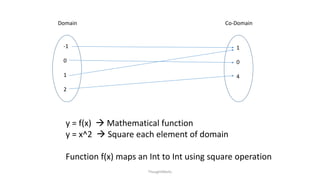
The document explores functional programming, its origins, and key concepts like pure functions, immutability, and recursion, highlighting its advantages such as easier debugging and parallelization, as well as its limitations including high barriers to entry and potential performance issues. It outlines applications in various companies and discusses functional programming jargon, emphasizing programming without assignment statements. The content is aimed at providing a foundational understanding of functional programming and its practical implications.