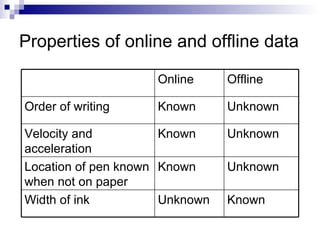
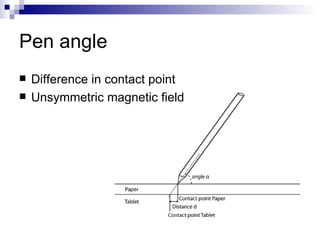
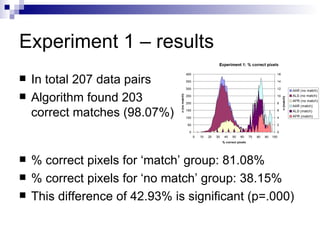
The document discusses a method for mapping online handwritten data to offline documents, addressing challenges such as resolution differences and pen angle discrepancies. Through experiments, it demonstrates a successful match accuracy of 98.07% and a 6.56% improvement in mapping quality when employing optimal rotation and resizing. The conclusion emphasizes the method's effectiveness in connecting online and offline data pairs, although it notes the slow processing speed and potential for enhancements.