the equipment or patient response.