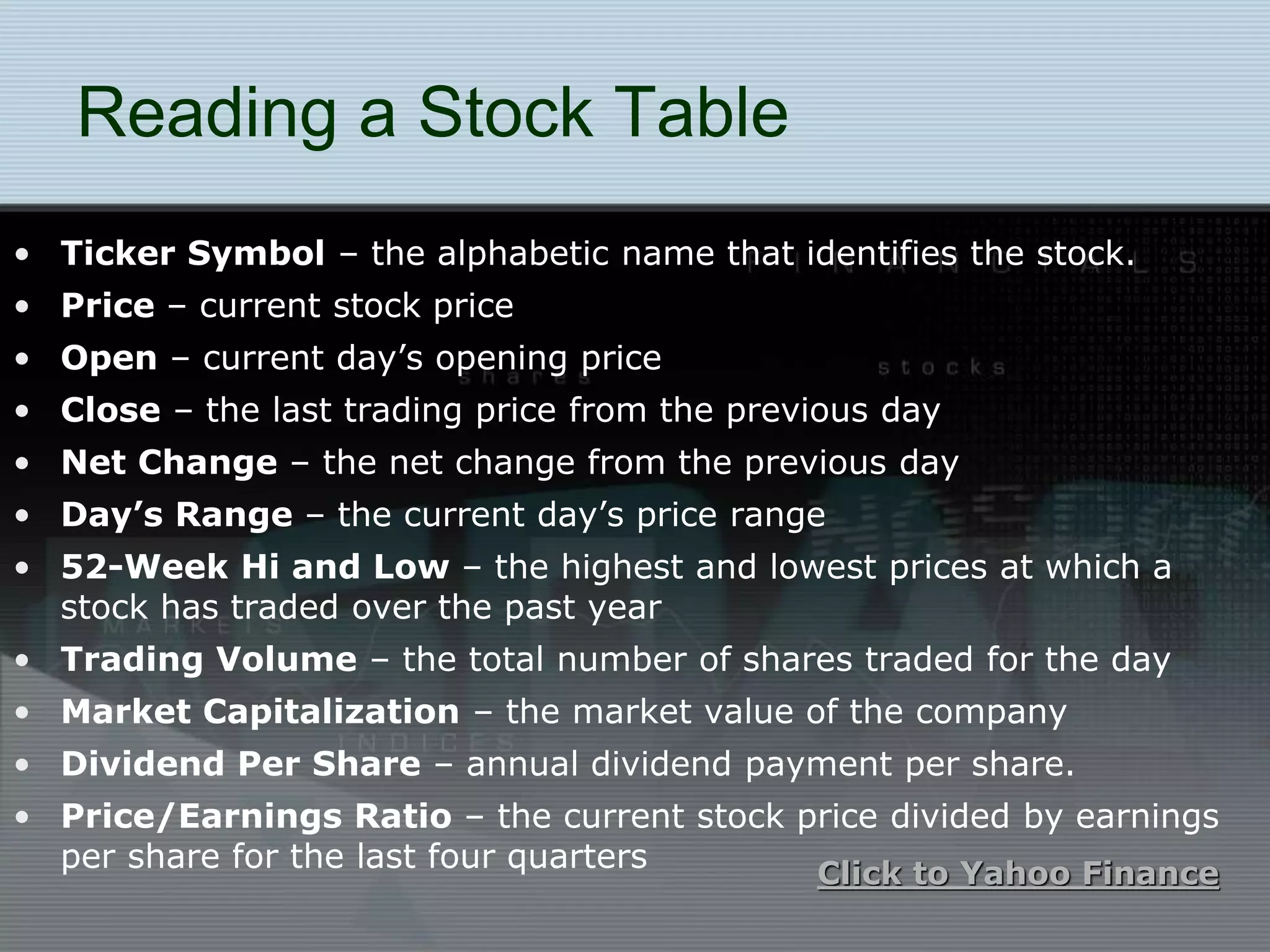
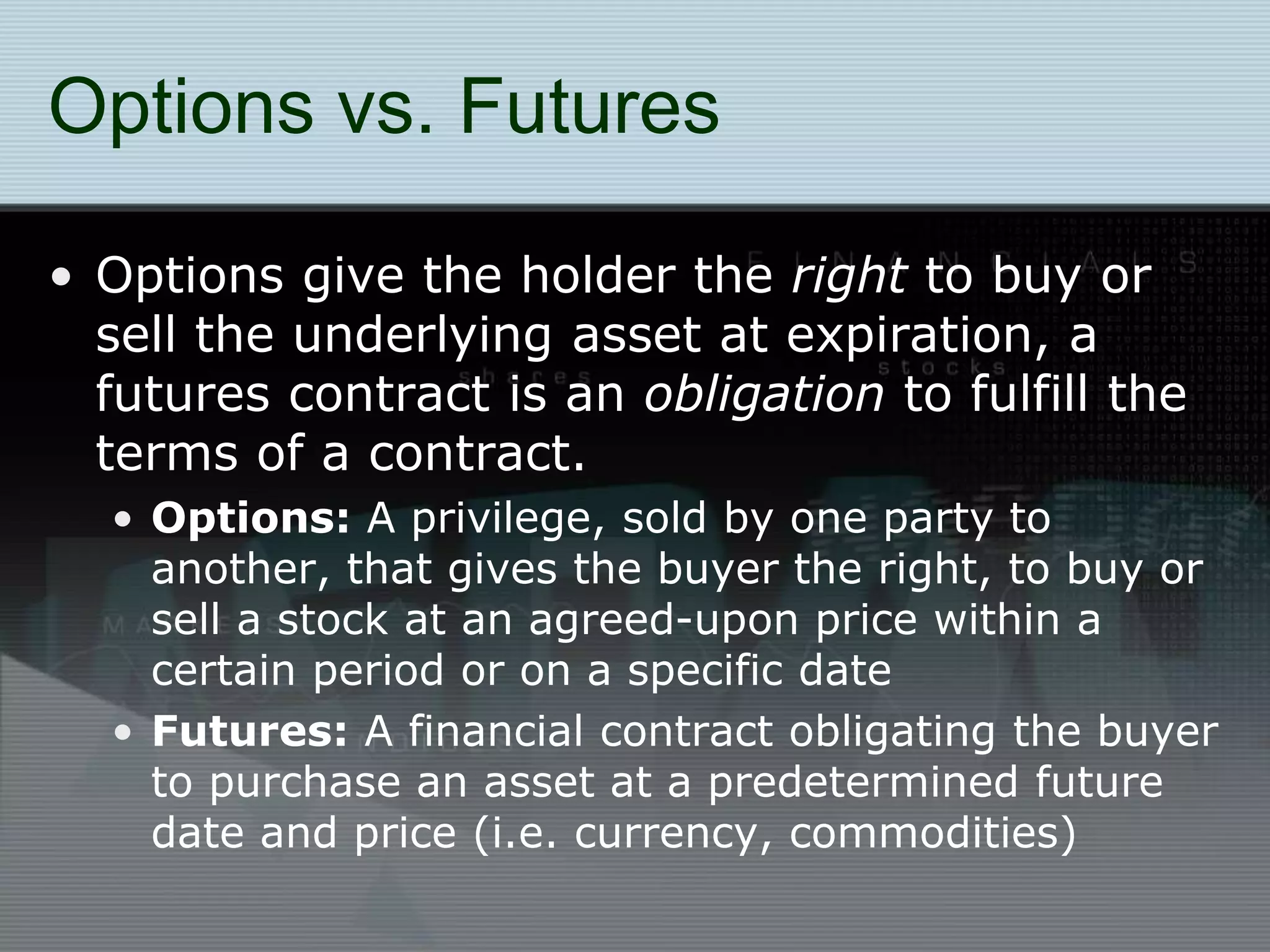
Stocks represent ownership in a publicly traded company. Common stock is the most common type and does not guarantee dividends, while preferred stock pays a fixed dividend. Stocks are bought and sold on exchanges like the NYSE and NASDAQ. Investing in stocks allows individuals to potentially profit from price appreciation or dividends. However, stock prices can fluctuate based on supply and demand as well as company performance and broader economic conditions.