Banking industry
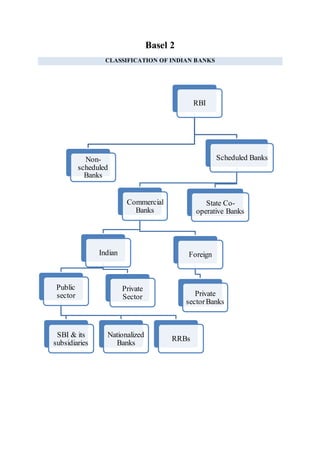
- 1. Basel 2 CLASSIFICATION OF INDIAN BANKS RBI Scheduled Banks State Co- operative Banks Commercial Banks Foreign Private sectorBanks Indian Private Sector Public sector RRBs Nationalized Banks SBI & its subsidiaries Non- scheduled Banks
- 2. ● Functions of Commercial banks 1) Intermediation function – Brokerage,Asset transformation 2) Transaction services 3) Financial services – Advisory, Transaction support (for Demand a/c),Custodian services ● Basel2 Focus: Strengthening of capital ● Based on 3 pillars ● CAR or CRAR = 𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐹𝑢𝑛𝑑 (𝑇𝑖𝑒𝑟 1 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑇𝑖𝑒𝑟 2) 𝑅𝑖𝑠𝑘 𝑊𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠 ∗ 100 As per Basel, this ratio should be minimum 8%. As per RBI, this ratio should be minimum 9%. OR CAR = 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 ( 𝑇𝑖𝑒𝑟 1 𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 + 𝑇𝑖𝑒𝑟 2 𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙) 𝑀𝑎𝑟𝑘𝑒𝑡 𝑟𝑖𝑠𝑘 + 𝐶𝑟𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑡 𝑟𝑖𝑠𝑘 + 𝑂𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑟𝑖𝑠𝑘 ∗ 100 Total capital = Tier 1+Tier 2 capital-Shareholding in other banks Tier 1= Ordinary capital + Retained earnings and share premium - Intangible assets. Tier 2= Undisclosed Reserves + GeneralBad Debt Provision + Revaluation Reserve + Subordinated Debt + Redeemable Preference shares (1) Minimum Capital Standards CRAR (Capital to Risk Weighted Assets Ratio) (2) Supervisory Review Respective central banks of a country will ensure the maintenance of minimum capital (3) Market Discipline Here, the role of banks stakeholders, maybe the customers, Government, shareholders, employees of the bank will ensure that whether banks are maintaining minimum capital or not.
- 3. Simply put, TIER 1CAPITAL Includes Equity Capital and Disclosed Reserves. 1) Equity capital includes instruments that cannot be redeemed at the option of the holders (meaning that the owner of the shares cannot decide on his own that he wants to withdraw the money he invested and so cannot leave the bank without the risk coverage). Like, Equity share capital and Equity share premium. 2) Disclosed Reserves includes Reserves held by a bank and thus money that no one but the bank can have an influence on. Reserves like, Statutory Reserves,General Reserves,Special Reserves and Capital Reserves. 3) Investment Fluctuation Reserves As Treasury profits are sensitive to fluctuations in interest rates,banks are advised to set aside a part of treasury income as IFR. It is created as a Revaluation Reserve,is a below-the-line item and a charge on Net Profit. RBI had permitted banks with CAR above 9%, to treat the entire balance in the IFR as Tier 1 Capital. (For Market risk hedge). Simply put, Capital (9%) Permanant Capital (Tier 1) 6% Supplemantary Capital (Tier 2) 3% Tier 1 Capital (1) Paid-up Share Capital (2) Free Reserves or DisclosedReserves - Statutory Reserves (Banks transfer 20% of its profits before dividend every year) - Share premium - Capital Reserves - Other Disclosed Reserves - IPDI (Innovative Perpetual Debt Instruments) for Tier 1 [Max 40% of Tier 1]
- 4. Innovative Perpetual Debt Instruments: This is perpetual in nature and is allowed to issue up to 15% of Total Tier 1 Capital. This is not issued with a Put Option, but it can be issued only with a Call option. And this Call Option can be exercised only when the instrument has run for at least 10 years. Interest due on IPDI in not payable and is also non-cumulative in case the CRAR of the issuing bank is less than regulatory minimum prescribed. And banks would be allowed to pay interest due with prior approval of RBI even when the payment of interest results in loss/increase. These instruments holders have the superiority to the claims of other investors in Equity shares and subordinated instruments. These are issued in the form of PerpetualNon-Cumulative Preference Shares (PNCPS) TIER 2 CAPITAL It consists of Undisclosed Reserves, Revaluation Reserves, General Provisions, Hybrid Instruments and Subordinated termdebt. Undisclosed Reserves:- These are not common, but are accepted by some regulators where a bank has made a profit but this has not appeared in normal retained profits or in generalreserves of the bank. Revaluation Reserves:- It is created when a company has an asset revalued and an increase in value is brought to account. Example, a bank owns the land and building if its head-offices and bought them for Rs.2 crore,century ago. And a current revaluation is very likely to show a large increase in value. This increase would be added to a Revaluation Reserve. Revaluation reserves can be taken as a part of Capital Fund at a discount of 55%. General Provisions:- It is created when a company is aware that a loss may have occurred but is not sure of the exact nature of that loss. It can be taken as a part of Capital Fund but max @ 1.25% of Risk Weighted Assets. Hybrid Instruments:- Preferred stocks are Hybrid Instruments. Debt Capital Instruments (Subordinated Debt):- Bonds issued by banks. It ranks lower than ordinary depositors of the bank. The debt providers (the lenders) have subordinate status in relationship to the normal debt. Example, when a promoter of a company invests money in the form of debt, rather than in the form of stock. And in case,of liquidation, the promoter would be paid just before stockholders. Subordinated debt is repayable after other debts have been paid. Example, Mezzanine debt (High return, followed by high risk). Upper Tier 2 Instruments:- The amount of Upper Tier 2Instruments issued by a bank along with other components of Tier 2 Capital cannot exceed 100% of Tier 1 Capital and these shall have minimum maturity of 15 years. Similar to IPDI,these instruments cannot be issued with a Call Option. And this Call Option can be exercised only after the instrument has run for at least 10 years and with the prior approval of RBI. And this can be exercised only once during the whole life of the instrument, but not after the lapse of 10 years from the date of issued.
- 5. Here the loss absorption is limited. Interest due on this instrument and the principle on redemption can be deferred,but would be cumulative. And this deferred can happen only if, CRAR of the issuing bank is less than regulatory minimum prescribed. However,banks are allowed to pay with theprior approval of RBI. While paying such unpaid interest and principle, banks are also allowed to pay compound interest at a rate not exceeding the coupon rate of the relative Upper Tier 2 bonds. The claims of the investors in these Upper Tier2 Instruments are deemed superior to the claims of investors in instruments eligible for inclusion in Tier1 capital. Simply put, NOTE: Reason for holding capital is that it should provide protection against unexpected losses. But this is not the same as expected losses-Provisions and Reserves are for expected losses. RISK WEIGHTED ASSESTS: When banks mobilize funds, these are Liabilities. When banks deploy funds, these are Assets. Major Assets could be in the form of Cash, SLR, Non-SLR investments, Loans and Advances,etc. All these Assets carry same risk. So, RBI assigned different types of risks to different Assets. Tier 2 Capital (1) Undisclosed Reserves and Cumulative Perpetual Preference shares (2) Revaluation Reserves (@45%) (3) General Provisions & Loss Reserves (4) Capital Reserves (Investments) (5) Upper Tier 2 Capital (6) Subordinated Debts & Unsecured Redeemable Loans (7) Investment Fluctuation Reserve
- 6. Fund based obligations Particulars Risk weightage (%) Cash 0 Loan against CGF (Guarantee) 0 Balances with other Banks 20 Education Loan 75 Retail Loan (Max. 5 Crore) 75 House Loan (Up to 30 Lakhs) 50 House Loan (≥ 30 Lakhs) 75 PersonalLoan 125 Credit cards 125 Capital market exposure 125 Commercial Real Estate 150 These are the risk weights provided or fixed by RBI for credit risk. Risk associated to banking RWA – 3 Types Credit Risk The risk that a party to a contractual agreement or transaction will be unable to meet its obligations or will default on commitments. Credit risk can be associated with almost any financial transaction. BASEL-II provides two options for measurement of capital charge for credit risk 1.Standardised approach (SA) - Under the SA, the banks use a risk-weighting schedule for measuring the credit risk of its assets by assigning risk weights based on the rating assigned by the external credit rating agencies. 2. Internal rating based approach (IRB) - The IRB approach, on the other hand, allows banks to use their own internal ratings of counterparties and exposures, which permit a finer differentiation of risk for various exposures and hence delivers capital requirements that are better aligned to the degree of risks. The IRB approaches are of two types: a) Foundation IRB (FIRB): The bank estimates the Probability of Default (PD) associated with each borrower, and the supervisor supplies other inputs such as Loss Given Default (LGD) and Exposure At Default (EAD). b) Advanced IRB (AIRB): In addition to Probability of Default (PD),the bank estimates other inputs such as EAD and LGD. The requirements for this approach are more exacting. The adoption of advanced approaches would require the banks to meet minimum requirements relating to internal ratings at the outset and on an ongoing basis such as those relating to the design of the rating system, operations, controls, corporate governance, and estimation and validation of credit risk components, Credit Risk • Counterparty not obliging his part of due. Market Risk • Banks participating in off-balancesheet items or derivative trading. Operational Risk • Risk due to Corporate Governance, failure in systems.
- 7. viz., PD for both FIRB and AIRB and LGD and EAD for AIRB. The banks should have, at the minimum, PD data for five years and LGD and EAD data for seven years. In India, banks have been advised to compute capital requirements for credit risk adopting the SA. Non fund based obligations These are converted into Fund based exposure, in which conversion factor is used. And then based on this value, RWA total amount is calculated. Balance sheet ofa Bank Liabilities 1. Paid-up Capital 2. Reserves & Surplus 3. Deposits -Demand Deposits -Term Deposits -Savings Deposits 4. Borrowings 5. Other Liabilities & Provisions Assets 1. Cash & Balances with RBI 2. Balances with Banks & money at call & short notice (like, Cash, SLR, Non-SLR, Loans & Advances) 3. Investments -In Govt. Securities -In India -In abroad -Govt. approved securities -Non-approved securities 4. Loans & Advances -Cash credit, Overdrafts -Term Loans -Bills purchased & discounted 5. Fixed Assets 6. Other Assets Financial performance of a Bank Income 1. Interest Income -Interest on Advances -Income on Investments 2. Other Income -Commission & Brokerage Expenditure
- 8. 1. Interest Expended -Interest on Deposits 2. Provisions & Contingencies -Provisions for NPAs 3. Operating Expenses -Wage Bill Net Profit Income-Expenditure Operating Profit Net Profit + Provisions & Contingencies Stress Test It measures the sensitivity of the portfolio of Assets and Liabilities of an individual institution or a financial system to changes in one of the risk factors like interest rate or exchange rates. The principle technique used by most of the banks for quantification of market risk is VaR. But, there are certain deficiencies of this technique. Therefore, Stress testing is used. Monetary policy - It deals with both lending and borrowing rates of interest for commercial banks. - Increase or decrease in the supply of currency. - Carry out OMO, interest rates. - To control inflation. - Depreciate domestic currency. Fiscal Policy - Change in government revenue and expenditure, taxation. - Open Market Operations(OMO) - This involves in sales and purchases of bond, government securities in financial markets. SLR Investments: - Banks are required to invest 23% of NDTL in Government and other approved securities as on the last Friday of the second preceding fortnight. - Ratio of liquid assets to NDTL (Net Demand and Time Liabilities) - Liquid assets like-cash in hand, excluding cash balances under CRR requirements, balances with SBI, RBI and other nationalized banks, gold and approved securities. NPV (Net Present Value) - Present value of future cash flows - 𝑁𝑃𝑉 = 𝐹𝑉 (1+𝐾𝑒) 𝑛 MNPV(Modified NPV)
- 9. - Assumes the intermediate cash flows will be reinvested in the project. IRR (Internal Rate ofReturn) - NPV=0 BCR (Benefit Cost Ratio)or(Profitability Ratio) = 𝑃𝑉( 𝐹𝑢𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒 𝑐𝑎𝑠ℎ 𝑓𝑙𝑜𝑤𝑠) 𝐼𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝐼𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑠𝑡𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 = 𝑁𝑃𝑉 𝐼𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝐼𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑠𝑡𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 EVA (Economic Value Added) Economic value generated by a company in excess of its Cost of Capital. = Income Earned-(Cost of Capital*Investment) BCR›1: Project accepted NPV›0: Project accepted IRR-Cost ofcapital›0: Project accepted NPAs (Non-Performing Assets) For Advances,if interest is due for more than 120 days. Substandard -50% of loaned amount due. Doubtful-20% of loaned amount due. Losses-‹20% of loaned amount due. REPO - One party sells certain securities to the second parties with an agreement to buy them back on a predetermined future date at a predetermined rate. - The rate at which RBI lends to commercial banks against Govt. securities. Reverse REPO - Buying the securities back in the open market. - The rate at which RBI borrows money from commercial banks. CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) - Banks need to maintain with itself in the form of cash reserves or by way of current account with RBI, as a certain percentage of NDTL. - RBI cannot pay any interest on CRR balances. - RBI empowered to vary CRR between 3 and 15%.
- 10. Financial Ratios Money multiplier (money supply in the market) = 𝑴𝟏( 𝑵𝒂𝒓𝒓𝒐𝒘 𝑴𝒐𝒏𝒆𝒚) 𝒐𝒓 𝑴𝟑( 𝑩𝒓𝒐𝒂𝒅 𝑴𝒐𝒏𝒆𝒚) 𝑴𝟎(𝑹𝒆𝒔𝒆𝒓𝒗𝒆 𝑴𝒐𝒏𝒆𝒚) M0 (Reserve Money) or (all currency in circulation) = C + CR + OD Where, C - Currency held by the people CR - Cash Reserves of the banks OD - Other Deposits with RBI M1 (Narrow Money) = M0 + Demand Deposits of all Commercial, Cooperative banks. M2 = M1 + Saving Deposits with Post Office M3 (Broad Money) = M2 + Time Deposits of all Commercial, Cooperative banks. M4 = M3 + Total Deposits with Post Offices Cost of Funds = (Interest paid on Deposits) + (Interest paid on Borrowings)/(Deposits + Borrowings) Cost of Deposits = Interest paid on Deposits/Deposits Cost of Borrowings = Interest paid on Borrowings/Borrowings Return of Funds= (Return on Advances + Return on Investments)/ (Advances + Investments) Return on Advances= Interest earned on Advances/ Advances Return on Investments= Interest earned on Investments/Investments Efficiency ratio=Operating Expenses/Net Interest Income + Non Interest Income CAR Net Advances/ Net NPAs Working Funds= Total Assets- Total Liabilities Net Interest Income/ Working Funds Non-Interest Income/ Working Funds Operating Profit/Working Funds Business per Employee Profit per Employee Provisions and Contingencies PARAMETERS Growth Growth in Total Deposits (%) Growth in Loans and Advances (%) Growth in Fee Income (%) - Income from Commissions, Exchange, Brokerage + Miscellaneous Income Growth in Operating Profit (%) Change in Market share of Deposits (basis points) Change in Market share of CASA (basis points) 3-year CAGR of Total Deposits (%) 3-year CAGR of Loans and Advances (%) 3-year CAGR of Fee Income (%) 3-year CAGR of Operating Profit (%)
- 11. Size Deposits (Rs.cr) Operating Profit (Rs.cr) Balance sheet Size (Rs.cr) Quality of Assets (Rs.cr) Total NPA growth rate (%) additions to gross NPA during the year expressed as a% of the average Net Advances. NPA coverage (%) - NPA provisions as at year end expressed as a% of gross NPA at year end. Net NPA /Net Advance (%) - gross NPAs Net of Provisions expressed as a % of Net Advances. Strength (Productivity and Efficiency) Cost/Income ratio (%) - Operating Expenditure expressed as a% of Operating Income. Cost/Average Asset ratio (%) - Operating Expenditure expressed as % of Average Asset. Operating Profit/Employee (Rs.cr) - Operating Profit divided by the Total no. of Employees Change in Return on Assets (Basis points) Increase in Operating Profit/Net Income (%) Quality of Earnings Return on Assets(%)-ratio of Net Profit to Total Assets. Fee Income/Total Income(%) ROCE (%)-Reported Net Profit/Average Net Worth of the Bank. Net Interest Income/Average Working Funds (basis points)-Interest Earnings as a% of AWF(Total Average Asset-Average Other Liabilities) Several institutional measures have been put in place to recover the NPAs. Like, Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRT), Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARC ) Float-funds in the process of collection Call money-‹15 days Term money-15 days to 1 year RAROC (income for risk)-Risk Adjusted Rate On Capital =2.33*weekly volatility *√52*(1-t) Here,2.33 give volatility at 99% confidence level. 52 convert the weekly price moments into an annual moment. Internal performance measured by EVA and RAROC MPBF (Maximum Permissible Bank Finance)
- 12. Method 1: 0.75(current Assets-current Liabilities other than Bank Borrowings) Method 2: (0.75*current Assets)-current Liabilities Soundness indicators: Capital (CAR) and Asset quality (NPAs) Investments by banks: SLR Investments Govt. and other approved securities which are eligible for being reckoned for maintaining the SLR. Banks are required to maintain SLR of 23% of NDTL in Govt. and other approved securities. Banks are required to invest a portion of their Deposits in Govt. securities as a part of their SLR requirements. It is in the form of cash,gold or Govt. approved securities as on the last Friday of the second preceding fortnight. Ratio of Liquid Assets to NDTL - Liquid Assets like cash in hand excluding cash balances under CRR requirements, balances with SBI, RBI and other nationalized banks, gold and approved securities like-securities of Central and State bodies, local bodies and securities guaranteed by Govt. Non SLR Investments Commercial Papers,Shares,Bonds and Debentures issued by the corporate sector and units of Mutual Funds. CHIPS (Clearing House Inter-bank Payment system) Used for international payments automatically. FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) Fed Reserves board of governors meets 8 times a year regarding Open Market Operations. LAF (Liquidity Adjustment Facility) Short term bonds like REPO,Reverse REPO MSS (Market Stabilization Scheme) Long term bonds with underlying Repo and Reverse Repo Investment Banking Falls under mixed banking Deposits Considered as both assets and liabilities of a bank Narrow banking Banks confine their investments to short term and risk-free Assets only.
- 13. Universal bank one stop Financial market like Commercial Banking, Investment Banking, Insurance etc Term money Maturity of 15 days Fiat money Issued by the state as a medium of exchange, unit of account and store of value acceptable with a jurisdiction. Unit banking Banks conduct its overall operation from a single office Govt. Debt market T-bill, T-Notes,T-bonds (US Treasury Debt Securities) Zero coupon bonds= securities that pay only the principle at maturity Floating rate coupon bonds= Bonds issued by US Govt. have a fixed coupon rates. A floating rate coupon is like a standard coupon bond but its coupon is indexed to some other short term interest rate,it changes overtime. Municipal Debt market= US Federal Govt. issues debt to finance Federal Govt. expenses,such as Health care and military expenses. Money Markets This market for short term borrowing and lending. FFR (FederalFund Rate) Banks with a reserves surplus may lend some of their reserves to banks with reserve deficit. Euro dollar rate It is the rate of interest on a dollar deposit in a European based bank. These are short term deposits from 3 months to 1 year. LIBOR (London Interbank Offer Rate) British bankers association publishes daily LIBOR rate. It is average interest rate that banks charge to each other for short term uncollateralized borrowings in the London market. These rates are very similar to Euro dollar rates.
- 14. Financial institutions classified as: 1) Term lending institution [IFCI, IIBI, EXIM bank, TFCI] -Extends long term finance to different industrial sectors. 2) Refinance institutions [NABARD, SIDBI, NHB] -Extends refinance to banks as well as non-banking financial intermediaries for on lending to agriculture, SSI and the housing sector. 3) Investment institution [LIC] - Deploy their Assets largely in marketable securities. FIU (Financial Intelligence Unit) Tracks the money laundering and related crimes. Discount rate Interest rate that banks pay to RBI, if they borrow money from it. Monetary policy It deals with both lending and borrowing rates of interest for commercial banks. It can increase or decrease the supply of currency as well as interest rate, carry out OMO,control credit Lowering of interest rates and/or depreciation of domestic currency and to control inflation. Held in every quarter. Financial Institutions Term Lending Refinance Investment
- 15. For evaluation and rating of Indian banks, suggested 6 key parameters, CAMELS: Difference between Money and Income Money is a stock and Income is a flow Bank rate Rate at which the Central Bank lends loans to the Commercial Banks Banks borrowfrom Money market to (1) Fill the temporary gaps of mismatches that arise in the normal business activities. (2) Meet the CRR requirements (3) Meet the sudden demand for funds arising due to large payments. The minimum maturity of a Treasury bill – 14 days. Supply of money refers to – total money in circulation. Loans and Advances are preferred investment because- they carry high rates ofinterest. Commercial banks create money by extending loans backed by Deposits. A high SLR investments results in low profitability of banks. Capital Adequacy Asset Quality Management Earning Performance Liquidity Systems